Directions for use Interpreting test results 35
Negative and positive peak pressure tympanograms (left or right shift)
Tympanogram with negative middle ear pressure
Conditions which cause negative middle ear pressure:
• Eustachian tube dysfunction
•Cold
• Allergies
• Vigorous sniffing
Tympanogram with positive middle ear pressure
Condition which causes positive middle ear pressure:
• Acute otitis media
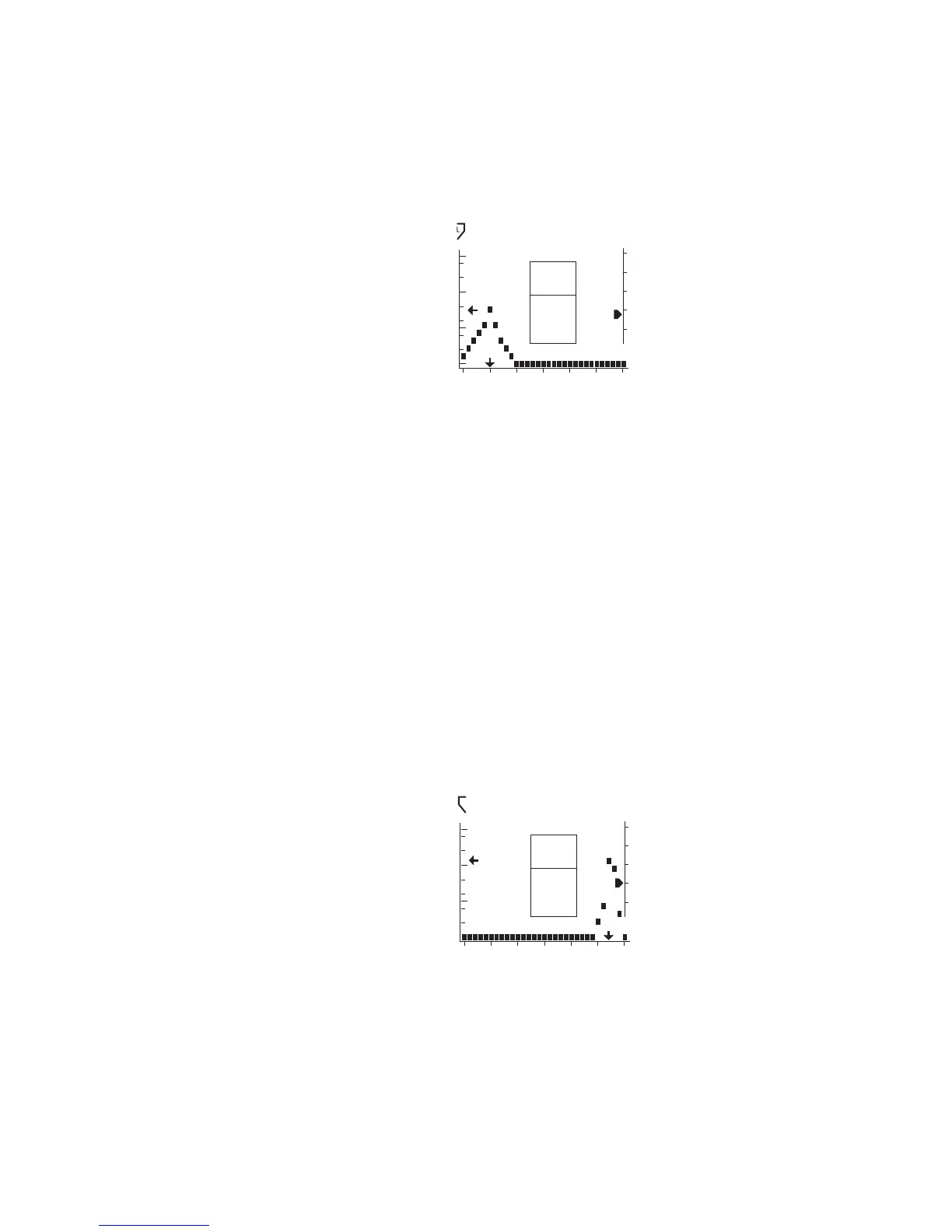
Negative pressure within the middle ear space will produce a tympanogram with
a negative tympanometric peak pressure. Some degree of negative pressure is
normal. Negative middle ear pressure often accompanies a cold or allergies, or
can be a result of eustachian tube dysfunction. Negative middle ear pressure is
not usually associated with effusion when peak Ya is normal. Vigorous sniffing
may be the most common cause of negative tympanometric peak pressure in
children.
-400 -200 0 200
2
0.5
0
1.0
1
1.5
PRESSURE - daPa
Ya - mmho
Vea
+200
LEFT EAR
Positive tympanometric peak pressure tympanograms reflect positive pressure
in the middle ear space. A high positive Tympanometric Peak Pressure (TPP) can
be indicative of acute otitis media, but only if the tympanometric peak is
extremely positive.
-400 -200 0 200
2
0.5
0
1.0
1
1.5
PRESSURE - daPa
Ya - mmho
Vea
+200
RIGHT EAR
R

 Loading...
Loading...