2600S-900-01 Rev. C / January 2008 Return to Section Topics 3-3
Series 2600 System SourceMeter
®
Instruments User’s Manual Section 3: Test Script Processor Interaction
Reading the buffer – Test data is stored in a buffer. See “How do I use the buffer?” on page 1-16
for details on recalling test data.
How do I interact with scripts using Test Script Builder?
Reference See “Using the Test Script Builder” in Section 2 of the Series 2600 Reference
Manual for details on the Test Script Builder.
The following function for factory script “KIGeneral” is stored in the non-volatile memory of the
Series 2600:
PulseVMeasureI(smu, bias, level, ton, toff, points)
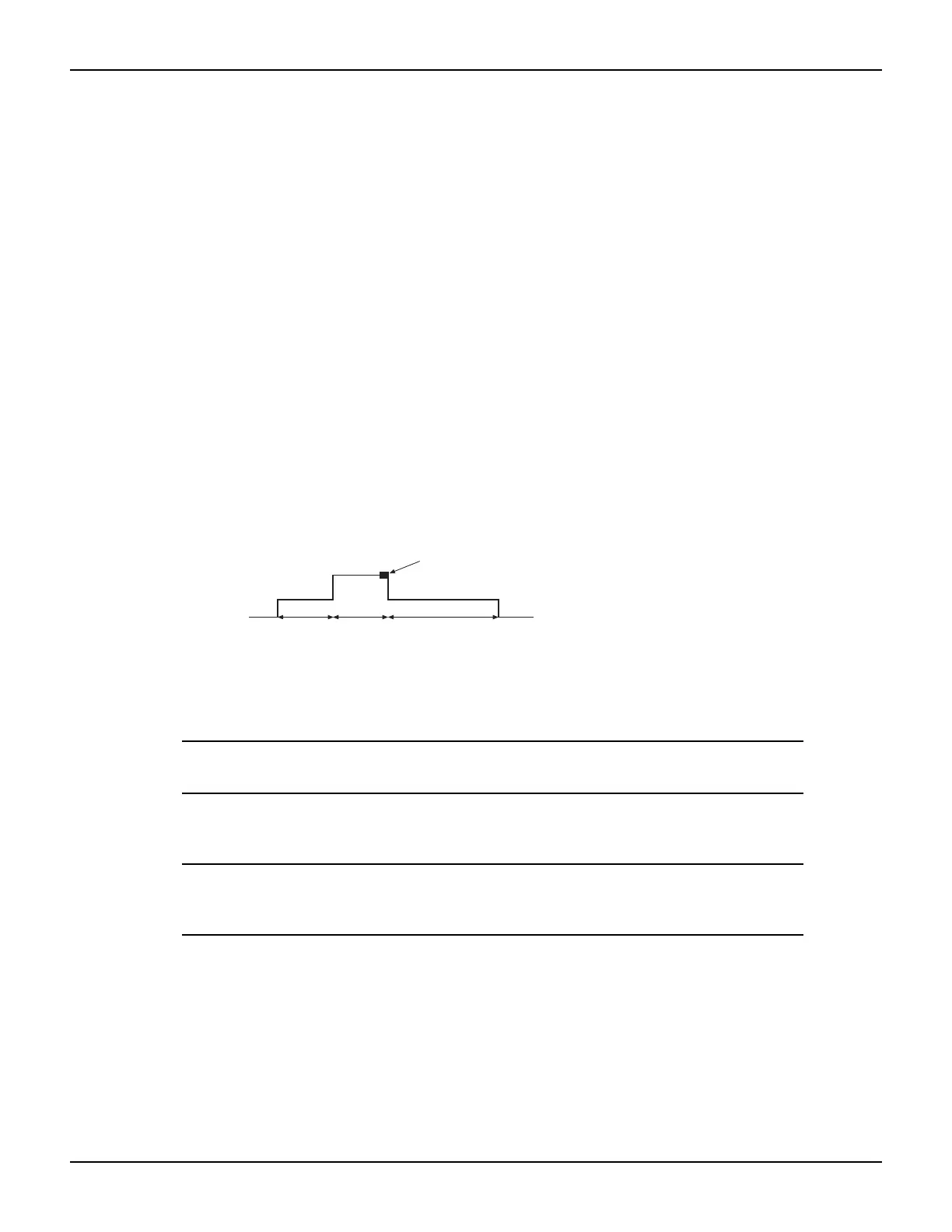
The above function performs a specified number of pulse V, measure I cycles:
• Sets the smu to output bias volts and dwell for ton seconds.
• Sets the smu to output level volts and dwell for ton seconds.
• Performs current measurement with the source at level volts.
• Sets the smu to output bias volts for toff seconds.
• Repeats the above sequence for points pulse-measure cycles.
Figure 3-1 shows one pulse-measure cycle for the function.
Figure 3-1
Pulse-measure cycle for the
level
bias
ton
bias
ton toff
Current measurement
PulseVMeasureI function
Running a factory script
Reference See “Factory scripts” in Section 2 of the Series 2600 Reference Manual for details
on running factory scripts.
NOTE All commands to run a factory script are to be executed from the
Instrument Console of the Test Script Builder.
The following steps explain how to run the PulseVMeasureI function and read the data stored in
the buffer.
NOTE The “KIGeneral” factory script is an autorun script. The script runs
automatically when the Series 2600 is turned on. The functions of the
script are ready to be called.
Step 1: Call the function
The following are example parameters for the PulseVMeasureI function which will perform three
pulse voltage, measure current cycles:
smu SMU A
bias -1V
level 1V
ton 1ms
toff 2ms
 Loading...
Loading...











