10
DEVICE EXPLANATION
10.13 Constants
10.13.3 Real number (E)
10 - 112
9
Parameters
10
Device Explanation
11
CPU Module Processing
Time
12
Procedure for Writing
Program to CPU ModuleAppendicesIndex
10.13.3 Real number (E)Note31
(1) Definition
Real numbers are devices which designate real numbers in the sequence program.
Specify it as E (example: K1234) in a sequence program.( Section 3.9.4)
(2) Designation range
(a) Setting range of real number
The setting range of the real number is as follows:
• For the single-precision floating-point data
- 2
128
< Device - 2
-126
, 0 , 2
-126
Device < 2
128
• For the double-precision floating-point data
Note10.30
- 2
1024
< Device - 2
-1022
, 0 , 2
-1022
Device < 2
1024
(b) The operations when an overflow or underflow occurs
The following table shows the operation of the CPU module when an overflow or
underflow occurs at the time of arithmetic operation.
Note31
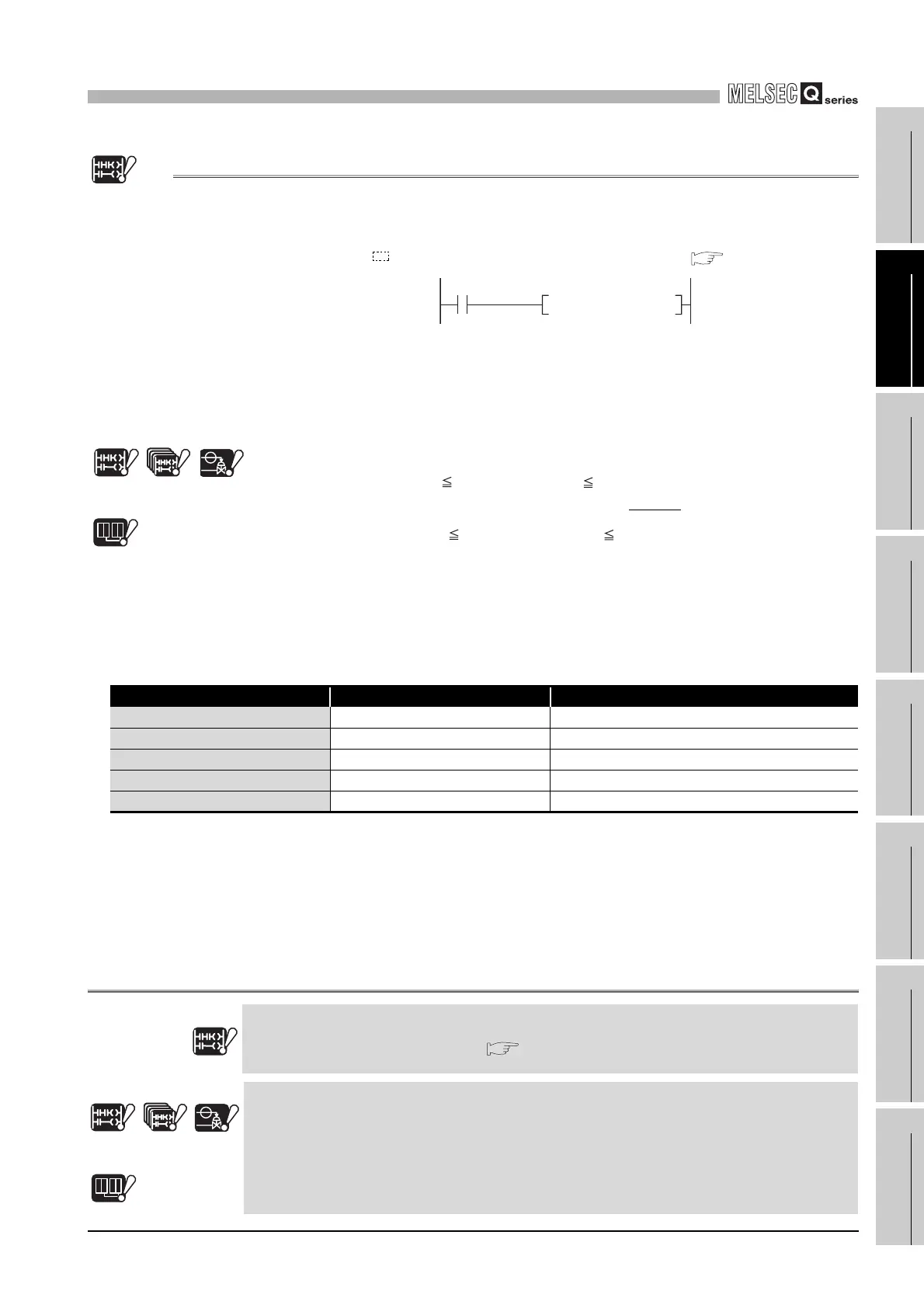
Figure 10.95 Specifying the real number
Table10.27 Operations when an overflow or underflow occurs
CPU module Operation at overflow Operation at underflow
Basic model QCPU 4100 Error occurrence 4100 Error occurrence
High Performance model QCPU 4100 Error occurrence 4100 Error occurrence
Process CPU 4100 Error occurrence 4100 Error occurrence
Redundant CPU 4100 Error occurrence Becomes 0 without error occurrence
Universal model QCPU 4141 Error occurrence Becomes 0 without error occurrence
Note10.29
Basic
When using the real number operation function for the Basic model QCPU, check the versions of
the CPU module and GX Developer. ( Appendix 4.1)
Note10.29
Basic
The Basic model QCPU, High Performance model QCPU, Process CPU, and Redundant CPU
cannot use the double-precision floating-point data.
High
Performance
Process
Redundant
Basic
Note10.30 Note10.30
Note10.30
Note10.30
X1
E1.234 D0EMOVP
High
Performance
Process
Redundant
Basic
Note10.30 Note10.30
Note10.30
Note10.30

 Loading...
Loading...











