
Do you have a question about the Keithley 2601 and is the answer not in the manual?
| Model | 2601 |
|---|---|
| Type | SourceMeter |
| Channels | 1 |
| Voltage Range | ±40V |
| Maximum Voltage | 40 V |
| Current Range | ±3A |
| Maximum Current | 3 A |
| Power | 20 W |
| Current Resolution | 10 pA |
| Measurement Resolution | 6.5 digits |
| Voltage Resolution | 100nV |
| Connectivity | USB, GPIB, Ethernet |
| Communication Interface | GPIB, RS-232 |
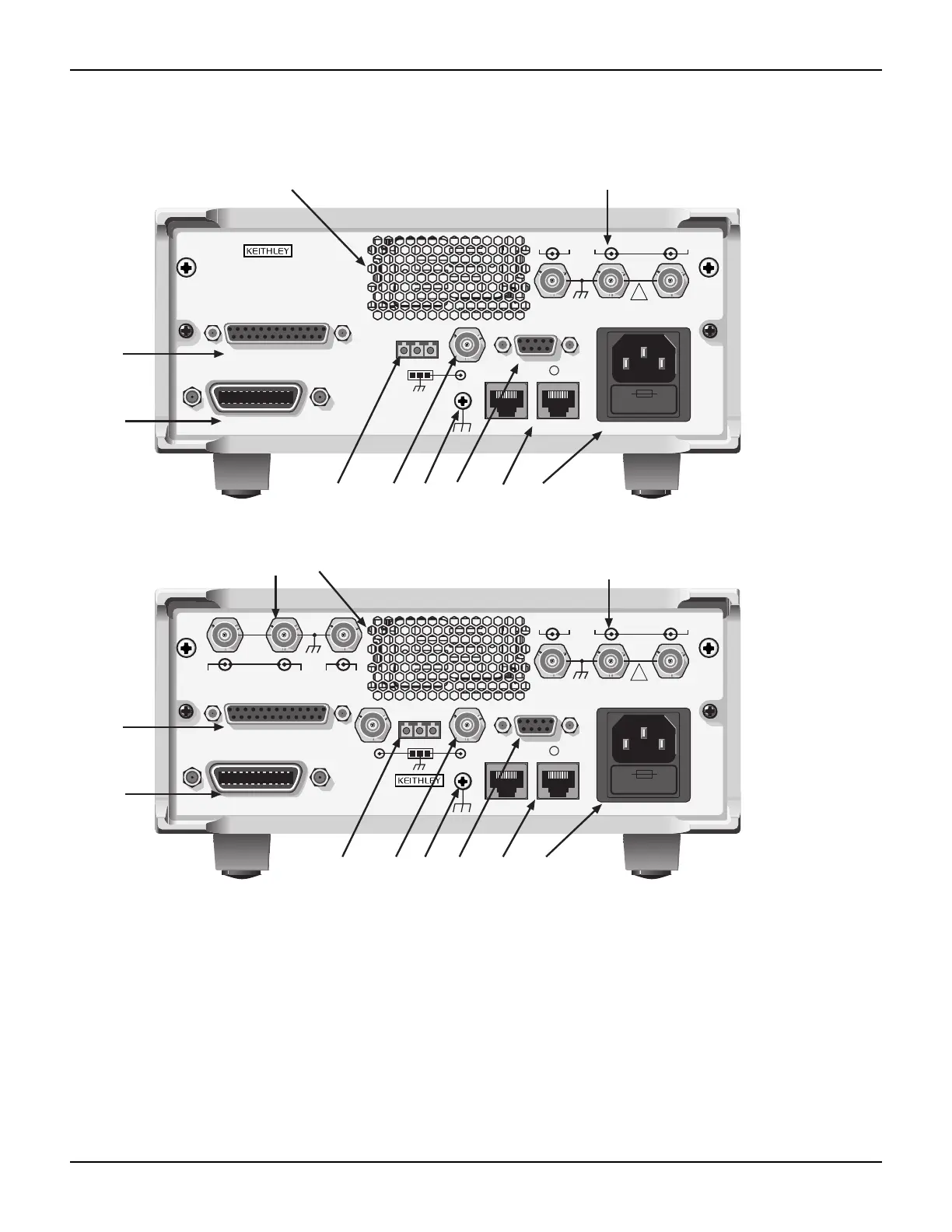
Overview of front and rear panel controls and layout.
Explanation of safety icons and terminology used in the manual.
Details the voltage and current sourcing and measuring specifications.
Step-by-step guide for connecting and powering on the instrument.
Procedure for setting up and executing voltage/current measurements.
Instructions for storing and recalling measurement data using internal buffers.
Setup for GPIB and RS-232 communication interfaces.
Overview of the TSB software and its interface elements.
Step-by-step guide for using TSB to control the instrument and take measurements.
Examples of controlling the instrument using LabVIEW and Visual Basic.
Definition and types of scripts (factory vs. user).
Procedure for executing scripts directly from the instrument.
Demonstrates running and modifying scripts using TSB.
Procedures for adding, deleting, and executing custom user scripts.
Connecting instruments and forming a TSP-Link system.
How to assign unique identifiers to instruments in a TSP-Link network.
Resetting the TSP-Link interface and verifying system communication status.
Accessing instruments and running scripts across the TSP-Link system.
Detailed technical and performance specifications for Models 2601 and 2602.
Detailed technical and performance specifications for Models 2611 and 2612.
Detailed technical and performance specifications for Models 2635 and 2636.
Overall specifications common to the Series 2600 product line.
Tips for adjusting settings to enhance speed and accuracy.
How to utilize the Digital I/O port for control and triggering.
Using Digital I/O to trigger other instruments or scanners.
Setting up and polling for instrument-generated service requests.
Procedures for saving measurement data to internal memory.
Connecting channels in series to achieve higher output voltages.
Connecting channels in parallel to achieve higher output currents.
Performing checks to detect poor connections or high resistance.
Methods and programming for accurate low-current measurements.











