Connection
−14−
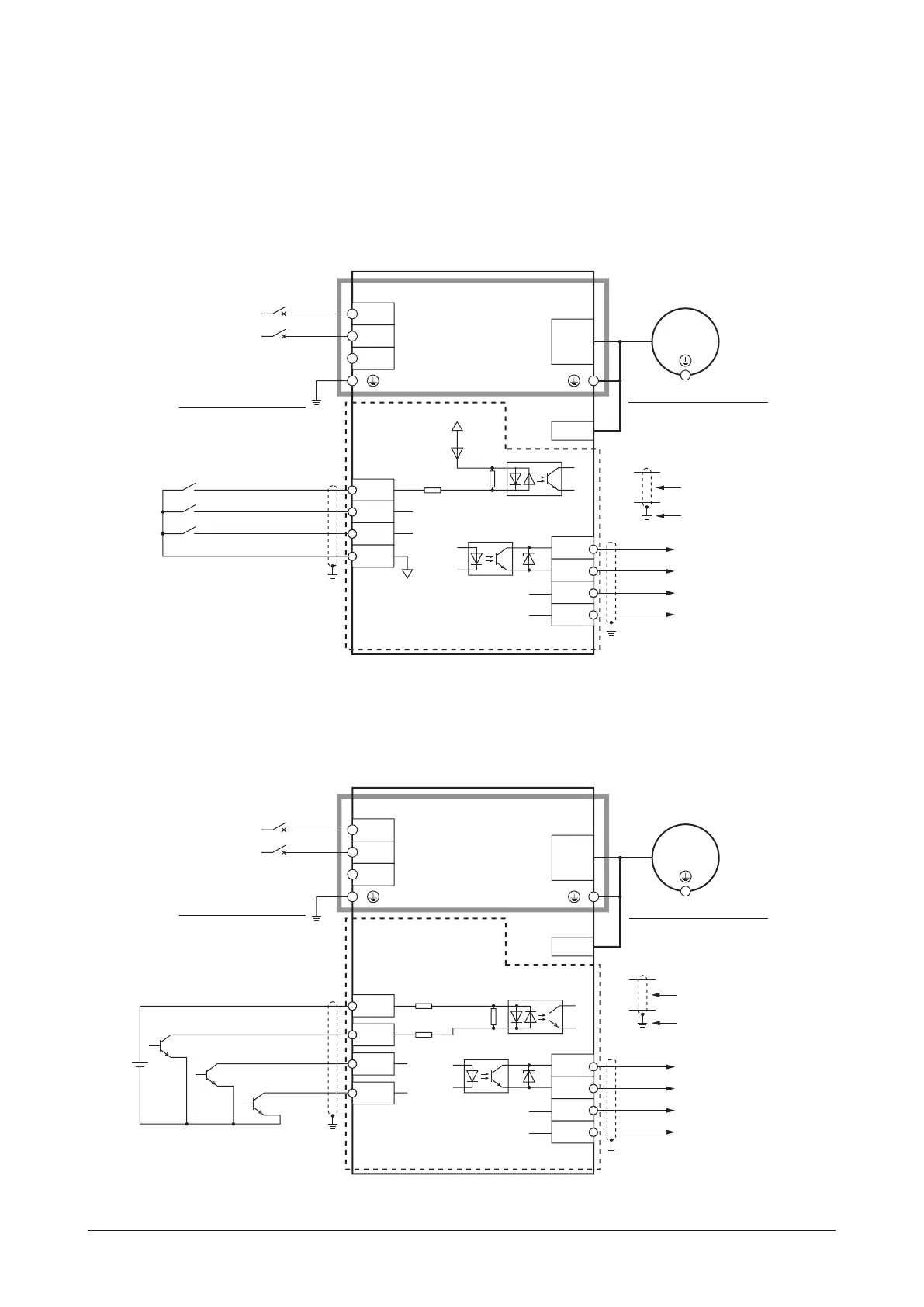
5.5 Connection diagram
The connection example is of the single-phase input. The power supply connection for the three-phase input is different.
(5.3 Connecting the power supply
⇒
p.12)
Sink logic
z
When using the built-in power supply
This is a connection example for when the built-in power supply is used for input signals.
The I/O signal in the brackets [ ] is the assignment at the time of shipment.
Grounding the driver
Be sure to ground.
Grounding the motor ∗
Be sure to ground.
Motor connection
L
Motor connector
CN1
CN2
N
NC
Motor
Main circuit
Control circuit
CN4
7
6
5
C1䠄0 V䠅
8
0 V
Power supply
connection
L
N
Circuit breaker
Shielded cable
Grounding
680 Ω
820 Ω
X1䠷REV䠹
X0䠷FWD䠹
+5 V
X2䠷M0䠹
Sensor
connector
CN3
4
3
2
1
䠷SPEED-OUT䠹
䠷ALARM-OUT1䠹
Y0+
Y0−
Y1+
Y1−
*
Be sure to ground. Refer to "5.2 Grounding" on p.11 for grounding.
z
When using the external power supply
This is a connection example for when the external power supply is used for input signals.
The I/O signal in the brackets [ ] is the assignment at the time of shipment.
Connecting input signals
20.4䡚28.8 VDC
100 mA or more
CN4
7
6
9
8
Shielded cable
Grounding
5 kΩ
680 Ω
820 Ω
X1䠷REV䠹
X0䠷FWD䠹
C0
X2䠷M0䠹
Motor conanection
L
Motor coannector
CN1
CN2
N
NC
Motor
Main circuit
Control circuit
Power supply
connection
L
N
Circuit breaker
Sensor
connector
CN3
4
3
2
1
Y0+
Y0−
Y1+
Y1−
䠷SPEED-OUT䠹
䠷ALARM-OUT1䠹
Grounding the motor ∗
Be sure to ground.
Grounding the driver
Be sure to ground.
*
Be sure to ground. Refer to "5.2 Grounding" on p.11 for grounding.
Refer to the p.16 for
connection of output signals.
Refer to the p.16 for
connection of output signals.

 Loading...
Loading...











