Configuring RADIUS-Based Mirroring ! 167
Chapter 6: Packet Mirroring
! If you are mirroring an IP session, the packet mirroring operation is enabled or
disabled on the MLPPP bundle as a whole. We recommend that you use the
Account-Session-ID RADIUS attribute rather than the User-Name attribute as
the trigger. Using the Account-Session-ID attribute is more efficient because the
JUNOSe software creates one secure policy that packet mirroring uses for all
links in the MLPPP bundle. If you use the User-Name attribute, a secure policy is
created for the first link, then removed and re-created for every other link.
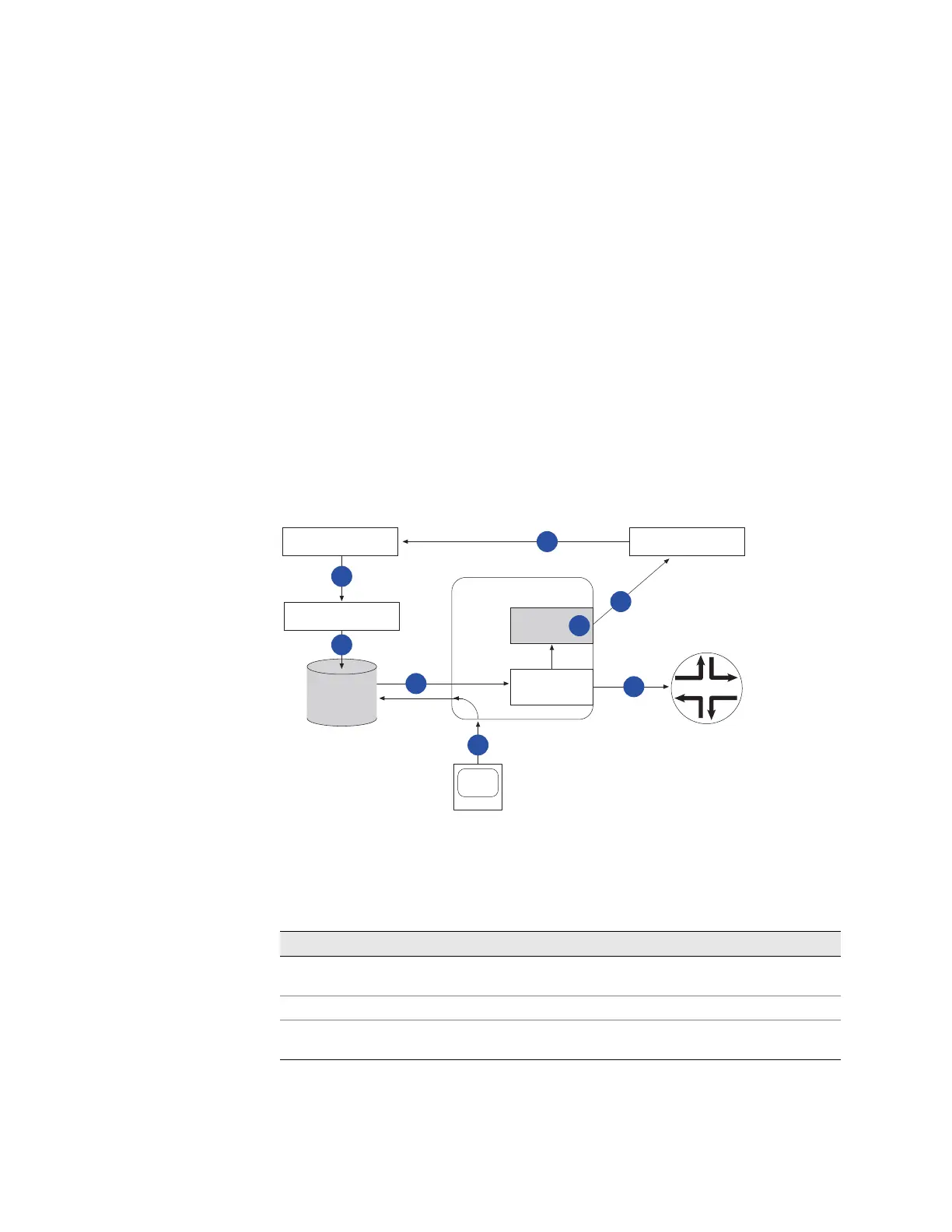
Sequence of Events
Figure 10 on page 167 shows the sequence of events that take place during
RADIUS-based mirroring. The tables after the figure describe the events indicated
by the numbers and letters in the figure. Table 30 on page 167 describes the
configuration process; Table 31 on page 168 describes the flow of traffic during a
mirroring operation that is initiated when the user logs on; and Table 32 on
page 168 describes the flow of traffic when mirroring a user who is already logged
in.
Figure 10: RADIUS-Based Packet Mirroring
To create a RADIUS-based packet mirroring environment, you must complete the
processes listed in Ta b l e 3 0 .
Ta b l e 31 indicates the sequence of steps for a packet mirroring operation that takes
place when a user starts a new session.
Table 30: Setting Up the RADIUS-Based Packet Mirroring Environment
Process Description
A The authorized individual requests packet mirroring of the user’s traffic and configures
the analyzer device to receive mirrored traffic.
B The ISP administration configures VSAs in the user’s RADIUS record.
C The E-series router administrator configures RADIUS server information and the
analyzer port connection to the analyzer device.
RADIUS
server
E-series router
Analyzer
interface
g013805
Mirrored
interface
Mirrored user
1
2
B
5
3
4
C
Destination
ISP administration
Requesting authority
A
Analyzer device

 Loading...
Loading...