i
PROGRAMMING
I
I
Soecial reaisters
D
I
The special registers
(D)
are data registers which have a predefined function. They
must not be written
too
in
the
sequence program, except for those indicated.
A
table
of
all
the
special registers and details
of
their functions is shown below.
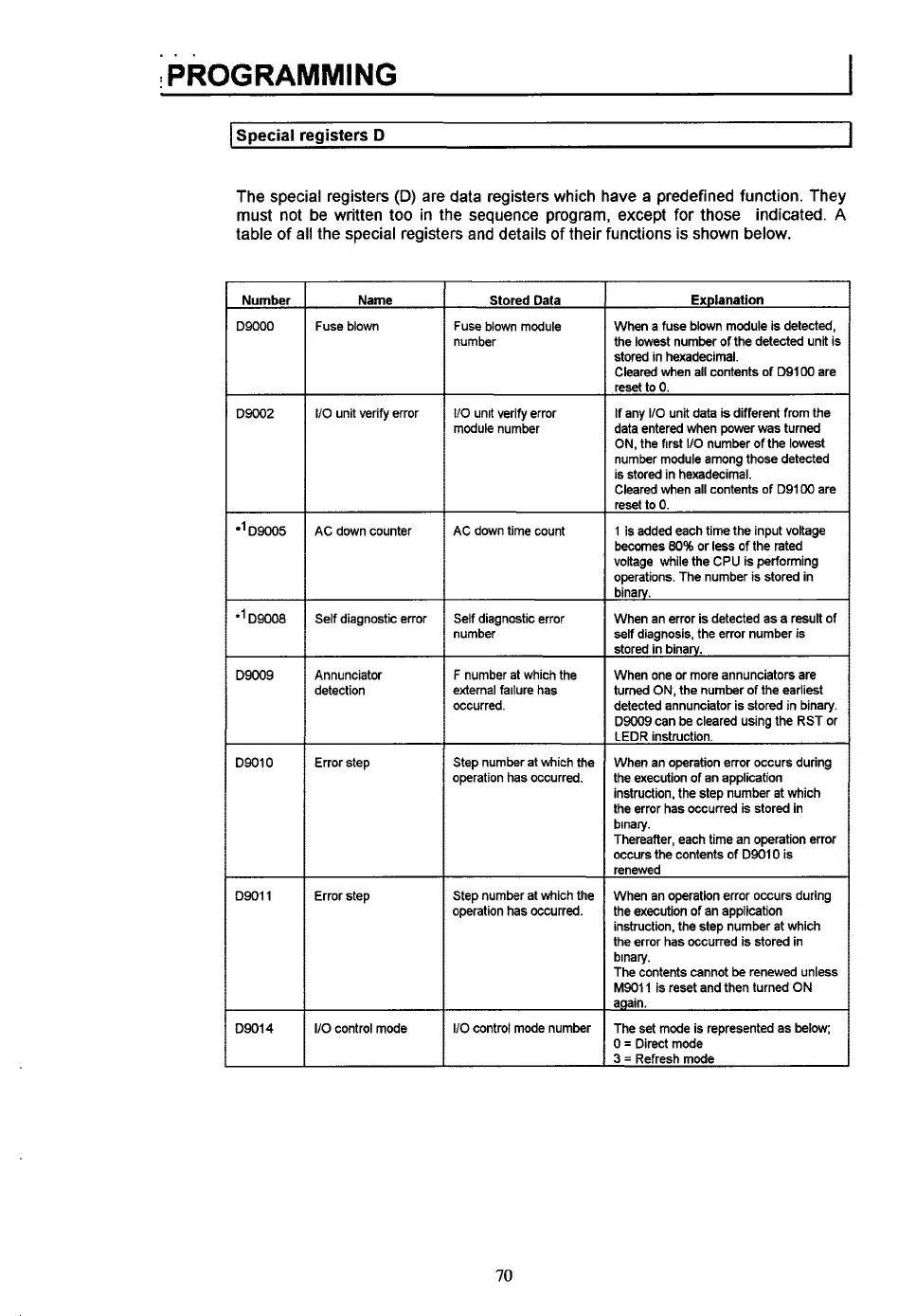
Number
D9000
D9002
D9005
*'D9008
D9009
D9010
D9011
D9014
Name
Fuse blown
I/O unit verify error
AC down counter
Self
diagnostic error
Annunciator
detection
Error step
Error step
I/O
control mode
Stored Data
Fuse blown module
number
110
unit verify error
module number
AC down time count
Self diagnostic error
number
F
number at which the
external failure has
occurred.
Step number at which the
operation has occurred.
Step number at which the
operation has occurred.
110
control mode number
Explanation
When
a
fuse blown module is detected,
the
lowest
number
of
the detected unit is
stored in hexadecimal.
Cleared when all contents of D91W are
reset
to
0.
If any
110
unit data is different from the
data entered when power was turned
ON, the first
110
number
of
the lowest
number module among those detected
is stored in hexadecimal.
Cleared when all contents of D91W are
reset
to
0.
1 is added each time the input voltage
becomes
80%
or
less
of the rated
voltage while the
CPU
is performing
operations. The number is stored in
binary.
When an error is detected as a result of
self diagnosis, the error number is
stored in binarv.
When one or more annunciators are
turned
ON,
the number of the earliest
detected annunciator is stored in binary.
D9009 can be cleared using the RST or
LEDR instruction.
When an operation error occurs during
the execution of an application
instruction, the step number at which
the error has occurred
is
stored in
binary.
Thereafter, each time an operation error
occurs the contents
of
D9010 is
renewed
When an operation error occurs during
the execution of an application
instruction, the step number at which
the error has occurred is stored in
binary.
The contents cannot be renewed unless
M9011 is reset and then turned
ON
again.
The set mode is represented as below;
0
=
Direct mode
3
=
Refresh mode
70

 Loading...
Loading...











