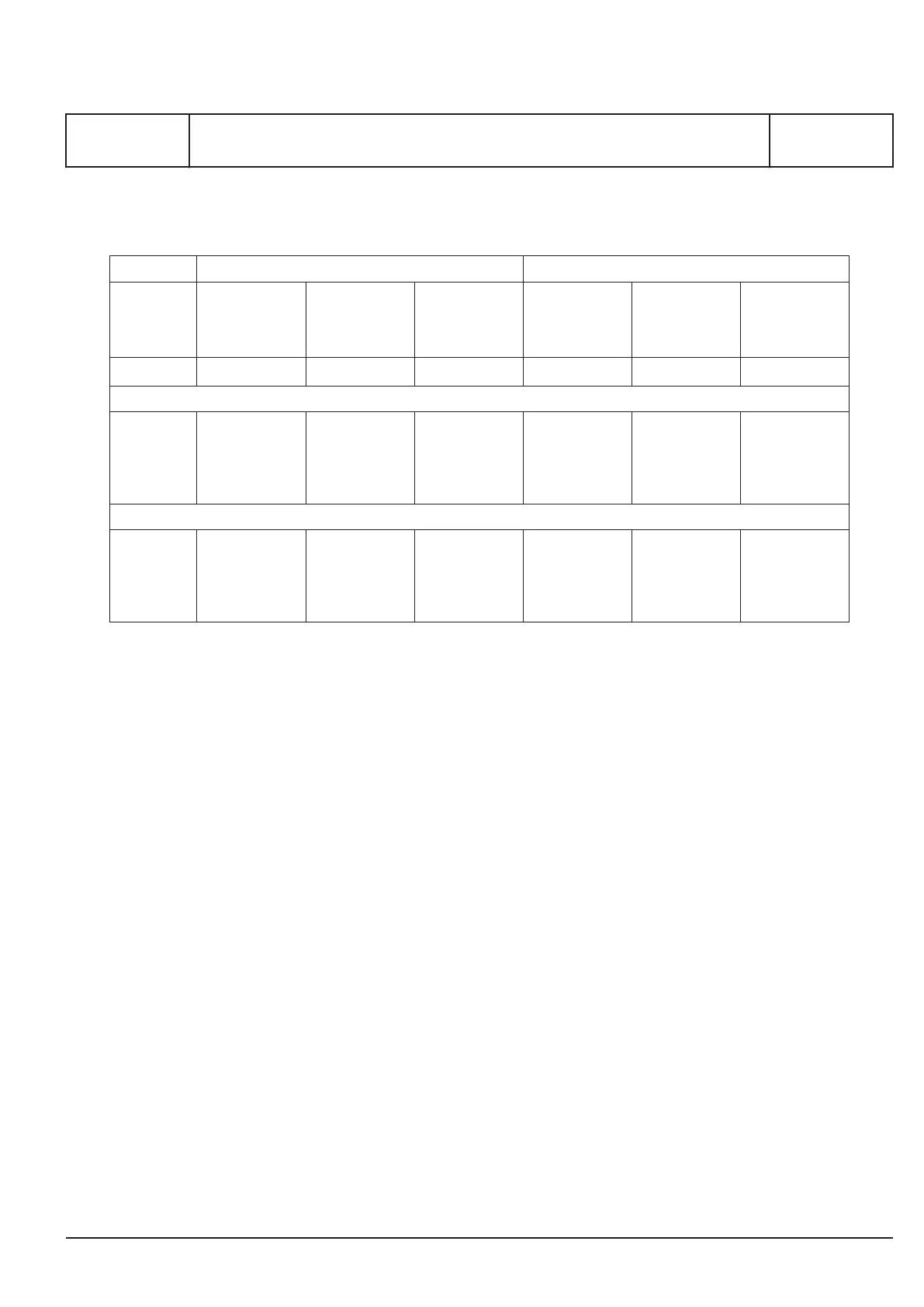
GenSet
Eng. type Moments of inertia Flywheel
Number of
cylinders
Continuous
rating
Moments
required total
J
min
Engine +
damper
Moments of
inertia
Mass Required
moment of
inertia after
flywheel *)
kW Kgm
2
Kgm
2
Kgm
2
kg Kgm
2
n = 720 rpm
5L27/38
6L27/38
7L27/38
8L27/38
9L27/38
1500
2100
2450
2800
3150
691
968
1129
1290
1451
207
264
291
353**)
381**)
403
403
403
403
403
1451
1451
1451
1451
1451
81
301
435
534
667
n = 750 rpm
5L27/38
6L27/38
7L27/38
8L27/38
9L27/38
1600
2100
2450
2800
3150
679
892
1040
1189
1338
207
264
291
353**)
381**)
403
403
403
403
403
1451
1451
1451
1451
1451
69
225
346
433
554
*) Required moment of inertia after flywheel is based on 403 Kgm
2
flywheel, and the most common damper.
The calucation is based on 42% engine acceleration.
Larger flywheel means lower alternator inertia demand, as total GenSet inertia is the final demand.
Selection of bigger flywheel for having lower alternator inertia demand, have to be approved by a torsional
vibration calculation.
The following flywheels are available:
J
J
J
=
=
=
403 Kgm
2
570 Kgm
2
801 Kgm
2
**) Incl. flexible coupling for two bearing alternator.
MAN Diesel & Turbo
1687148-5.2
Page 1 (1)
Moment of inertia
D 10 30 0
L27/38S, L27/38
2015.11.27

 Loading...
Loading...