7-12 | ni.com
Chapter 7 Counters
Which Method Is Best?
This depends on the frequency to be measured, the rate at which you want to monitor the
frequency and the accuracy you desire. Take for example, measuring a 50 kHz signal. Assuming
that the measurement times for all measurements are configured the same, Table 7-2
summarizes the results.
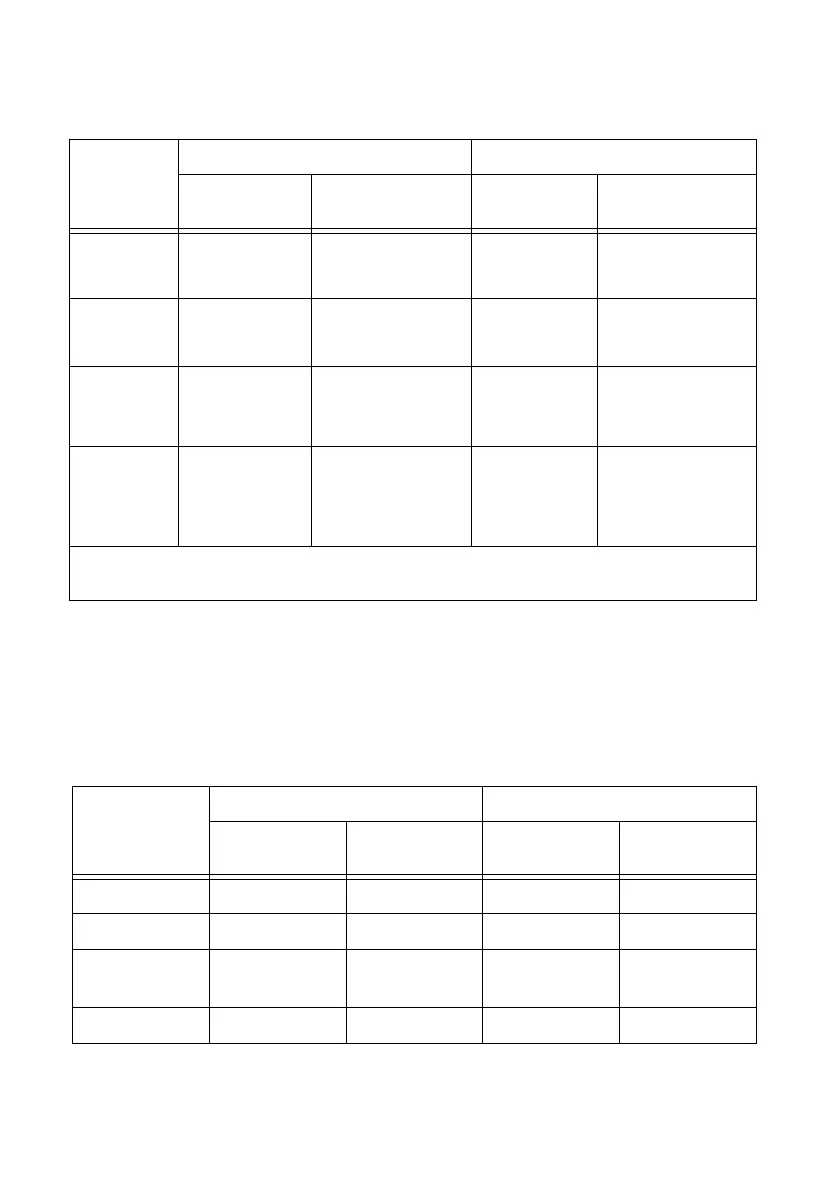
Table 7-1. Frequency Measurement Methods
Variable
One Counter Two Counters
— Averaged
High
Frequency
Large Range
fk Known
timebase
Known timebase Known timebase
T
gating period
Maximum
frequency
error (Hz)
fk
Maximum
error (%)
Note: Accuracy equations do not take clock stability into account. Refer to your device specifications for
clock stability.
Table 7-2. 50 kHz Frequency Measurement Methods
Variable
One Counter Two Counters
— Averaged
High
Frequency
Large Range
fx 50,000 50,000 50,000 50,000
fk 100 M 100 M 1,000 100 M
Measurement
time (mS)
0.02 1.02 1 1
N — 50 — 50
1
gating period
-------------------------------
fx
fx
fk fx–
---------------×
fx
fx
Nfkfx–×
-------------------------
×
fx
fx
Nfkfx–×
-------------------------×
fx
Nfkfx–×
-------------------------
fx
Nfkfx–×
-------------------------

 Loading...
Loading...











