What to do if the no load voltage frequency falls off on my Generac Power Systems XT-EFI Portable Generator?
- KKelly ElliottJul 28, 2025
First, verify that the rotor is spinning. Then, proceed to problem 3 for further troubleshooting steps.

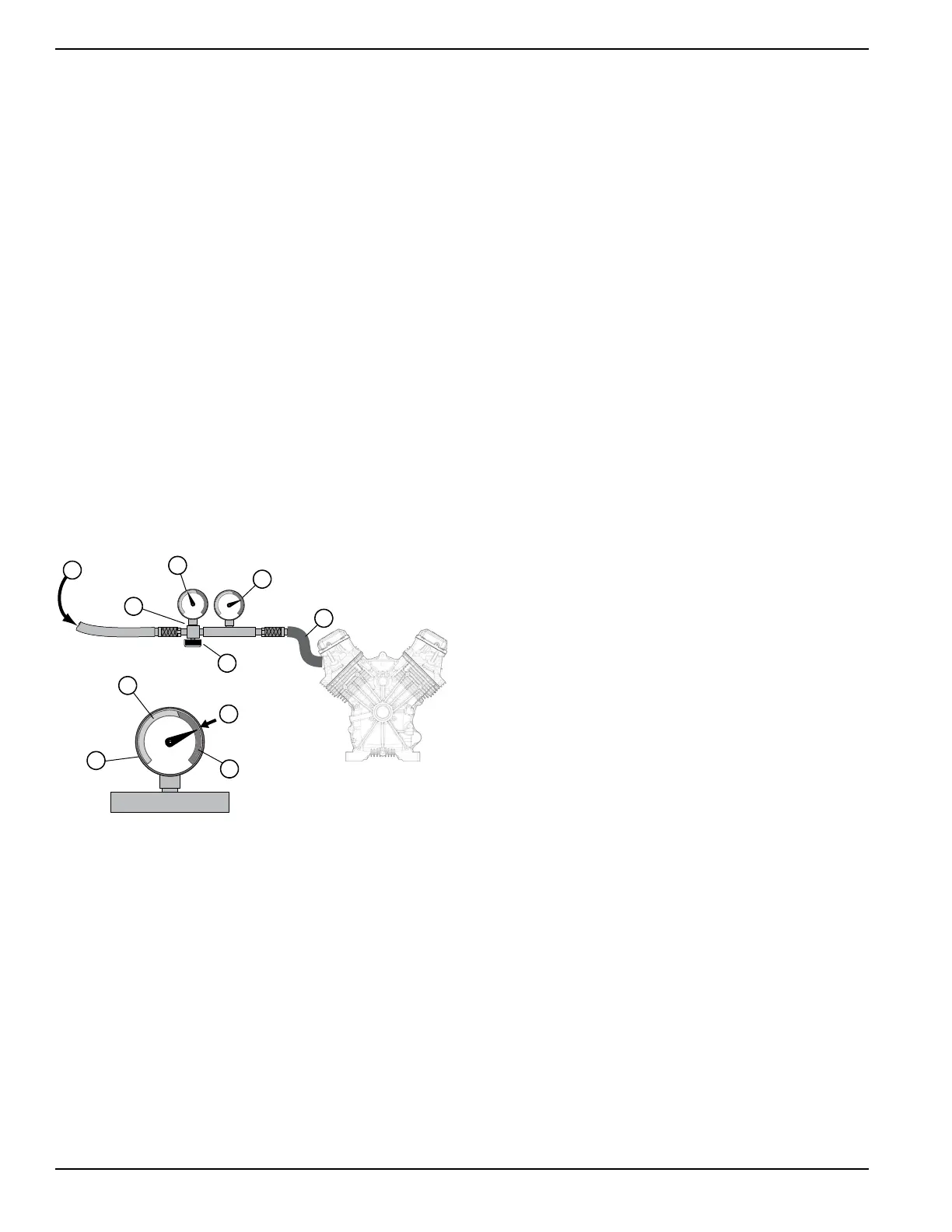
What to do if the no load voltage frequency falls off on my Generac Power Systems XT-EFI Portable Generator?
First, verify that the rotor is spinning. Then, proceed to problem 3 for further troubleshooting steps.
| Brand | Generac Power Systems |
|---|---|
| Model | XT-EFI Series |
| Category | Portable Generator |
| Language | English |
Guides users through diagnosing AC output problems using flowcharts and specific tests.
Outlines diagnostic steps for a generator that produces no or very low output voltage.
Guides users through diagnosing AC output problems for brush type generators.
Outlines diagnostic steps for a generator that produces no or very low output voltage.
Provides troubleshooting steps for generators with incorrect voltage and frequency output.
Guides diagnosis for voltage/frequency drops when electrical load is applied.
Steps to diagnose generators that output excessively high voltage without load.
Procedure to adjust the voltage regulator to achieve the correct output voltage.
Guides users through diagnosing engine issues using flowcharts and specific tests.
Troubleshooting steps for a generator recoil cord that will not pull.
Diagnostic steps for an engine that starts with difficulty and runs unevenly.
Troubleshooting for engines that crank but fail to start, focusing on fuel and spark.
Steps to diagnose and resolve engines that exhibit unstable or fluctuating idle speeds.
Diagnostic procedures for engines that fail to crank, checking battery, starter, and switch.
Troubleshooting for engines that crank but fail to start, focusing on fuel, spark, and ignition.
Troubleshooting for engines that start and then immediately shut off, checking oil level and pressure.
Steps to diagnose why the generator's battery is not charging, checking charger and circuit.
Tests the engine's ignition system for proper spark generation using a spark tester.