166
Using Tasks Section 4-2
4-2-4 Designing Tasks
We recommend the following guidelines for designing tasks.
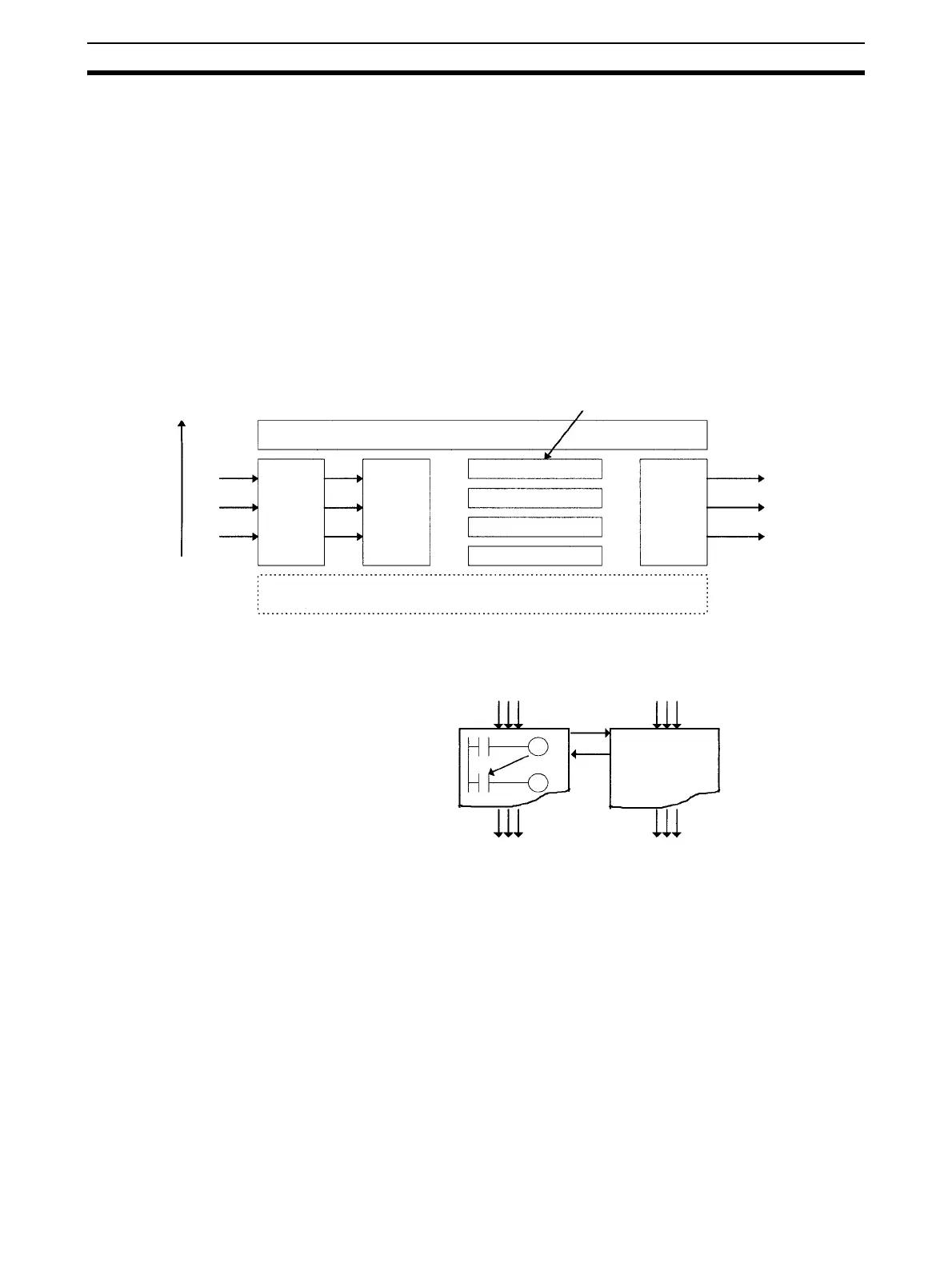
1,2,3... 1. Use the following standards to study separating tasks.
a) Summarize specific conditions for execution and non-execution.
b) Summarize the presence or absence of external I/O.
c) Summarize functions.
Keep data exchanged between tasks for sequence control, analog
control, man-machine interfacing, error processing and other pro-
cesses to an absolute minimum in order to maintain a high degree
of autonomy.
d) Summarize execution in order of priority.
Separate processing into cyclic and interrupt tasks.
2. Be sure to break down and design programs in a manner that will ensure
autonomy and keep the amount of data exchanged between tasks (pro-
grams) to an absolute minimum.
3. Generally, use an overall control task to control the READY/Standby status
of the other tasks.
4. Allocate the lowest numbers to tasks with the highest priority.
Example: Allocate a lower number to the control task than to processing
tasks.
5. Allocate lower numbers to high-priority interrupt tasks.
6. A task in READY status will be executed in subsequent cycles as long as
the task itself or another task does not shift it to Standby status. Be sure to
insert a TKOF(821) (TASK OFF) instruction for other tasks if processing is
to be branched between tasks.
7. Use the Initial Task Execution Flag (A20015) or the Task Start Flag
(A20014) in the execution condition to execution instructions to initialize
tasks. The Initial Task Execution Flag will be ON during the first execution
of each task. The Task Start Flag each time a task enters READY status.
Input
proces-
sing
Overall
control
(may in-
clude error
processing
in some
cases)
Breakdown by function
Error processing
Sequence control
Analog control
Man-machine interfacing
Interrupt
Output
processing
Breakdown by execution and non-execution conditions
Order priority
External I/O
External outputs
Minimize data
exchange
 Loading...
Loading...











