© National Instruments | 7-13
M Series User Manual
From these results, you can see that while the measurement time for one counter is shorter, the
accuracy is best in the sample clocked and two counter large range measurements. For another
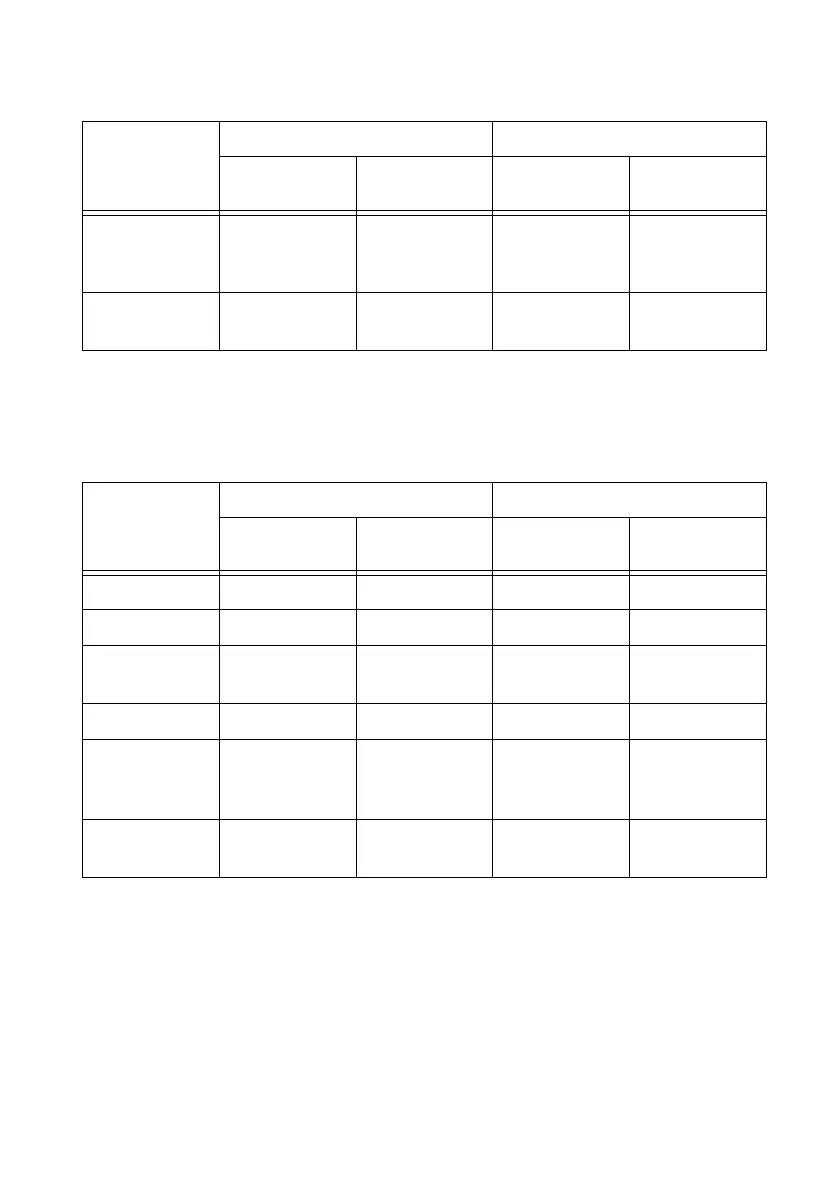
example, Table 7-3 shows the results for 5 MHz.
• Using one counter for low frequency measurements is a good method for many
applications. However, the accuracy of the measurement decreases as the frequency
increases.
• Measuring with one counter (averaged) measures high and low frequency signals
accurately. The advantage of this method is that it requires only one counter. Disadvantages
include the possibility of FIFO overflow at high frequencies and high N for this method.
These measurements take more time and consume some of the available PCI or PXI
Maximum
frequency error
(Hz)
25 0.5 1,000 0.5
Maximum error
(%)
0.05 0.001 2 0.001
Table 7-3. 5 MHz Frequency Measurement Methods
Variable
One Counter Two Counters
— Averaged
High
Frequency
Large Range
fx 5 M 5 M 5 M 5 M
fk 100 M 100 M 1,000 100 M
Measurement
time (mS)
0.0002 1.0002 1 1
N — 5,000 — 5,000
Maximum
frequency error
(Hz)
263 k 50 1,000 50
Maximum error
(%)
5.26 0.001 0.02 0.001
Table 7-2. 50 kHz Frequency Measurement Methods (Continued)
Variable
One Counter Two Counters
— Averaged
High
Frequency
Large Range

 Loading...
Loading...











