
Do you have a question about the National Instruments NI USB-621x and is the answer not in the manual?
| Model | NI USB-621x |
|---|---|
| Category | Computer Hardware |
| Interface | USB |
| Analog Input Resolution | 16 bits |
| Analog Input Sample Rate | 250 kS/s (aggregate) |
| Analog Output Channels | 2 |
| Analog Output Resolution | 16 bits |
| Digital I/O Channels | 8 |
| Counter/Timers | 2 |
| Operating System Compatibility | Windows, Linux |
| Power Supply | USB powered |
| Device Type | Data Acquisition Device |
| Analog Input Channels | 16 single-ended or 8 differential |
| Analog Input Range | ±10 V |
| Operating Temperature | 0 °C to 50 °C |
Details on installing the NI-DAQmx software, including step-by-step instructions for setup and configuration.
Non-software-specific information for installing USB DAQ devices.
How to program DAQ devices using NI-DAQ driver software, functions, and VIs.
Details the signals found on the I/O connectors, including AI, AO, and PFI signals.
Describes supported ground-reference settings (DIFF, RSE, NRSE) for analog input.
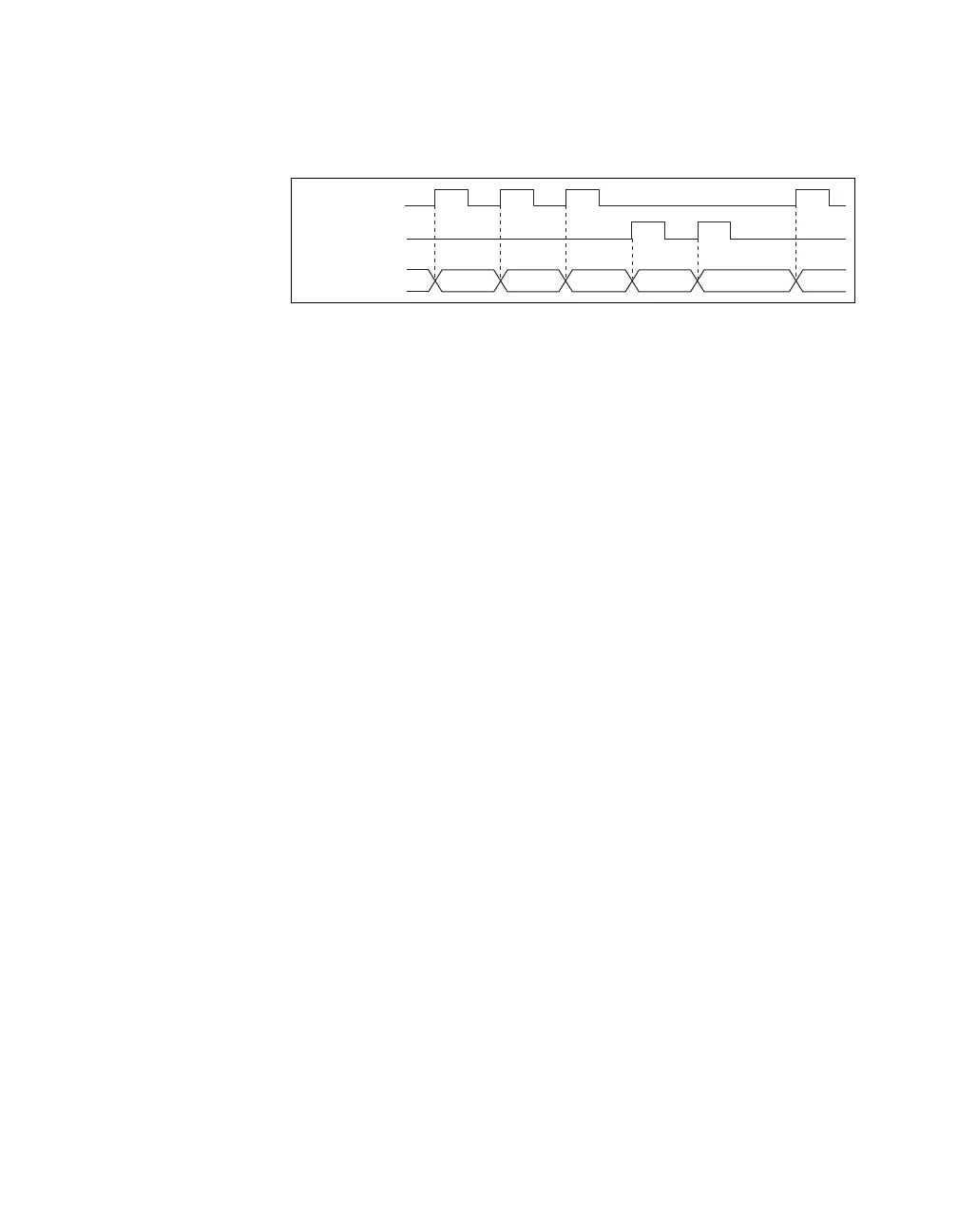
Issues to consider for accurate multichannel scanning, such as settling time and channel order.
Explains software-timed vs. hardware-timed acquisitions and buffered vs. non-buffered modes.
Details the support for start, reference, and pause triggers for analog input.
Summarizes the various timing signals used for analog input operations.
Guidance on using M Series devices for analog input applications in software.
How to connect floating signal sources, including when to use differential or single-ended configurations.
How to connect ground-referenced signal sources and common connection configurations.
Diagrams and explanations for differential connections with floating signal sources.
Explains software-timed vs. hardware-timed generations for analog output.
Details the support for start and pause triggers for analog output operations.
Explains various methods for measuring frequency using the device's counters.
Details applications for counter outputs, including pulse and train generation.
Describes arm start, start, and pause triggers for counter operations.
How to generate triggers using digital signals, specifying source and edge.









