34
Group 21 Short block
Inspecting the crankshaft
Clean the crankshaft carefully in all channels after dis-
assembly and inspect thoroughly to determine if over-
haul is really necessary.
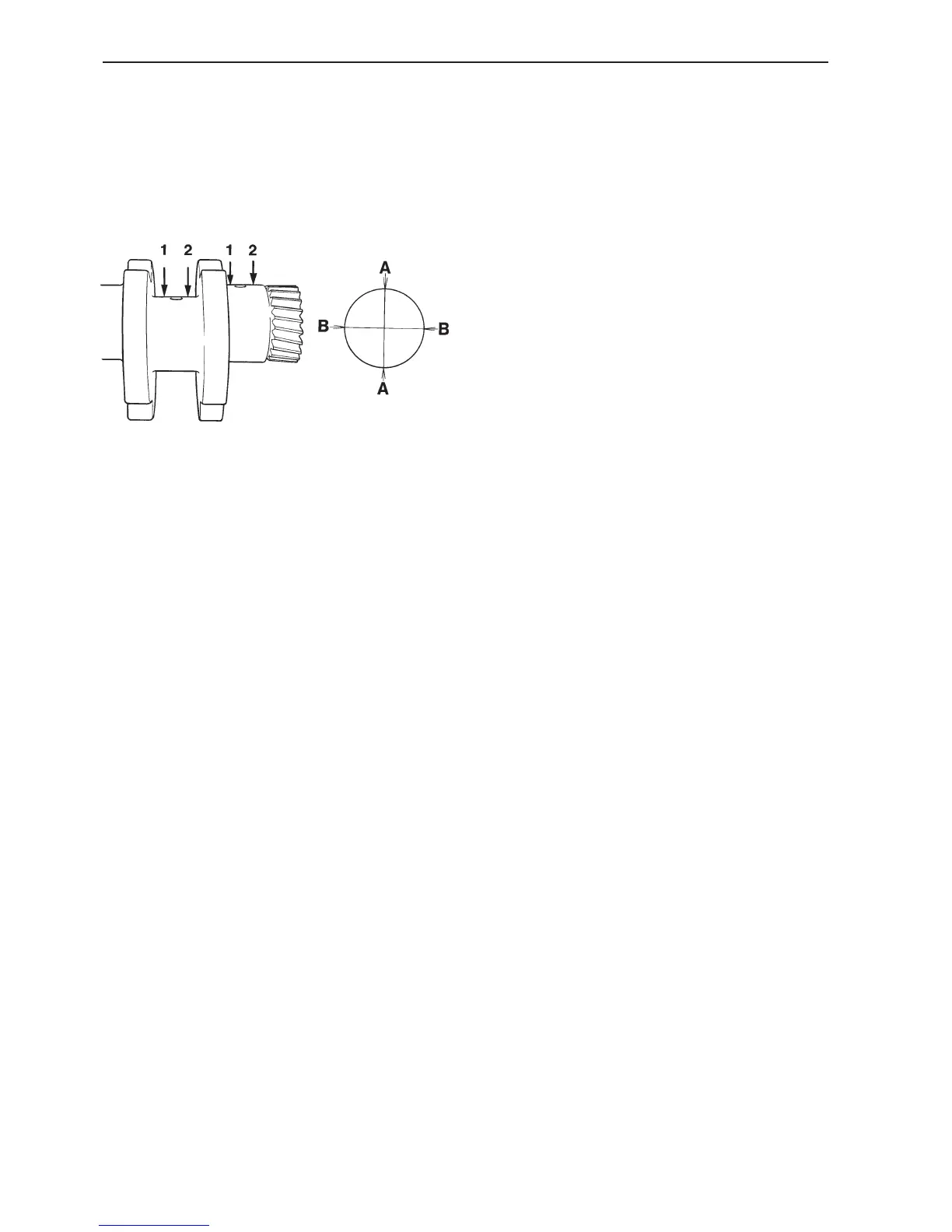
1. Check wear and ovality with a micrometer. Mea-
sure the diameters “A-A” and “B-B” at points “1”
and “2”.
Max. permissible taper and ovality in the main
and big-end journals is 0.05 mm*. Grind the crank-
shaft to a suitable undersize dimension, if these
values are exceeded. Bearing shells are available
in two oversizes.
NOTE! Check first which oversize bearing shells are
available for the engine type in question.
2. Measure lengthwise crookedness in the crank-
shaft (runout). Lay the crankshaft on a pair of V-
blocks placed under the front and rear main bear-
ing journals. Alternately, the crankshaft can be
set up between centers. Measurements shall be
done on the center main bearing journal(s).
Max. lengthwise crookedness (runout) refer to
“Wear tolerances”.
If these values are exceeded, the crankshaft
must be straightened or replaced.
3. Check that the crankshaft seal mating surfaces
on the crankshaft are not worn or damaged.
* Max. wear, refer to “Technical data”.
Inspection of main and big end
bearings
Check the main and big-end bearing shells and the
front crankshaft bush. Change worn bearing shells, or
any with damaged bearing surfaces.

 Loading...
Loading...