VESDA PipeNetwork Design Guide VESDA by Xtralis
12 www.xtralis.com
4.4 Return Area Protection
4.4.1 In-ceiling or Floor Void Sampling
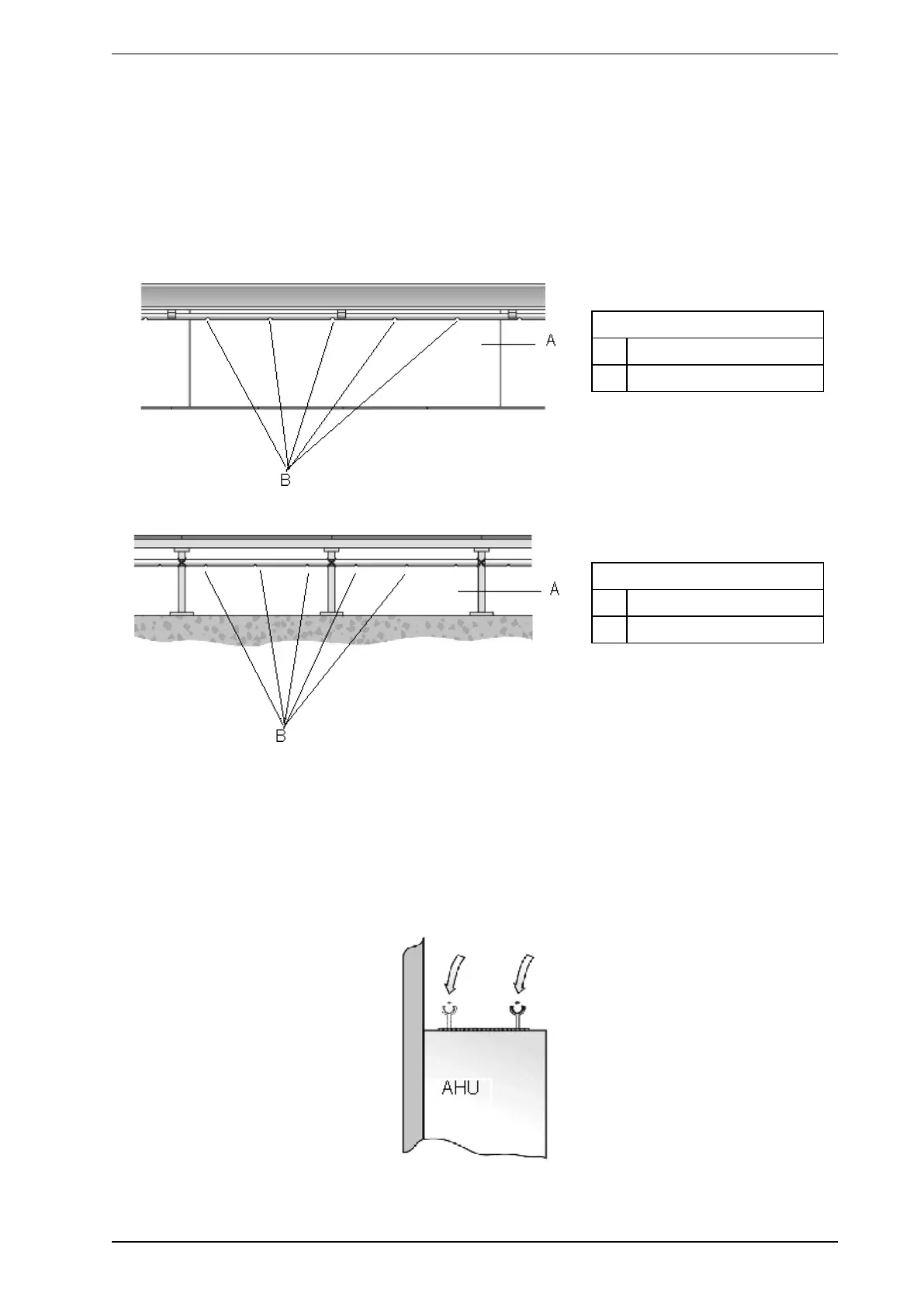
Some applications use ceiling and under floor voids as return air plenums (ducts). The pipe network is
designed to monitor the air flowing through the return air plenums. In-ceiling or floor void sampling is also used
to monitor any cabling and equipment that may be installed in the ceiling and floor voids. In instances where
the airflow is perpendicular to the pipe then it is recommended that sampling holes have a 30° orientation to
the airflow. Refer to Figure 4-12 on page 15.
Legend
A Ceiling Void
B Sampling Holes
Figure 4-5: Ceiling void sampling
Legend
A Floor Void
B Sampling Holes
Figure 4-6: Floor Void Sampling
4.4.2 Return Air Sampling
Smoke tends to travel with any mechanically generated air flow. Correctly positioning sampling holes in a pipe
network across the return air grille of an Air Handling Unit (AHU) or an exhaust ventilation system, ensures
that any smoke is detected at the earliest stage. Air samples from inside a duct carrying the exhaust air may
also be collected, refer to Figure 4-8 for details. It is recommended that the sampling holes face between 20
and 45 degrees from the direction of the greatest airflow. Refer to Figure 4-7 for further information.
Figure 4-7: Cross section of pipe position on a return air grille

 Loading...
Loading...











