10 TUNING THE CHASSIS 30
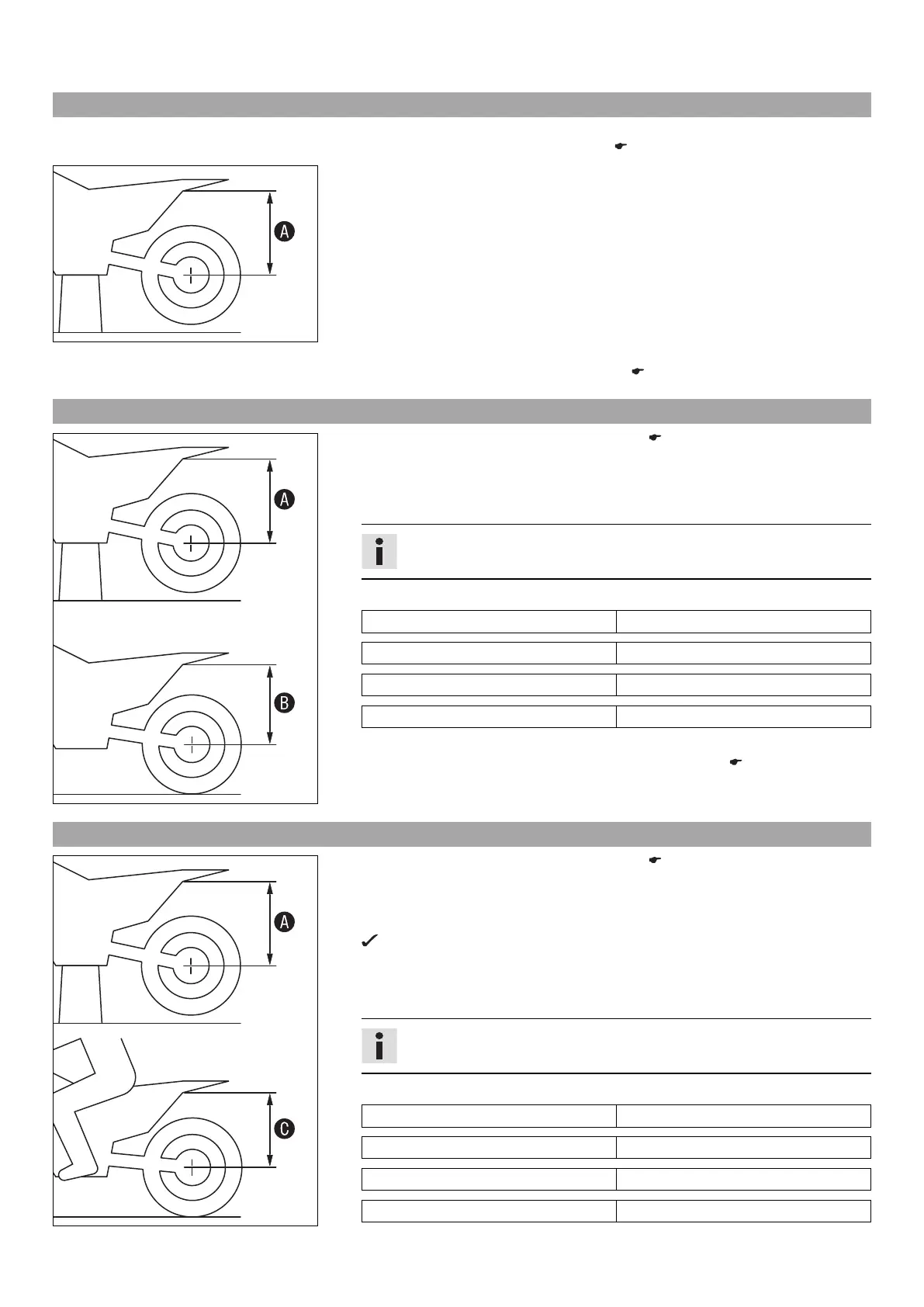
10.6 Measuring rear wheel sag unloaded
Preparatory work
– Raise the motorcycle with the lift stand. ( p. 36)
400988-10
Main work
– Measure the vertical distance between the rear axle and a fixed point such as a
marking on the side cover.
–
Note down the value as dimension
A
.
Finishing work
– Remove the motorcycle from the lift stand. ( p. 36)
10.7 Checking the static sag of the shock absorber
400989-10
–
Measure distance
A
of rear wheel unloaded. ( p. 30)
– Hold the motorcycle upright with the aid of an assistant.
– Measure the distance between the rear axle and the fixed point again.
–
Note down the value as dimension
B
.
Info
The static sag is the difference between measurements
A
and
B
.
– Check the static sag.
Static sag (SX‑F EU) 30 mm (1.18 in)
Static sag (SX‑F USA) 30 mm (1.18 in)
Static sag (SX‑F Factory Edition) 30 mm (1.18 in)
Static sag (XC‑F) 30 mm (1.18 in)
» If the static sag is less or more than the specified value:
–
Adjust the spring preload of the shock absorber. x ( p. 31)
10.8 Checking the riding sag of the shock absorber
400990-10
–
Measure distance
A
of rear wheel unloaded. ( p. 30)
– With another person holding the motorcycle, the rider, wearing full protective cloth-
ing, sits on the seat in a normal sitting position (feet on footrests) and bounces up
and down a few times.
The rear wheel suspension levels out.
– Another person now remeasures the distance between the rear axle and a fixed
point.
–
Note down the value as dimension
C
.
Info
The riding sag is the difference between measurements
A
and
C
.
– Check the riding sag.
Riding sag (SX‑F EU) 90 mm (3.54 in)
Riding sag (SX‑F USA) 100 mm (3.94 in)
Riding sag (SX‑F Factory Edition) 100 mm (3.94 in)
Riding sag (XC‑F) 100 mm (3.94 in)

 Loading...
Loading...