13
Configuring static route FRR
A link or router failure on a path can cause packet loss and even routing loop. Static route fast reroute
(FRR) enables fast rerouting to minimize the impact of link or node failures.
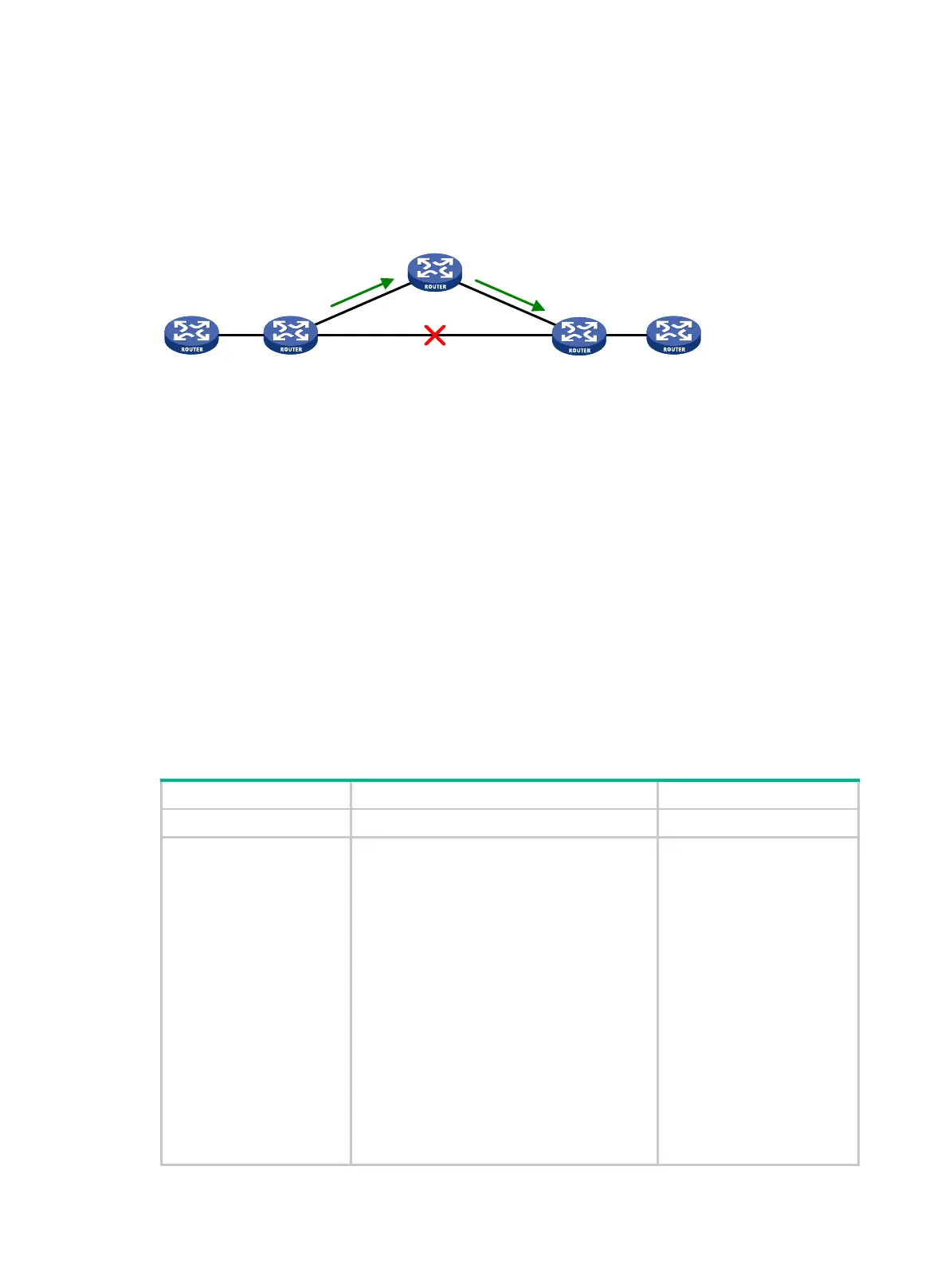
Figure 1 Network diagram
As shown in Figure 1, upon a link failure, packets are directed to the backup next hop to avoid traffic
interruption. You can either specify a backup next hop for FRR or enable FRR to automatically select
a backup next hop (which must be configured in advance).
Configuration guidelines
Do not use static route FRR and BFD (for a static route) at the same time.
Static route does not take effect when the backup output interface is unavailable.
Equal-cost routes do not support static route FRR.
The backup output interface and next hop must be different from the primary output interface
and next hop.
To change the backup output interface or next hop, you must first remove the current setting.
Static route FRR is available only when the state of primary link (with Layer 3 interfaces staying
up) changes from bidirectional to unidirectional or down.
Configuring static route FRR by specifying a backup next hop
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Configure static route
FRR.
• Method 1:
ip route-static dest-address
{ mask-length | mask } interface-type
interface-number [ next-hop-address
[ backup-interface interface-type
interface-number [ backup-nexthop
backup-nexthop-address ] ] ]
[ permanent ] [ preference preference ]
[ tag tag-value ] [ description text ]
• Method 2:
ip route-static vpn-instance
s-vpn-instance-name dest-address
{ mask-length | mask } interface-type
interface-number [ next-hop-address
[ backup-interface interface-type
interface-number [ backup-nexthop
backup-nexthop-address ] ] ]
[ permanent ] [ preference preference ]
[
tag-value ] [
text ]
By default, static route FRR
is disabled.
Router A
Router B Router E
Backup nexthop:
Router C
Nexthop:
Router D
 Loading...
Loading...











