ENGINE
2.13
ENGINE INSPECTION PROCEDURES
Cylinder Head Inspection
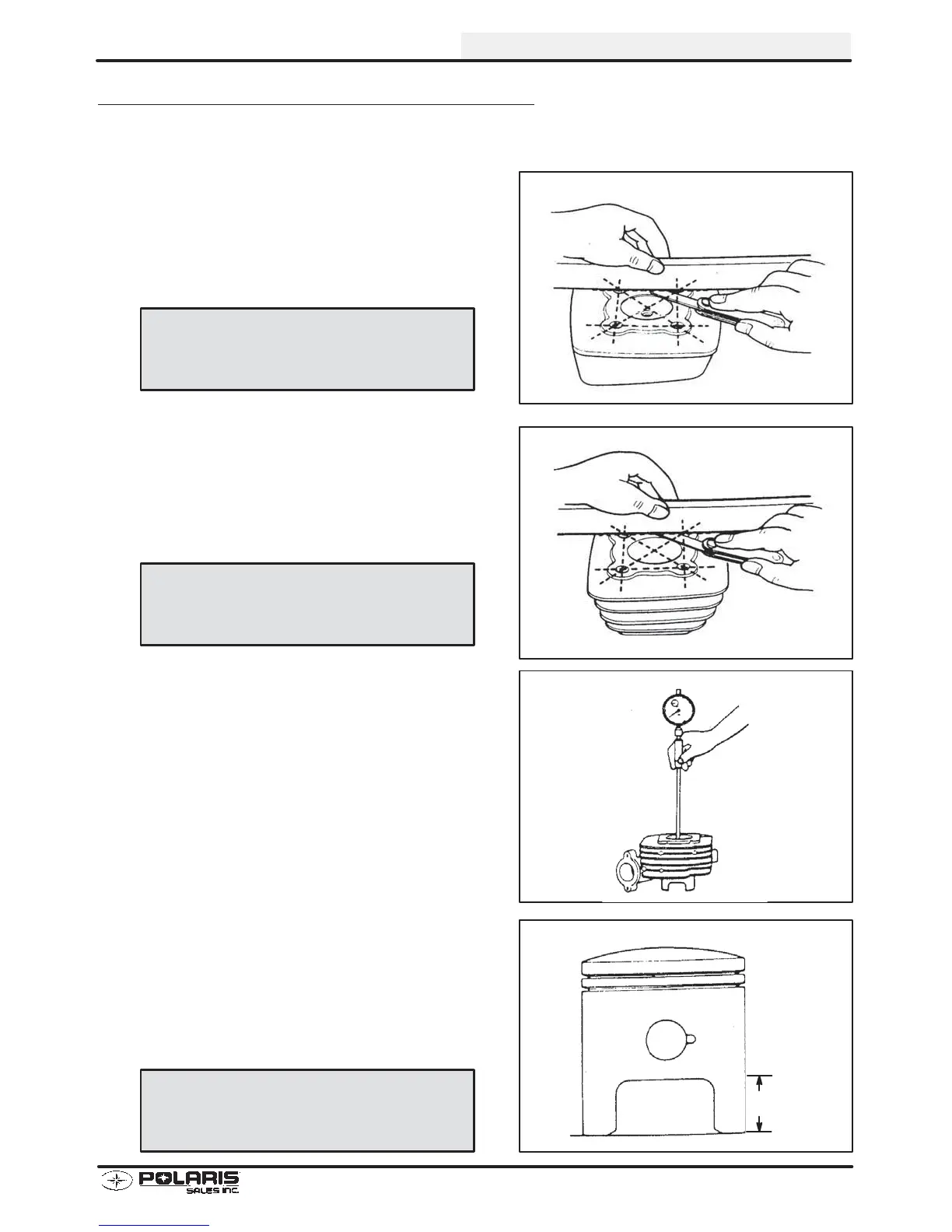
1. Inspect the surface of the cylinder head for
warpage. Clean all gasket residue completely from
sealing surface. Use a feeler gauge and straight
edge. Measure the gap six(6) different ways as
shown in illustration at left. Normal gap should be
.002
″
(0.05 mm) or less. If gap is excessive,
resurfacing head or replacement is needed.
Cylinder Inspection
2. Inspect the surface of the cylinder for warpage.
Clean all gasket residue completely from sealing
surface. Use a feeler gauge and straight edge.
Measure the gap six(6) different ways as shown in
illustration at left. Normal gap should be .002″ (0.05
mm) or less. If gap is excessive, resurfacing
cylinder or replacement is needed.
3. Inspect the cylinder walls for damage or scoring.
The cylinder bore must be de-glazed whenever new
piston rings are installed. If cylinder wear or
damage is excessive, it will be necessary to
oversize the cylinder using a new oversize piston
and rings. See Honing to Oversize in this chapter.
Inspect cylinder for out of round.
PIston Inspection
4. Inspect the piston for scoring or cracks in piston crown
or pin area. Excessive carbon buildup below the ring
land is an indication of piston, ring, or cylinder wear. If
damage is excessive, replace piston. Piston-to-cylinder
clearance should not exceed .0047″ (0.12 mm).
Measure the piston 5/8″ (15 mm) from bottom. Then
measure inside diameter of cylinder. The difference
between these measurements should not exceed
.0047″ (0.12 mm).
Cylinder Head Warp
Service Limit:
.002I (0.05 mm)
Cylinder Warp
Service Limit:
.002I (0.05 mm)
5/8″ (15 mm)
Piston to Cylinder Clearance:
.0047I (0.12 mm)

 Loading...
Loading...











