Rammer Repair Ramming System
wc_tx001547gb.fm 103
5.5 Inspecting the Spring System
See Graphic: wc_gr001329rm
Over time, the constant compression and release of the spring
pressure can cause the springs to wear out. If the rammer feels to be
hitting with less force, it is possible that the springs are worn and
should be replaced.
A broken spring causes the rammer to jump erratically. This condition
is more noticeable on hard soils. Do not run the rammer if a broken
spring is suspected. Doing so may damage other rammer parts.
Replace both the top and the bottom spring sets even if only one set is
worn or damaged.
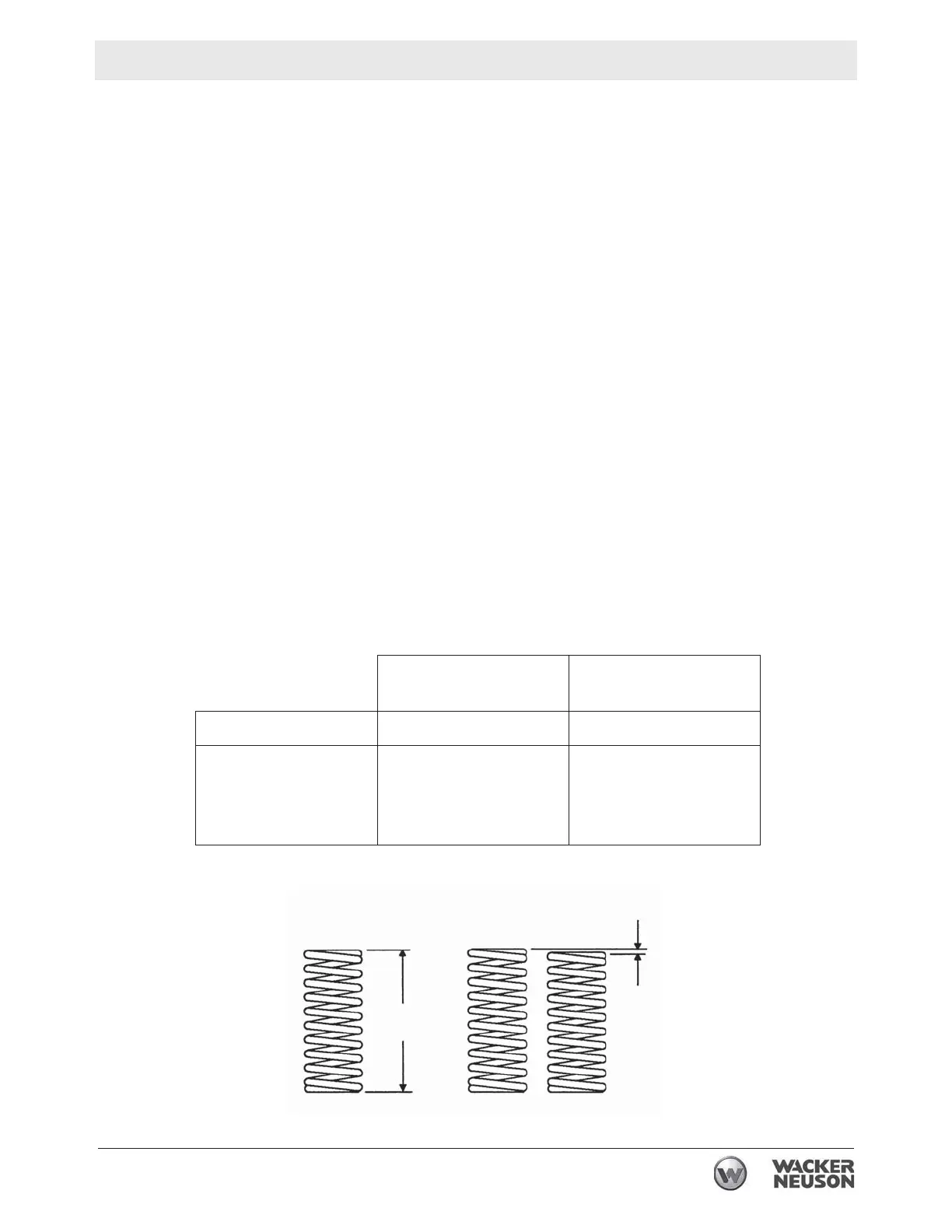
5.5.1 Remove the springs from the cylinder and check them for minimum
spring free height and maximum spring height difference per the table
below. Replace the springs if they do not meet the given specifications.
5.5.2 If a spring has broken, inspect the inside of the spring cylinder wall for
burrs, gouges, and cracks as follows:
• Slide the piston guide inside the cylinder. Check that the piston
guide moves freely but without excessive side play.
• Hone the cylinder to remove the ridges and the burrs that were
cut into the cylinder wall by the spring movement.
• Replace the cylinder if it is badly worn.
Minimum spring free
height (a)
Maximum spring
height difference (b)
BS 500, BS 50 194 mm (7 21/32 in.) 5 mm (3/16 in.)
BS 600, BS 60
BS 700, BS 70
BS 650, BS 65V
DS 720, DS 70
217 mm (8 9/16 in.) 5 mm (3/16 in.)
wc_
r001329rm
a
b

 Loading...
Loading...