Getting Connected to MindSphere
Getting Started, 05/2018 75
Appendix
A.1 Overview of datatypes
A.1.1 Overview of S7 datatypes
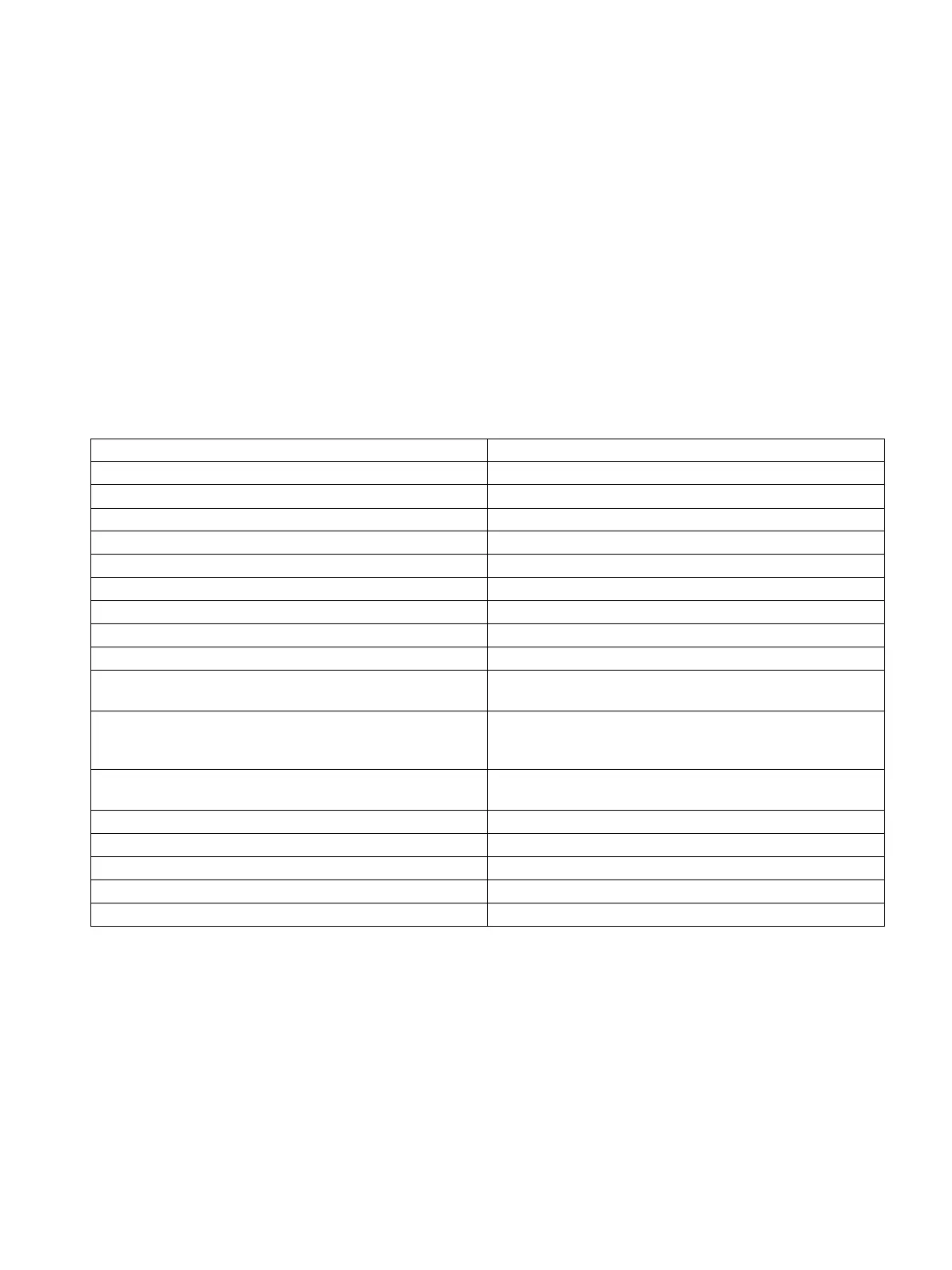
Address format examples
DB15.DBX6.3 Reads 3rd bit of byte 6 of datablock 15
DB15.DBB4 Reads a byte starting from offset 4 of datablock 15
DB15.DBBYTE4 Reads a byte starting from offset 4 of datablock 15
DB15.DBCHAR6 Reads a char starting from offset 6 of datablock 15
DB15.DBW10 Reads a word starting from offset 10 of datablock 15
DB15.DBWORD10 Reads a word starting from offset 10 of datablock 15
DB15.DBINT12 Reads an int starting from offset 12 of datablock 15
DB15.DBDW24 Reads a double word starting from offset 24 of datablock 15
DB15.DBDWORD24 Reads a double word starting from offset 24 of datablock 15
DB15.DBDINT28 Reads a double int starting from offset 28 of datablock 15
DB15.DBREAL32 Reads a floating point number starting from offset 32 of
datablock 15
DB15.DBSTRING10 Reads a string starting from offset 12.10th byte is maximum
string length (254) and 11th byte is actual string length.If
11th byte is AA, 170 bytes read starting from 12th byte.
1)
DB15.DBSTRING10,100 Reads a string starting from offset 10. Length of the string is
100 bytes. (Maximum string length is 254)
1)
T4 Reads 4th timer
1)
C5 Reads 5th counter
1)
QX35.1 Reads 1st bit of 35th byte of output
1)
MD16 Reads a double word of memory starting from offset 16
1)
IB40 Reads a byte of input starting from offset 40
1)
1)
Only timer and counters don't need variables.
 Loading...
Loading...











