58 Rockwell Automation Publication 440R-UM013F-EN-P - July 2021
Chapter 11 Troubleshooting
can install a separate SELV supply for your safety system and leave it
ungrounded (no protective ground).
Check Safety Device Inputs
(Step 3)
This step only applies to CI, DI, DIS, and SI safety relays. Each safety relay has
a status indicator for its inputs.
Table 14
shows the voltage levels that are viewed on an oscilloscope versus a
digital multimeter.
Check Voltage-free Contacts
Safety devices (for example; interlock switches, E-stops, or cable pull switches)
with voltage-free contacts must be connected to the pulse testing outputs. You
can use a digital multimeter to measure the input levels.
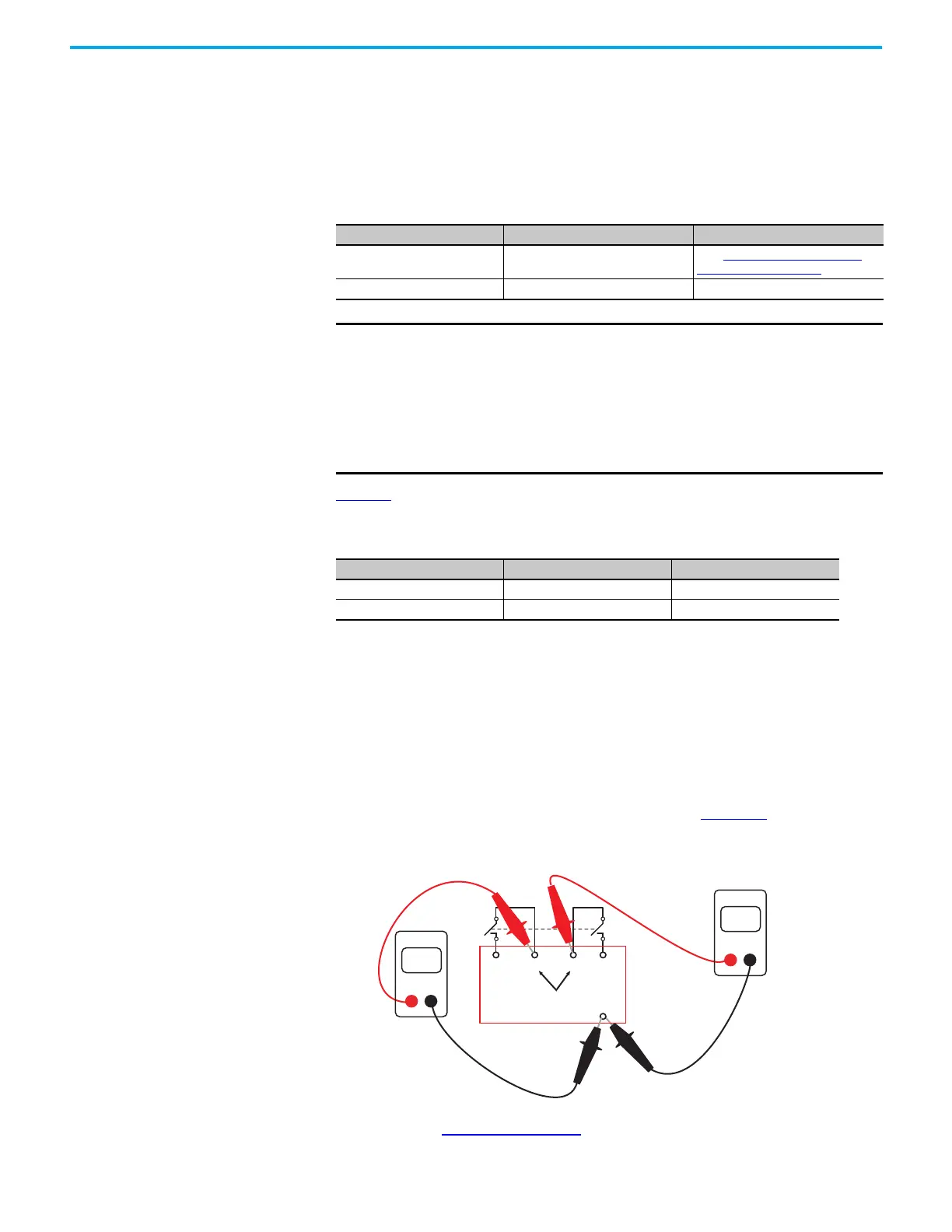
Check CI Safety Relay
1. With the device contacts open, measure the voltage at the pulse testing
outputs with a digital multimeter, as shown in Figure 60. The voltage
must be 18…19V on both pulse testing outputs of the CI safety relay.
Figure 60 - Typical Voltage Measurements of the CI Safety Relay
2. Check the voltage at each of the inputs with the device contacts closed, as
shown in Figure 61 on page 59. The values must be very close to the values
measured at terminals S11 and S21.
Table 13 - Input Indicator
IN, IN1, and IN2 Indicator Status Action
Green Both channels are closed
Go to Check the Single Wire Safety
Circuit (Step 4) on page 64.
Off One or both input channels are open Continue with this section.
IMPORTANT The following factors affect the value that is measured at the relay
inputs:
• Voltage-free contacts
•Pulse testing waveforms
• Capacitance
• Length of wire
• Contact resistance
• Channel sequence
Table 14 - ON/OFF Voltage
Measurement Device Turn ON Voltage Turn OFF Voltage
Oscilloscope 11V 5V
Digital Multimeter 6…8V 3…4V
S11 S21S12
19
19
S22
A2
Volts
DMM
Volts
DMM

 Loading...
Loading...









