▄ Cisco ASR 903 Router Design and Deployment Guide
Revertive : No
Nominated Interfaces
Interface SigType Mode/QL Prio QL_IN ESMC Tx ESMC Rx
Internal NA NA/Dis 251 QL-SEC NA NA
*Gi0/1/1 NA Sync/En 10 QL-PRC - -
Gi0/1/0 NA Sync/En 20 QL-PRC -
PTP Configuration
The Precision Time Protocol (PTP), as defined in the IEEE 1588 standard, synchronizes with nanosecond accuracy
the real-time clocks of the devices in a network. The clocks in are organized into a master-member hierarchy. PTP
identifies the switch port that is connected to a device with the most precise clock. This clock is referred to as the
master clock. All the other devices on the network synchronize their clocks with the master and are referred to as
members. Constantly exchanged timing messages ensure continued synchronization. 1588 PTP can be used to
synchronize clocking and time.
The following modes are supported on the ASR903.
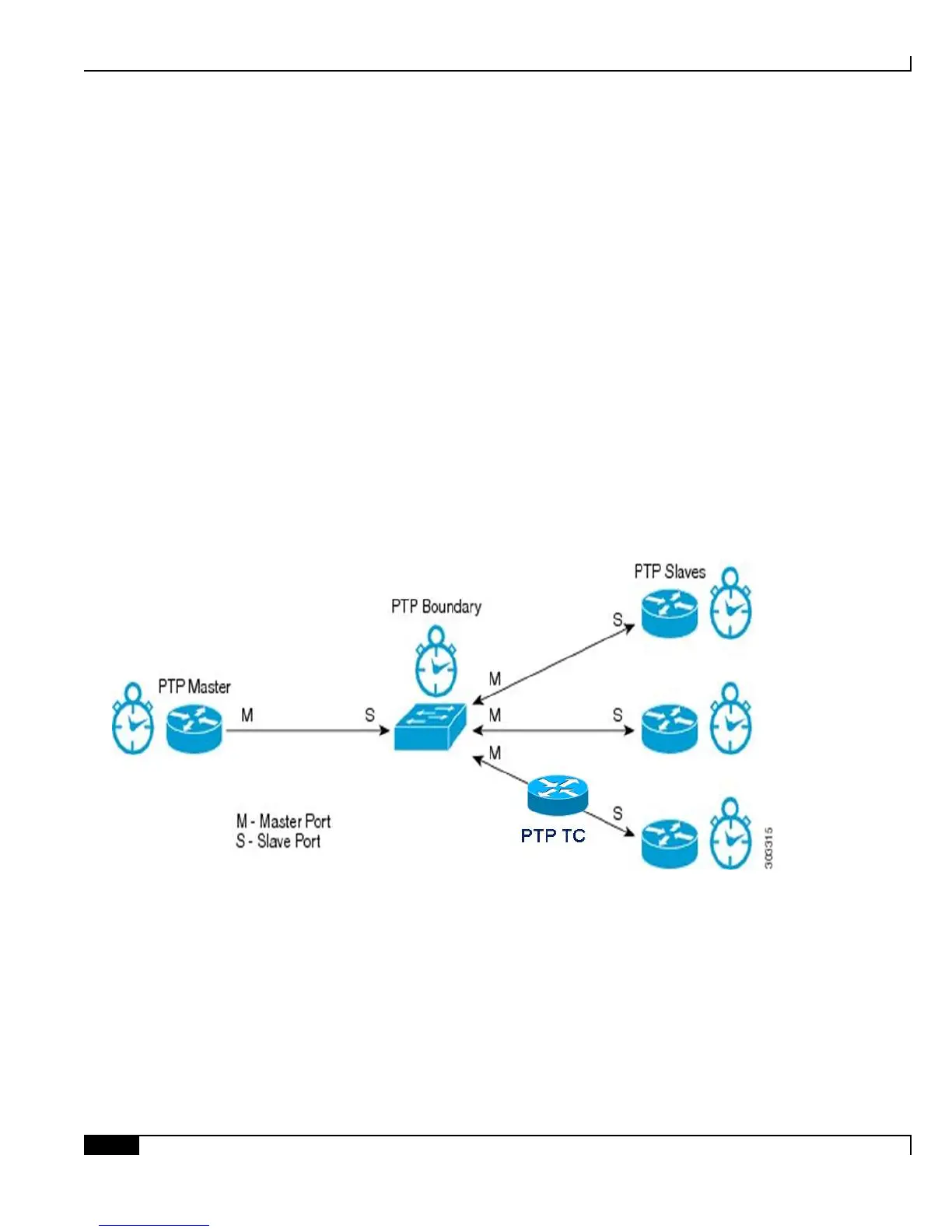
Figure 30. PTP Modes
• Master Clock: one master clock port, requires 10 Mhz, 1PPS and ToD
• Slave Clock: one slave clock port
• Boundary: one master clock port and one or more slave ports.
• Hybrid: use sync-e for frequency and PTP for time/phase.
• Transparent: just time-stamp PTP packets which transit the router.
Here is the topology to use for PTP configuration. ASR903-R1 and R2 will be configured as BC, ASR903-R3 as
TC, and ASR903-R4 as slave to synchronize with R1 and R2.

 Loading...
Loading...







