37
Basic Concepts Section 2-1
(DIFD and % instructions) are set to OFF. This prevents differentiation
outputs from being output unexpectedly at the start of operation.
• An upwardly differentiated instruction (DIFU or @ instruction) will output
ON only when the execution condition is ON and flag for the previous
value is OFF.
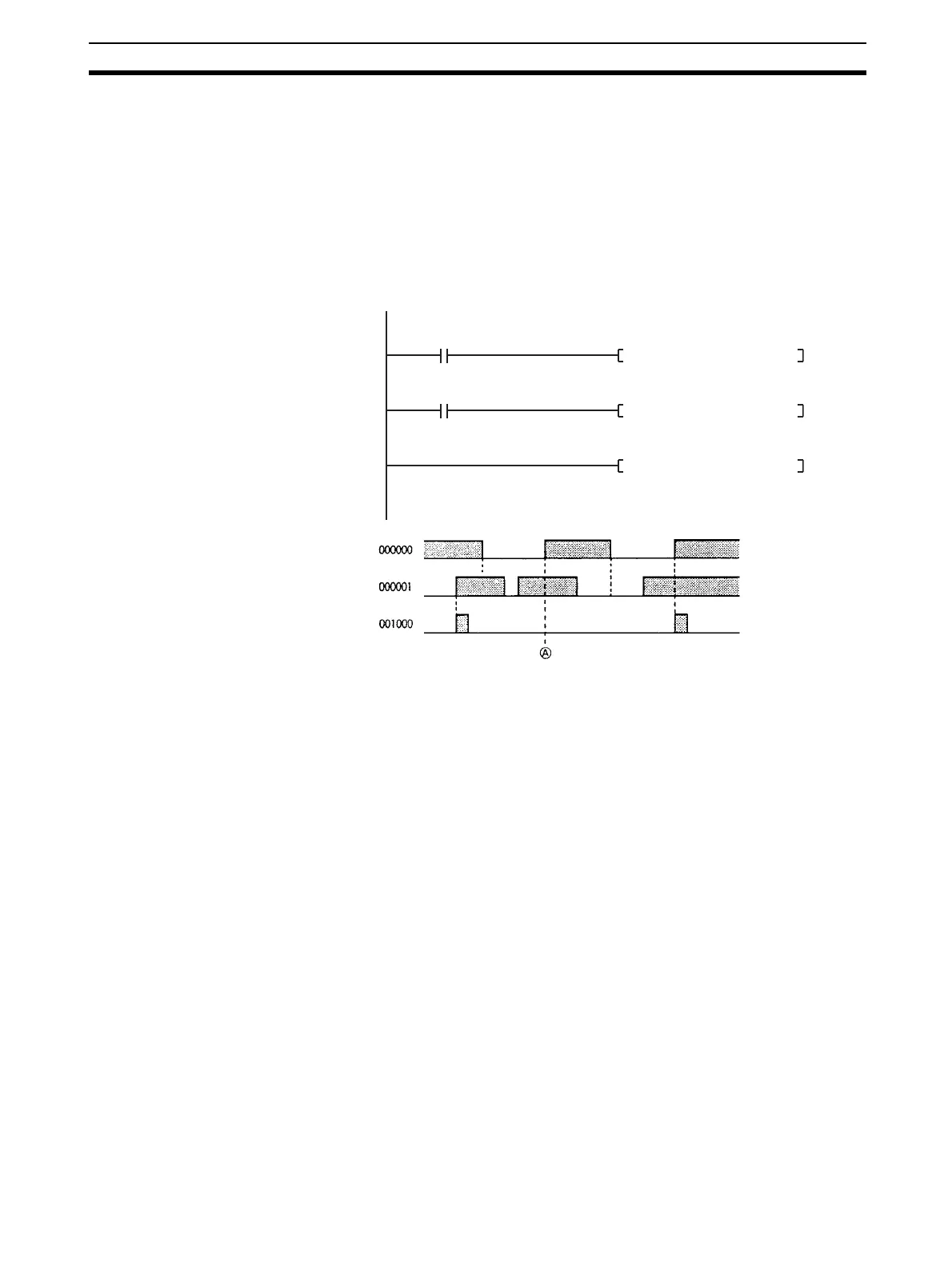
• Use in Interlocks (IL - ILC Instructions)
In the following example, the previous value flag for the differentiated
instruction maintains the previous interlocked value and will not output a
differentiated output at point A because the value will not be updated
while the interlock is in effect.
• Use in Jumps (JMP - JME Instructions): Just as for interlocks, the pre-
vious value flag for a differentiated instruction is not changed when the
instruction is jumped, i.e., the previous value is maintained. Upwardly and
downwardly differentiate instructions will output the execution condition
only when the input status has changed from the status indicated by the
previous value flag.
Note a) Do not use the Always ON Flag or A20011 (First Cycle Flag) as
the input bit for an upwardly differentiated instruction. The instruc-
tion will never be executed.
b) Do not use Always OFF Flag as the input bit for a downwardly dif-
ferentiated instruction. The instruction will never be executed.
IL is
executing
IL is
executing
(002)
IL
(013)
DIFU 001000
(003)
ILC
0000
00
0000
01
 Loading...
Loading...











