23
Basic Concepts Section 2-1
Note Operands are also called the first operand, second operand, and so on, start-
ing from the top of the instruction.
2-1-3 Instruction Location and Execution Conditions
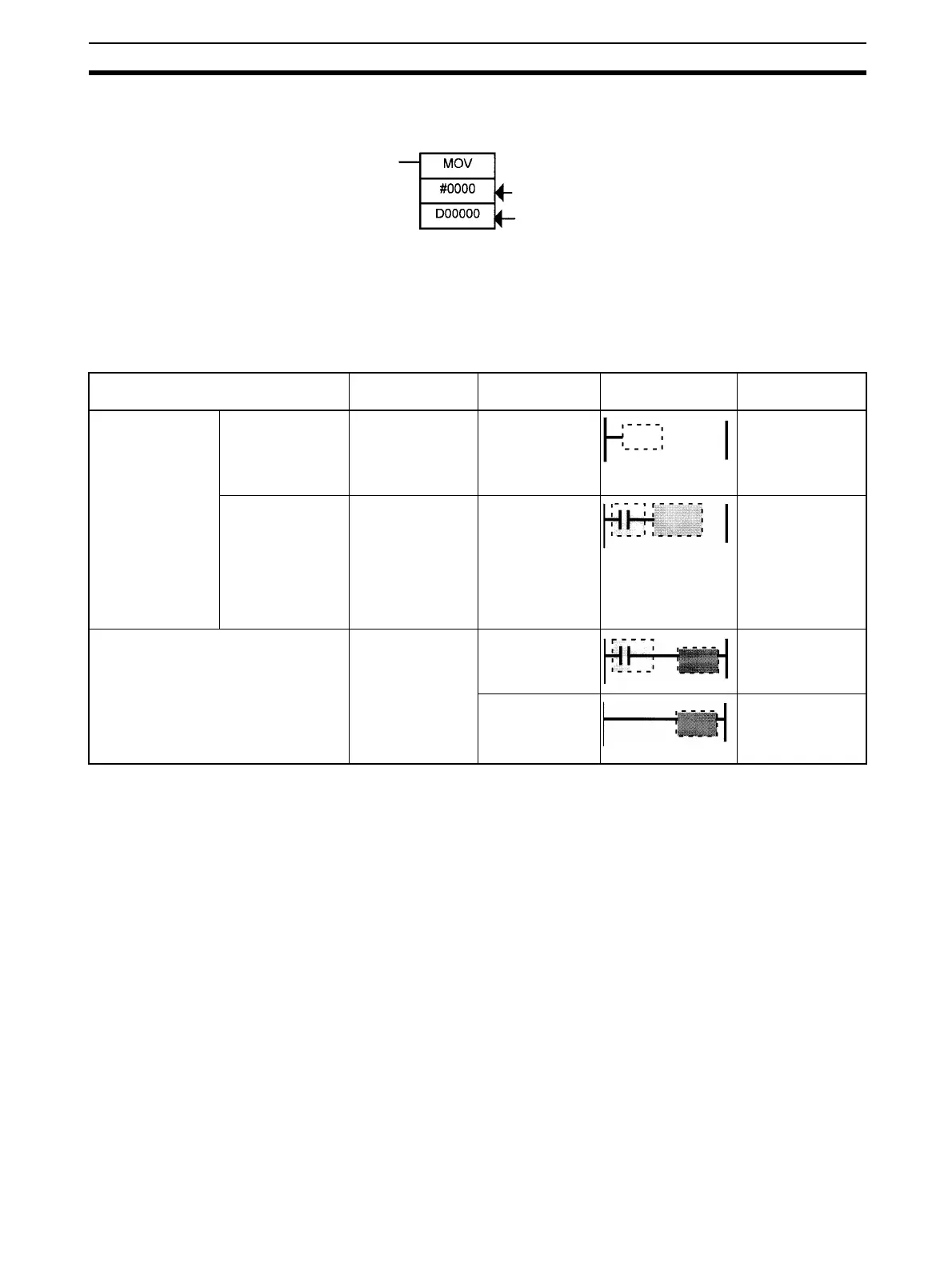
The following table shows the possible locations for instructions. Instructions
are grouped into those that do and those do not require execution conditions.
See
SECTION 3 Instruction Functions Instructions for details on individual
instructions.
Note 1. There is another group of instruction that executes a series of mnemonic
instructions based on a single input. These are called block programming
instructions. Refer to the CS/CJ Series CPU Units Instruction Reference
Manual for details on these block programs.
2. If an instruction requiring an execution condition is connected directly to
the left bus bar without a logical start instruction, a program error will occur
when checking the program on a Programming Device (CX-Programmer
or Programming Console).
First operand
Second operand
Instruction type Possible location Execution
condition
Diagram Examples
Input instructions Logical start (Load
instructions)
Connected directly
to the left bus bar
or is at the begin-
ning of an instruc-
tion block.
Not required. LD, LD TST(350),
LD > (and other
symbol compari-
son instructions)
Intermediate
instructions
Between a logical
start and the out-
put instruction.
Required. AND, OR, AND
TEST(350), AND
> (and other ADD
symbol compari-
son instructions),
UP(521),
DOWN(522),
NOT(520), etc.
Output instructions Connected directly
to the right bus
bar.
Required. Most instructions
including OUT and
MOV(021).
Not required. END(001),
JME(005),
FOR(512),
ILC(003), etc.
 Loading...
Loading...











