1
10
100
1000
10000
1 1,5 2
2,5 3 3,5 4 4,5 5 5,5 6 6,5 7 7,5 8 8,5 9 9,5 10
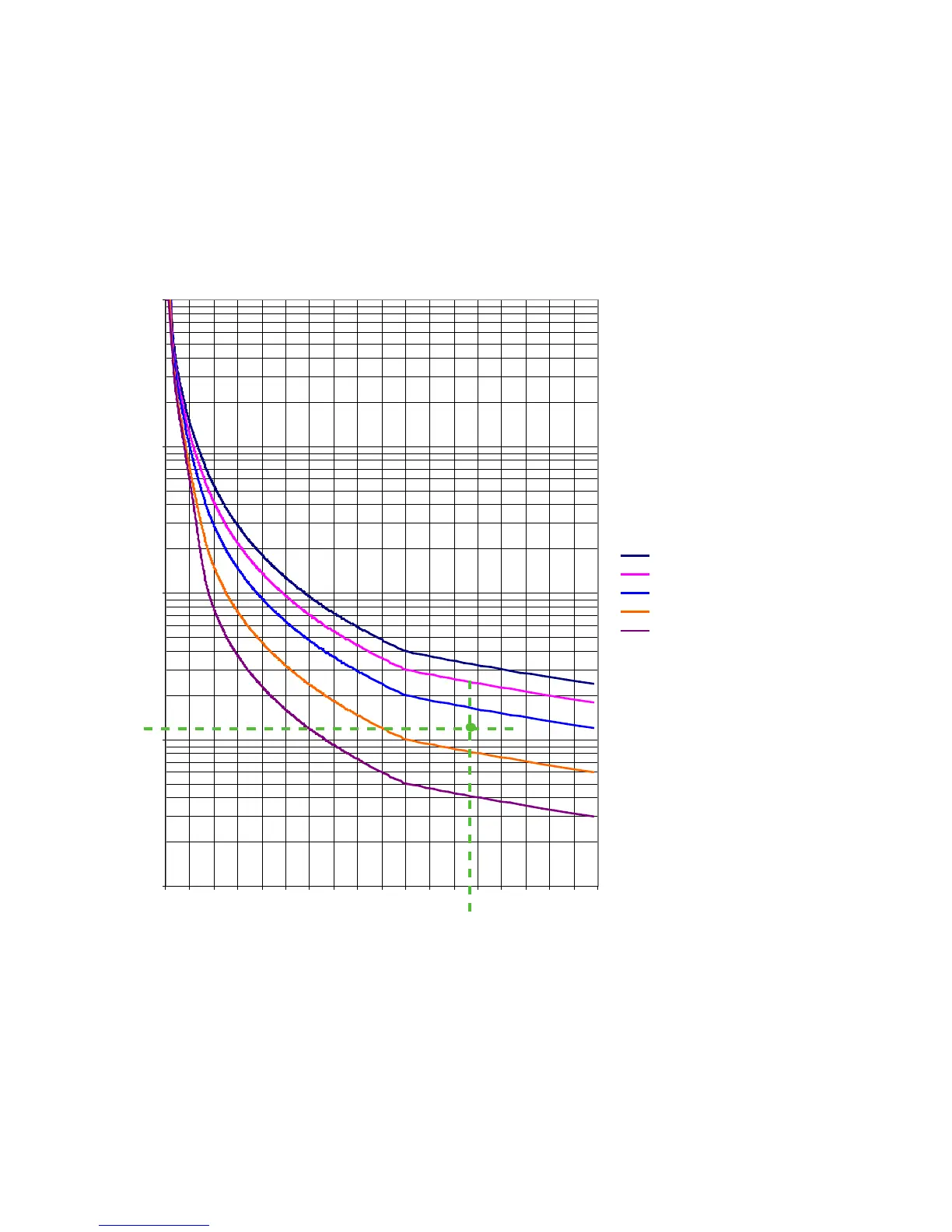
Example of trip class selection:
Select the trip class so that the motor is thermally protected, even when the rotor is stalled. This means that the tripping curve of a
cold motor has to be below the coordination point Ia/Ie and tE whereas Ia is the actual current, Ie is the nominal current of the mo-
tor and tE is the maximal heating time as defined by the motor manufacturer. Example: Motor with enhanced safety has the data:
• Power = 7.5 kW
• Relation I
a
/I
e
= 7.4
• Heating time t
E
= 11 s
The following diagram shows the tripping time for cold motors at symmetric load:
The trip classes 5 and 10 are allowed because the appropriate times (3 s, 7 s) are below the time tE of the motor
I
a
/I
e
=7,4
t
E
=11s
—
Example for the trip class selection for a given motor
39

 Loading...
Loading...