(Skew/Period)*360
5. When "from" edge is either, the calculation is (Skew/half-Period)*180.
Positive Duty Cycle measurement algorithm
Positive Duty Cycle is the ratio of the positive pulse width to the signal period, expressed as a percentage.
PositiveWidth is defined in Positive Pulse Width, following.
Positive Pulse Width measurement algorithm
Positive Pulse Width is the time the signal remains above the mid reference level. It is the distance from a rising edge to the next
falling edge.
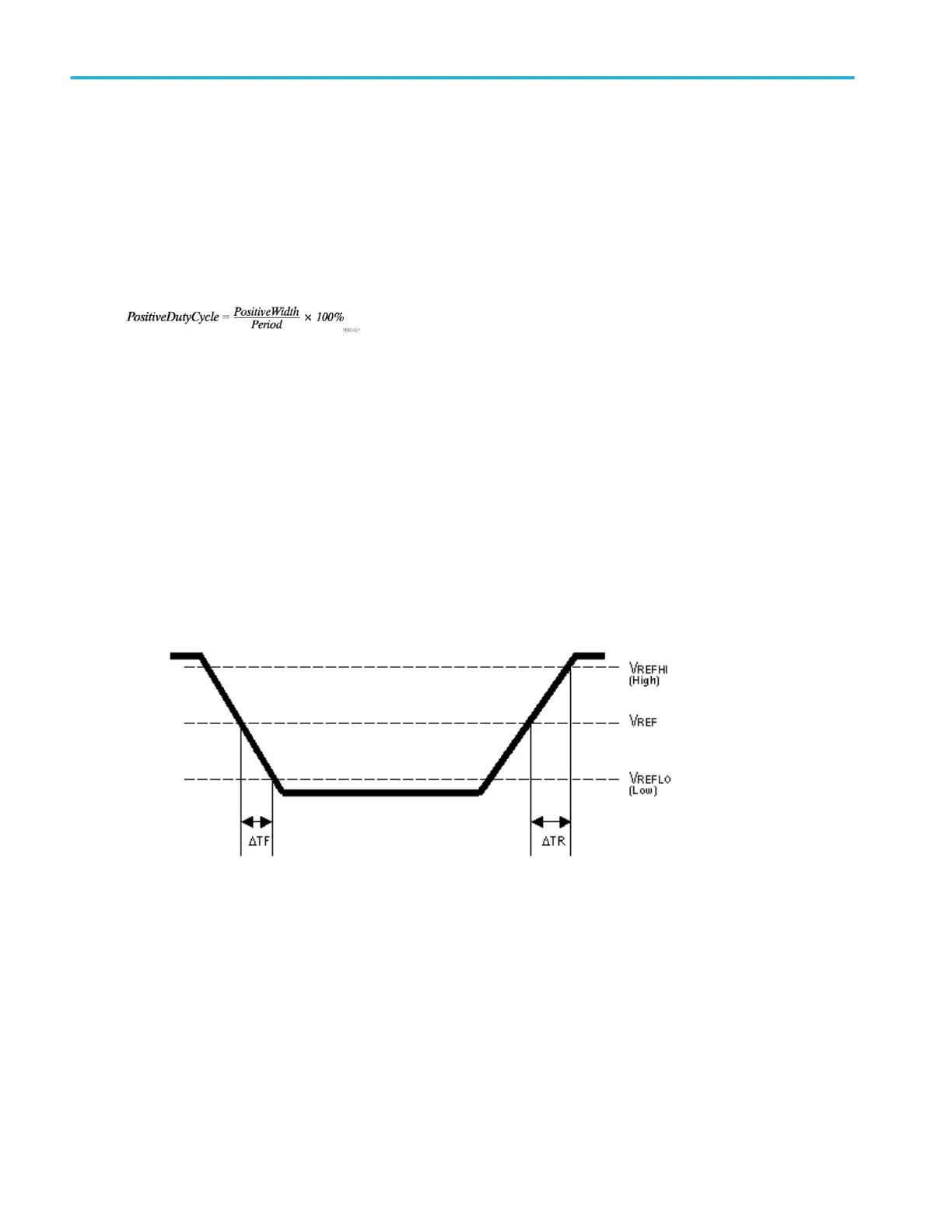
Rising Slew Rate measurement algorithm
Rising Slew Rate is the rate of change in value as an edge transitions from the low or mid reference level to the mid or high
reference level. The levels are configurable.
In the diagram below, the Rising Slew Rate from mid ref to high ref is calculated using the following equation:
(VREFHI - VREF)/ΔTR
Rise Time measurement algorithm
Rise Time is the time required for an edge to rise from the low reference level to the high reference level. By default the
measurement is from reference level 10% amplitude to 90% amplitude.
The following figure shows a rising edge with the two crossings necessary to calculate a Rise Time measurement.
1. Searching from Start to End, find the first sample in the measurement zone less than LowRef.
2. From this sample, continue the search to find the first (positive) crossing of LowRef. The time of this crossing is the low rise
time or TLR. (Use linear or sin interpolation if necessary.)
3. From TLR, continue the search, looking for a crossing of HighRef. Update TLR if subsequent LowRef crossings are found. If
a HighRef crossing is found, it becomes the high rise time or THR. (Use linear or sin interpolation if necessary.)
4. RiseTime = THR – TLR
Measurement algorithms
452 MSO54, MSO56, MSO58, MSO58LP, MSO64 Help
 Loading...
Loading...