Troubleshooting and fault elimination
9-3
BA9300SU EN 2.1
9.2 Fault analysis with the history buffer
• The history buffer is used to trace faults.
• Fault messages are stored in the order of their occurrence.
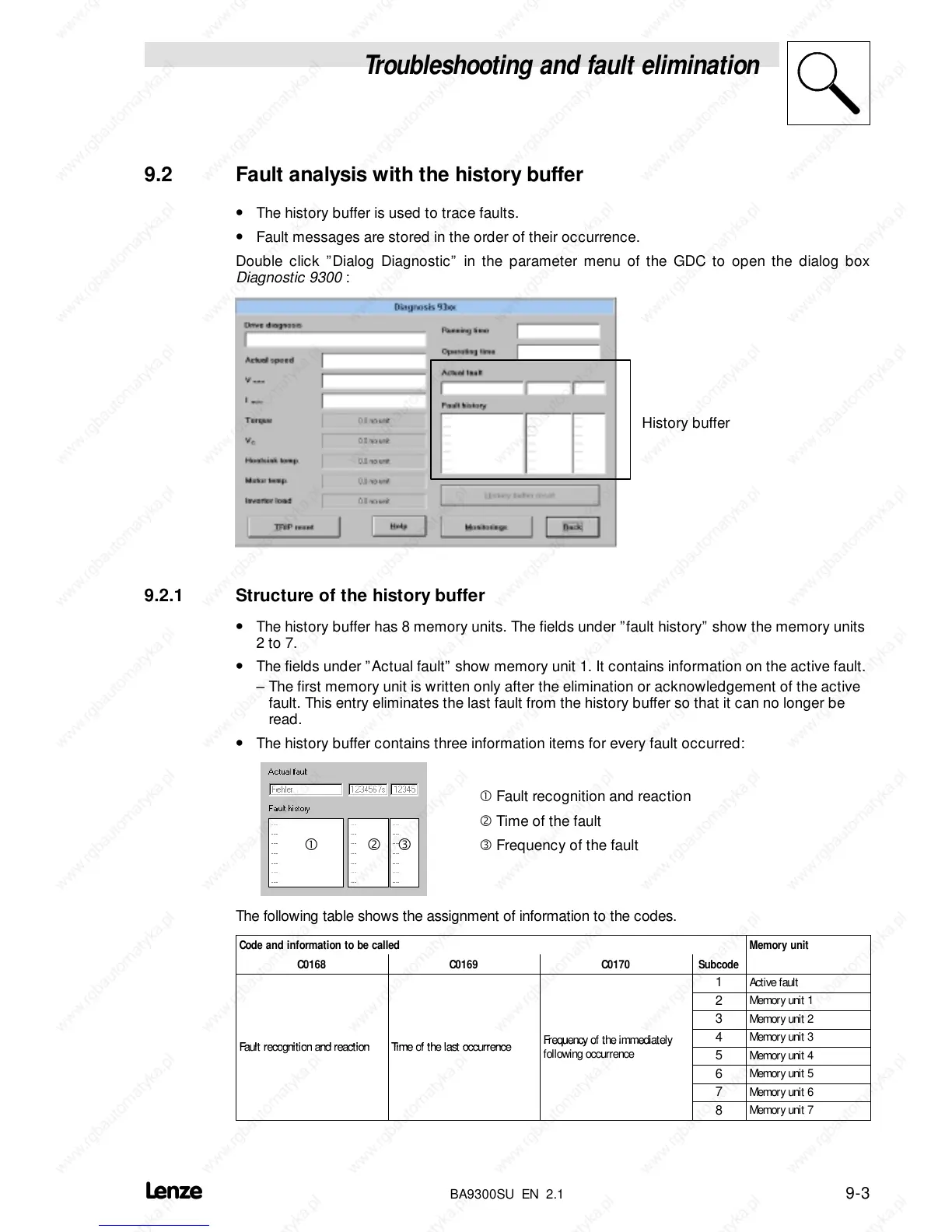
Double click ”Dialog Diagnostic” in the parameter menu of the GDC to open the dialog box
Diagnostic 9300 :
History buffer
9.2.1 Structure of the history buffer
• The history buffer has 8 memory units. The fields under ”fault history” show the memory units
2to7.
• The fields under ”Actual fault” show memory unit 1. It contains information on the active fault.
– The first memory unit is written only after the elimination or acknowledgement of the active
fault. This entry eliminates the last fault from the history buffer so that it can no longer be
read.
• The history buffer contains three information items for every fault occurred:
Fault recognition and reaction
ó Time of the fault
ì Frequency of the fault
óì
The following table shows the assignment of information to the codes.
Code and information to be called Memory unit
C0168 C0169 C0170 Subcode
1
Active fault
2
Memory unit 1
3
Memory unit 2

 Loading...
Loading...