27
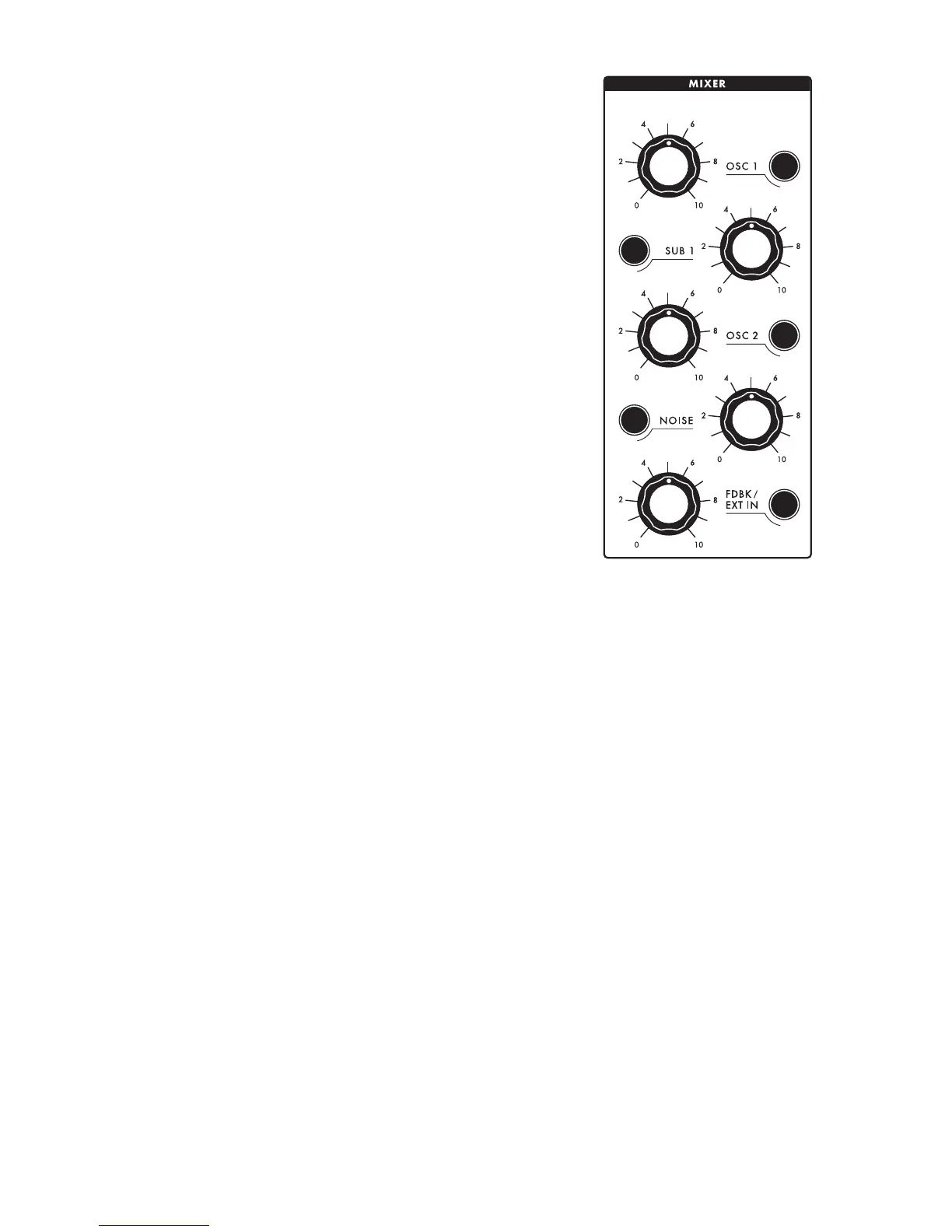
MIXER SECTION
The mixer lets you combine audio signals from each of the Sub
37’s four internal audio sources as well as an external audio source
or mixer feedback. Each mixer source has a dedicated knob for
controlling its relative level as well as a mute button. The beauty
of having dedicated mute buttons is that you can leave an audio
source’s level at a pre-set amount and instantly bring it in or
out with the push of a button. When a level knob is turned fully
counterclockwise, its input is effectively turned off. Turning it
clockwise from 0 increases the level until it reaches its maximum
at 10. Mixer settings higher than 5 will overdrive the input of the
filter, meaning that you can specify which sources are distorted
and which simply pass through the filter.
MIXER CONTROLS
OSC 1
Use this knob to control oscillator 1’s level. Settings higher than 5
push the level beyond unity, imparting gentle filter distortion. A
setting of 5 or below delivers a clean signal to the filter.
SUB OSC
Use this knob to control the sub oscillator’s level. Settings higher
than 5 push the level beyond unity, imparting gentle filter distortion.
A setting of 5 or below delivers a clean signal to the filter. The Sub
37’s sub oscillator is always tuned exactly one octave below oscillator
1’s pitch, and its waveform is always a square wave. Typically, the sub oscillator adds a solid foundation
to the Sub 37’s sound. It is especially useful for crafting monstrous Moog bass patches.
OSC 2
Use this knob to control oscillator 2’s level. Settings higher than 5 push the level beyond unity,
imparting gentle filter distortion. A setting of 5 or below delivers a clean signal to the filter.
NOISE
Use this knob to control the Sub 37’s pink noise generator level. Settings higher than 5 push the level
beyond unity, imparting gentle filter distortion. Noise is useful for programming punchy percussion
and other non-pitched sounds.
Whereas an oscillator generates a pitched waveform, noise is a non-pitched sound source. The two
most common types of noise are white noise and pink noise. Just as white light contains all colors
of the visual spectrum in equal proportion, white noise contains a random distribution of all audible
frequencies. Every frequency has equal amplitude. We hear white noise as a constant ssshh sound,
like an FM radio between stations. Because of the way our brains respond to white noise, the higher
frequencies sound more prominent than the lower ones.
The Sub 37’s noise generator produces a signal called pink noise. Pink noise has equal amplitudes
in every octave, making it sound deeper than white noise - more like the sound of a waterfall. Many
synthesists consider pink noise more useful than white noise.
FDBK / EXT IN:
When nothing is plugged into the EXT IN jack on the left side of the Sub 37, the FDBK / EXT IN
knob takes the output of the mixer and feeds it back into this mixer channel, resulting in a variety of
distorted, sometimes chaotic, sometimes mellow qualities.
Warning: This control can increase the output volume considerably!

 Loading...
Loading...