RFSoC Data Converter Evaluation Tool User Guide 34
UG1287 (v2018.2) October 1, 2018 www.xilinx.com
Chapter 4: Clocking
Resets
The following reset sources are in the design:
• pl_resetn0 (from PS to PL)
This active Low reset is asserted by the PS during initialization.
• ddr4_sync_rst (or c0_ddr4_ui_clk_sync_rst from the PL DDR memory interface group
(MIG))
This active High reset is asserted by the PL DDR MIG. It is synchronized to the UI clock
coming out the PL DDR MIG.
• User-controlled reset block
This reset block is used to control the reset of FIFOs in both the RF-ADC datapaths
(adc_0, adc_1) and RF-DAC datapath (dac_0). It has an AXI4-Lite interface through which
the reset register can be accessed. Each bit of the register can be used to drive reset to
the block appropriately.
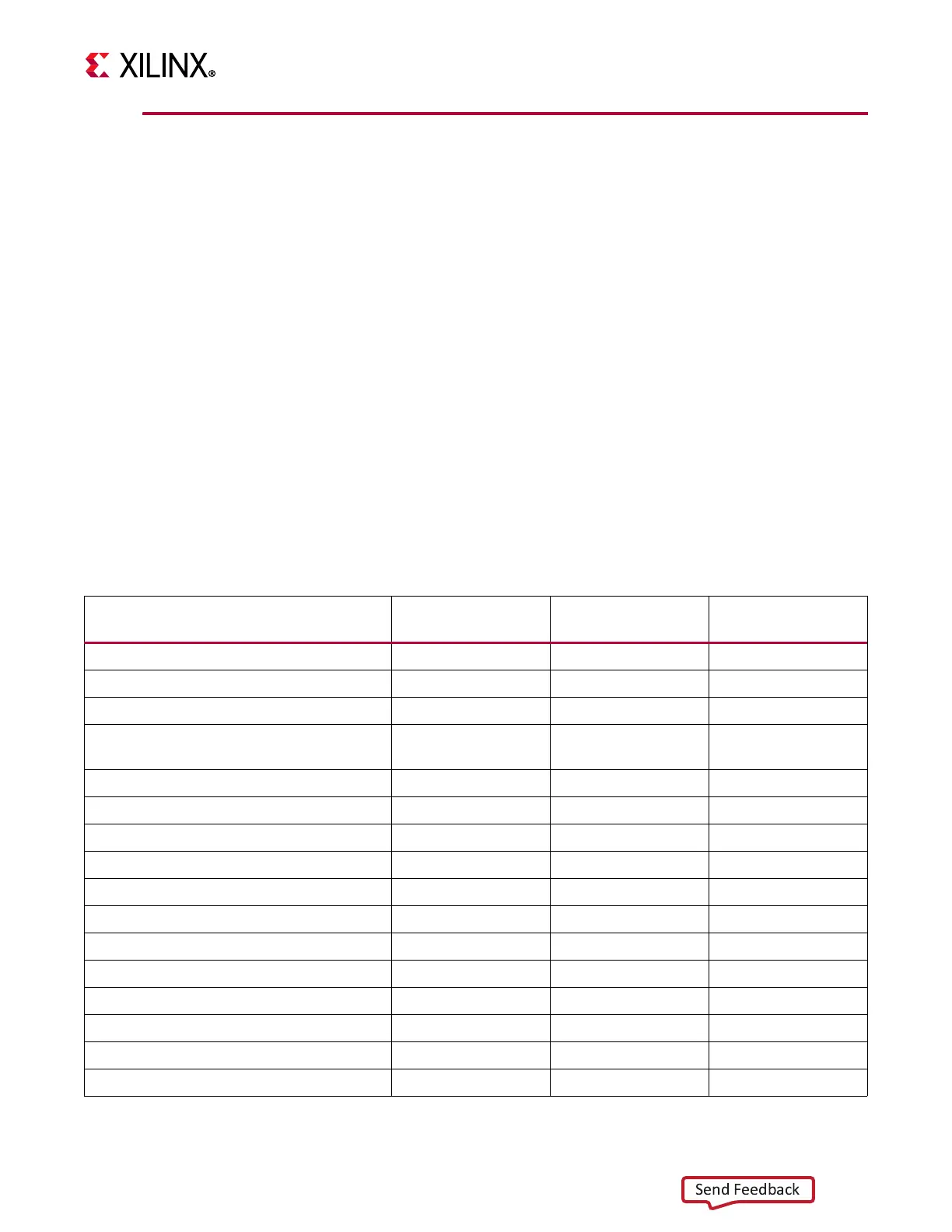
Table 4-3: Reset Distribution in the Evaluation Tool Design
Logic Block pl_resetn0 ddr4_sync_rst
User-controlled
Reset Block
PL DDR MIG X
DAC DMA X
ADC DMA X
RF data converter AXIS slave and master
interfaces (so, s1, and m0)
X
ADC_0 block AXIS data FIFO x (reset_0_n)
ADC_1 block AXIS data FIFO x (reset_1_n)
ADC_2 block AXIS data FIFO x (reset_2_n)
ADC_3 block AXIS data FIFO x (reset_3_n)
ADC_4 block AXIS data FIFO x (reset_4_n)
ADC_5 block AXIS data FIFO x (reset_5_n)
ADC_6 block AXIS data FIFO x (reset_6_n)
ADC_7 block AXIS data FIFO x (reset_7_n)
DAC 0 block- output AXIS data FIFOs x (dac reset_0_n)
DAC 1 block- output AXIS data FIFOs x (dac reset_1_n)
DAC 2 block- output AXIS data FIFOs x (dac reset_2_n)
DAC 3 block- output AXIS data FIFOs x (dac reset_3_n)
 Loading...
Loading...