TP-6774 2/14a74 Section 8 Component Testing and Adjustment
Grounding electrical equipment. Hazardous voltage can
cause severe injury or death. Electrocution is possible
whenever electricity is present. Ensure you comply with all
applicable codes and standards. Electrically ground the
generator set, transfer switch, and related equipment and
electrical circuits. Turn off the main circuit breakers of all
power sources before servicing the equipment. Never contact
electrical leads or appliances when standing in water or on wet
ground because these conditions increase the risk of
electrocution.
Short circuits. Hazardous voltage/current can cause
severe injury or death. Short circuits can cause bodily injury
and/or equipment damage. Do not contact electrical
connections with tools or jewelry while making adjustments or
repairs. Remove all jewelry before servicing the equipment.
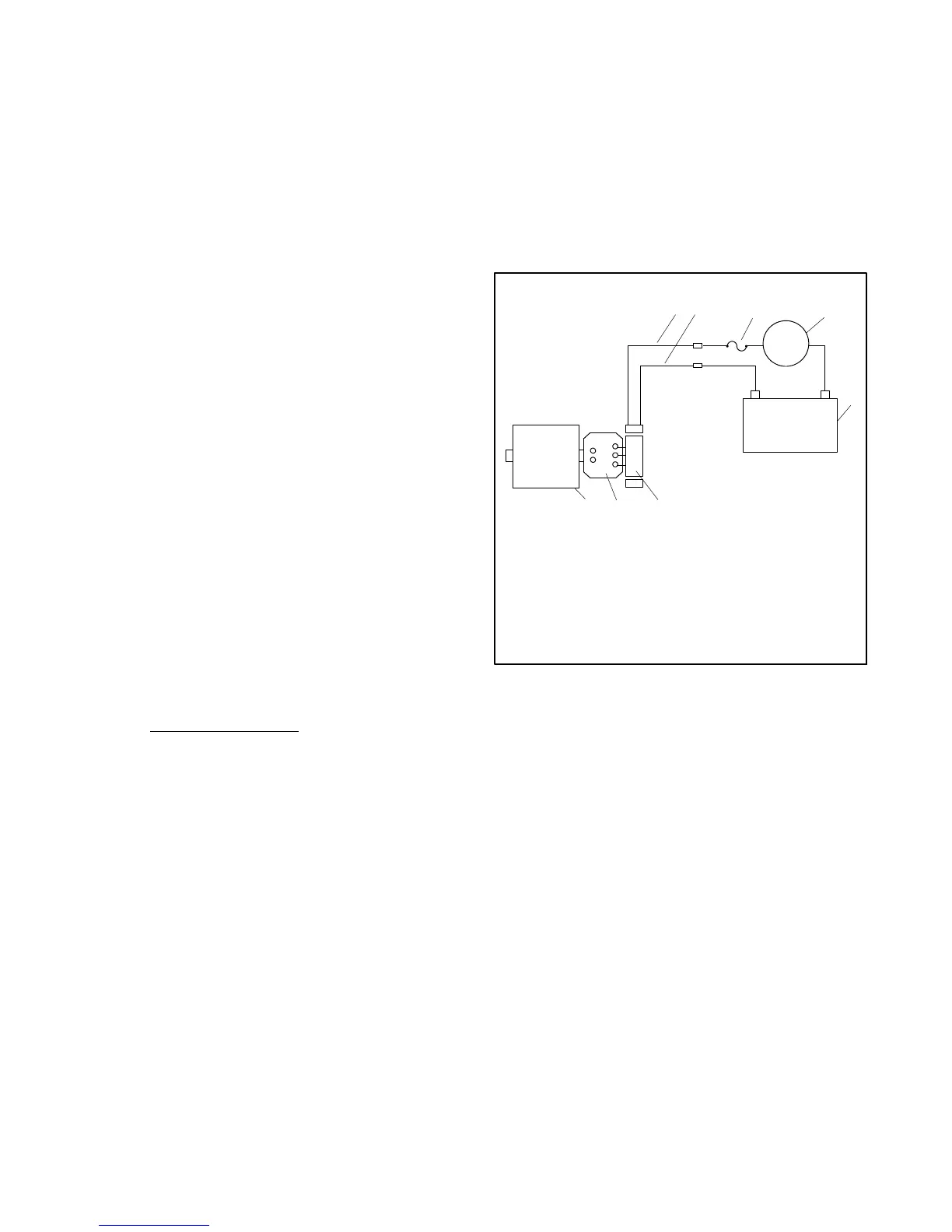
Separate Excitation Procedure:
Perform the following procedure to use an external
voltage source to excite the main field (rotor).
1. Remove the junction box cover and disconnect the
black FN and FP leads from the alternator at the
ADC IId (+) and (--) terminals.
2. Connect a DC ammeter, 10-amp fuse, and a
12-volt automotive battery to the positive (FP) and
negative (FN) exciter leads (or brush leads) as
shown in Figure 8-3. Note and record the ammeter
reading.
Note: The approximate ammeter reading should be the
battery voltage divided by the specified rotor
resistance. See Section 1, Specifications, for the
specified rotor resistance values.
Example :
12 volts (battery voltage)
3.5 ohms (rotor resistance)
= 3.4 amps (rotor current)
3. Start the engine and check that the ammeter
reading remains stable. An increasing meter
reading indicates a shorted rotor. A decreasing
meter reading to zero or an unstable reading
suggests a running open. Refer to Section 8.8,
Rotor, to test the rotor. If the ammeter reading is
stable, proceed to step 4.
4. Check for AC output across the stator leads; see
Section 8.9, Stator. Compare the readings to the
AC output values shown in Section 1,
Specifications. If the readings vary considerably, a
faulty stator is likely. Refer to Section 8.9, Stator,
for further information.
5. If this test shows that the rotor and stator are in
good condition, check the wiring and fuses. Check
the controller settings and connections. See
Section 7, Controller.
AC
F+
F--
AC
AC
+
-
+
12 3
4
5
678
TP563274
-
1. FN lead (disconnected in step 1)
2. FP lead (disconnected in step 1)
3. 10-amp fuse
4. DC ammeter
5. 12V battery
6. Exciter (or brushes/slip rings)
7. Rectifier module
8. Main field (rotor)
FP
FN
Figure 8-3 Separate Excitation Connections

 Loading...
Loading...



