10-114
IPv4 Access Control Lists (ACLs)
Enable ACL “Deny” Logging
Enabling ACL Logging on the Switch
1. If you are using a Syslog server, use the logging < ip-addr > command to
configure the Syslog server IPv4 address(es). Ensure that the switch can
access any Syslog server(s) you specify.
2. Use logging facility syslog to enable the logging for Syslog operation.
3. Use the debug destination command to configure one or more log destina-
tions. (Destination options include logging and session. For more informa-
tion on debug, refer to “Debug and Syslog Messaging Operation” in
appendix C, “Troubleshooting”, in the Management and Configuration
Guide for your switch.)
4. Use debug acl or debug all to configure the debug operation to include ACL
messages.
5. Configure one or more ACLs with the deny action and the log option.
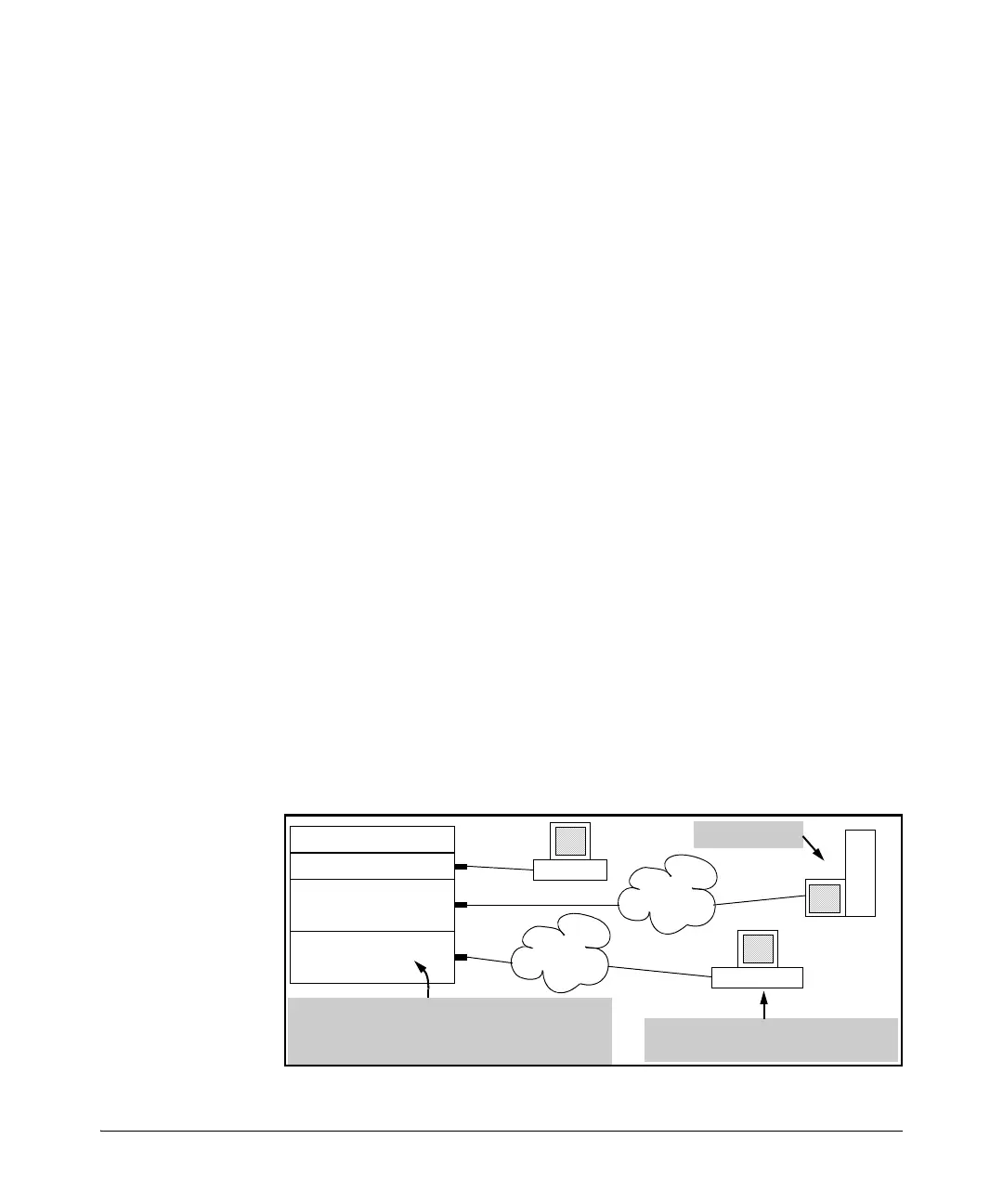
For example, suppose that you want to configure the following operation:
■ On VLAN 10 configure an extended ACL with an ACL-ID of “NO-
TELNET” and use the RACL in option to deny Telnet traffic entering
the switch from 10.10.10.3 to any routed destination. (Note that this
assignment will not filter Telnet traffic from 10.10.10.3 to destinations
on VLAN 10 itself.)
■ Configure the switch to send an ACL log message to the current
console session and to a Syslog server at 10.10.20.3 on VLAN 20 if the
switch detects a packet match denying a Telnet attempt from
10.10.10.3.
(This example assumes that IPv4 routing is already configured on the switch.)
Figure 10-44. Example of an ACL Log Application
VLAN 20
10.10.20.1
Subnet 20
10.10.20.3
VLAN 10
10.10.10.1
10.10.10.3
Subnet 10
Syslog Server
Apply the extended ACL “NO TELNET” as a
RACL here to deny Telnet access to inbound,
routed Telnet traffic from IP address
10.10.10.3.
Block Telnet access to routed
destinations from this host.
Switch
Console
Console RS-232 Port
 Loading...
Loading...











