4 Understanding Programming
4-18
CP2E CPU Unit Software User’s Manual(W614)
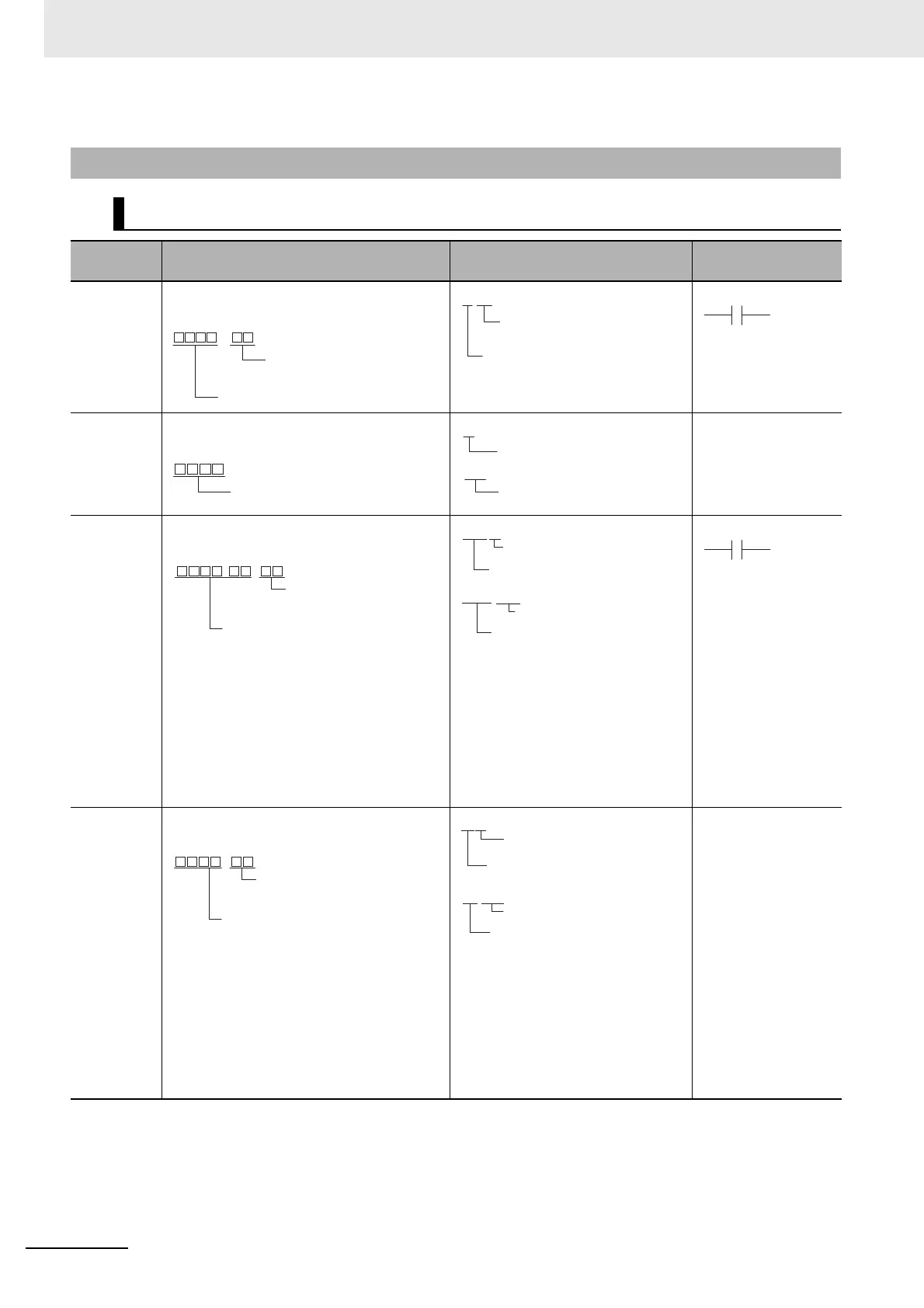
4-4-5 Specifying Data in Operands
Specifying Addresses
Operand Description Example
Application
examples
Specifying
bit
addresses
The word address and bit number are speci-
fied directly to specify a bit.
Specifying
word
addresses
The word address is specified directly to
specify a 16-bit word.
MOV 3 D200
Specifying
offsets for bit
addresses
In brackets, specify the number of bits to off-
set the specified starting bit address.
A symbol can also be specified for the start-
ing bit address. Only Holding, Work, and DM
Area addresses can be used regardless of
whether a physical address or symbol is
used.
A constant or word address in I/O memory
can be used for the offset. If a word address
is specified, the contents of the word is used
as the offset.
Specifying
offsets for
word
addresses
In brackets, specify the number of words to
offset the specified starting bit address.
A symbol can also be specified for the start-
ing word address. Only Holding, Work, and
DM Area addresses can be used regardless
of whether a physical address or symbol is
used.
A constant or word address in I/O memory
can be used for the offset. If a word address
is specified, the contents of the word is used
as the offset.
MOV 3 D0[200]
Bit number
(00 to 15)
Word address
.
Bit number 02
1
Word address CIO 1
.02
1.02
Word address
3
Word address CIO 3
D200
Word address D200
Offset Constant
0 to 15 or word
address in I/O memory
Starting bit address
.
10.00[2]
Number of bits to offset the address
→Specify 10.02
Starting bit address
10.00 [W0]
Number of bits to offset the address
When W0 = &2→
Specify
10.02
Starting bit address
10.00[2]
Starting word address
Offset Constant of 0 or
higher or word address in
I/O memory
[]
D0[2]
Number of words to offset the address
→Specify D2
Startin
word address
D0 [W0]
Starting word address
Number of bits to offset the address
When W0 = &2→
Specify
D2
 Loading...
Loading...











