Implementing Multicast Routing on Cisco IOS XR Software Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers
Information About Implementing Multicast Routing
MCC-8
Multicast Configuration Guide
OL-
prunes are sent directly towards the source sending traffic, an RP and shared trees are unnecessary and
are disallowed. SSM is used to optimize bandwidth utilization and deny unwanted Internet broadcast
traffic. The source is provided by interested receivers through IGMPv3 membership reports.
In SSM, delivery of datagrams is based on (S,G) channels. Traffic for one (S,G) channel consists of
datagrams with an IP unicast source address S and the multicast group address G as the IP destination
address. Systems receive traffic by becoming members of the (S,G) channel. Signaling is not required,
but receivers must subscribe or unsubscribe to (S,G) channels to receive or not receive traffic from
specific sources. Channel subscription signaling uses IGMP to include mode membership reports, which
are supported only in Version 3 of IGMP (IGMPv3).
To run SSM with IGMPv3, SSM must be supported on the multicast router, the host where the
application is running, and the application itself. Cisco
IOS XR software allows SSM configuration for
an arbitrary subset of the IP multicast address range 224.0.0.0 through 239.255.255.255. When an SSM
range is defined, existing IP multicast receiver applications do not receive any traffic when they try to
use addresses in the SSM range, unless the application is modified to use explicit (S,G) channel
subscription.
PIM Shared Tree and Source Tree (Shortest Path Tree)
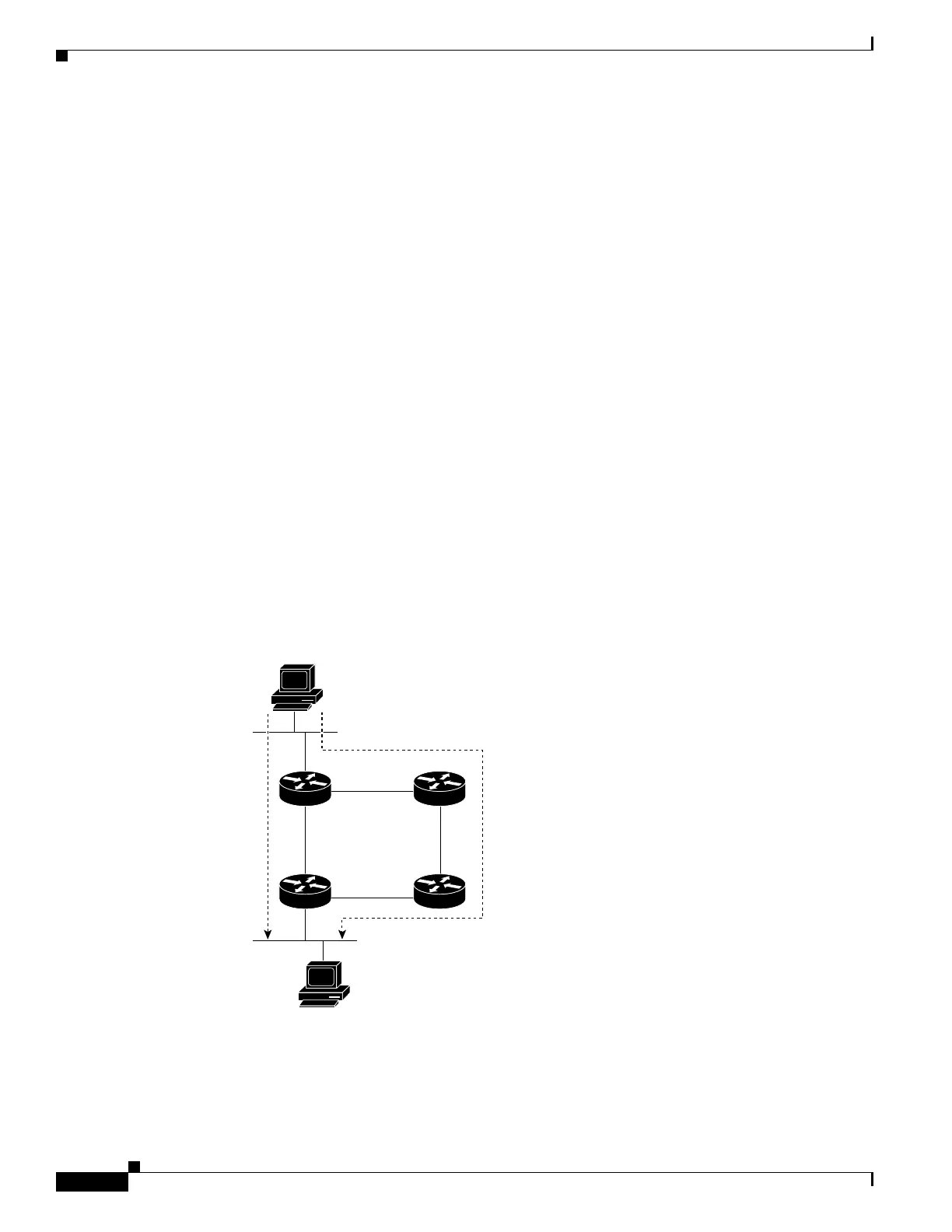
In PIM-SM, the rendezvous point (RP) is used to bridge sources sending data to a particular group with
receivers sending joins for that group. In the initial setup of state, interested receivers receive data from
senders to the group across a single data distribution tree rooted at the RP. This type of distribution tree
is called a shared tree or rendezvous point tree (RPT) as illustrated in
Figure 3. Data from senders is
delivered to the RP for distribution to group members joined to the shared tree.
Figure 3 Shared Tree and Source Tree (Shortest Path Tree)
Unless the spt-threshold infinity command is configured, this initial state gives way as soon as traffic
is received on the leaf routers (designated router closest to the host receivers). When the leaf router
receives traffic from the RP on the RPT, the router initiates a switch to a data distribution tree rooted at
Router A
Source
Receiver
Router C RP
Router B
Shared tree
from RP
Source tree
(shortest
path tree)
52647

 Loading...
Loading...















