GE Analytical Instruments ©2006 12-1 DLM 14291 Rev. A
Figure 12-1: Setup for Nitrite Measurement
12. MEASUREMENT OF NITRIC OXIDE AND NITRITE IN LIQUID
SAMPLES
Nitric oxide reacts with dissolved oxygen to form nitrite (NO
2
-
). In the absence of
oxyhemoglobin or superoxide anion, nitrite will be the major oxidation product of
NO. This includes most cell culture systems, perfusates and other liquid samples.
To measure nitrite, the purge vessel contains a reducing agent (1% wt/vol of NaI or
KI in acetic acid) to convert nitrite to nitric oxide.
I
-
+ NO
2
-
+ 2H
+
-> NO + 1/2I
2
+ H
2
O
For most applications, ~5 mL of the reducing agent is prepared in the purge vessel
and this volume is sufficient for measurement of 20-50 samples, depending on the
volume of sample injected. As the reagent is depleted, the solution will turn
yellow due to formation of I
3
-
Apparatus for Nitrite Reduction
Figure 12-1 shows the setup of the purge vessel for nitrite reduction. Since acetic
acid is volatile and less corrosive than mineral acids, a gas bubbler containing
NaOH is not required.
The outlet of the purge
vessel is connected to
the IFD filter to prevent
liquid from entering the
chemiluminescence
reaction cell. The outlet
of the IFD is connected to
the inlet of the standard
flow restrictor (do not
use the Nafion drier).
The reduction is

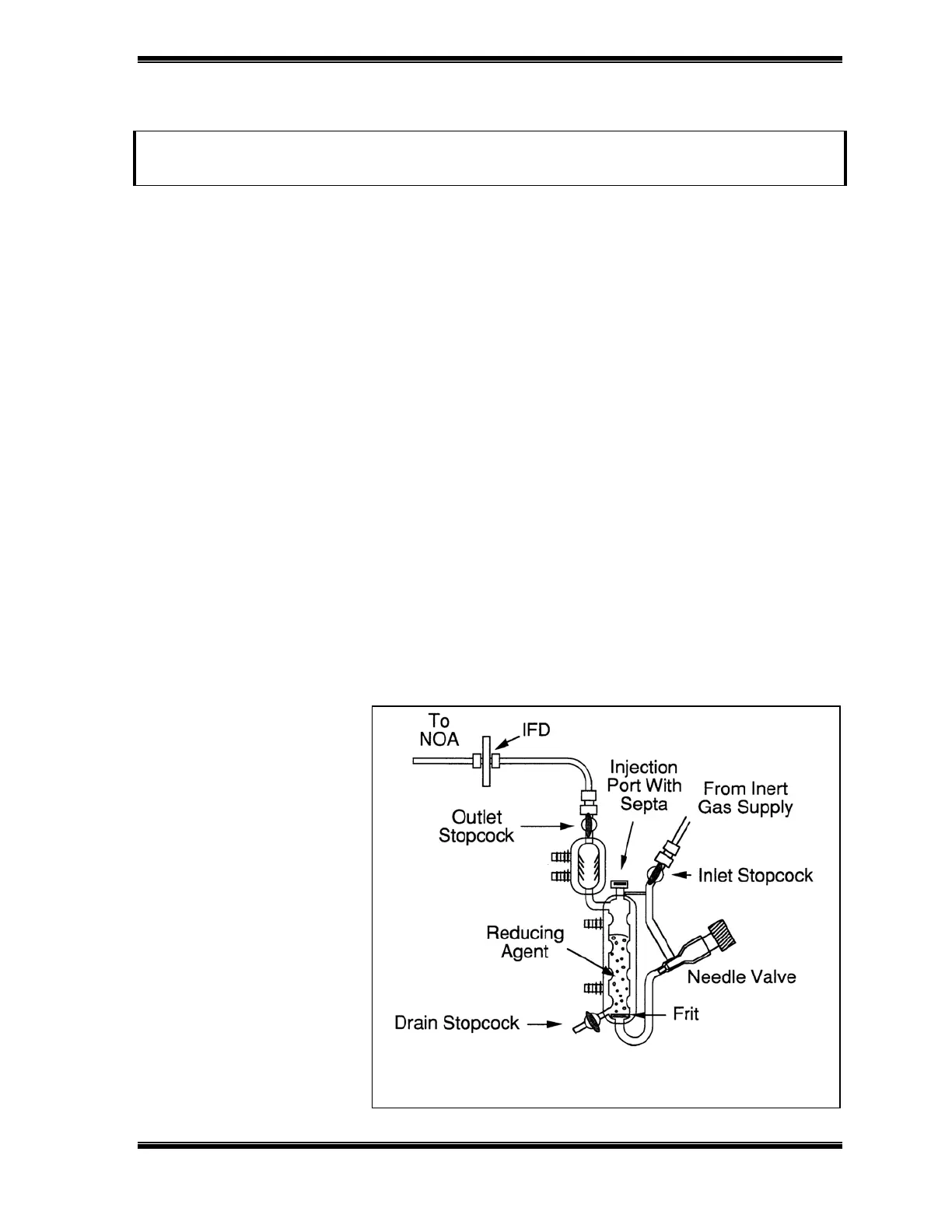 Loading...
Loading...