▪ The System controller can send RS-232 messages to the transmitter by using LW3
protocol methods, see settings in section 8.7.7 on page 82.
▪ The Transmitter can send RS-232 messages to the HDTV or the Extender by using LW3
protocol methods; in section 8.7.7 on page 82.
4.3.1. Serial interface
Technical background
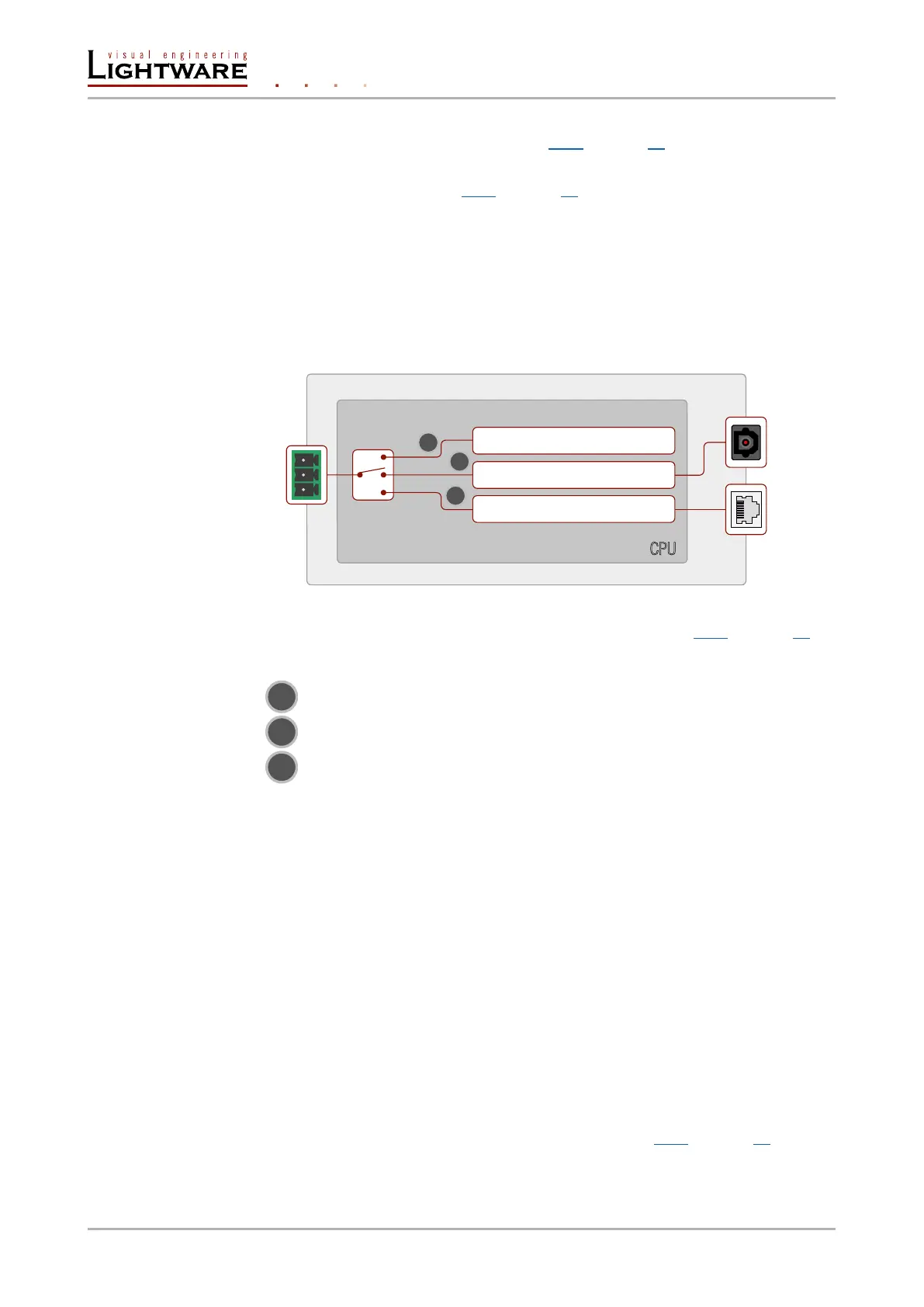
Serial data communication can be established via the local RS-232 port (Phoenix connector)
or via the optical line. The RS-232 ports – which are connected to the microcontroller – can
be congured separately (e.g. if the Baud rates are different, the microcontroller does the
conversion automatically between the ports). The RS-232 port can be switched to Control
mode, Command Injection mode, or can be Pass-through mode; see the gure below.
The block diagram of the serial interface
All settings are available in the LDC software, see settings in section 6.6.1 on page 39.
The following settings are dened:
The Local serial port is in Control mode.
The Local serial port is in Pass-through mode.
The Local serial port is Command Injection mode.
Control mode
The incoming data from the given port is processed and interpreted by the Microcontroller.
The mode allows to control the transmitter directly. LW2 or LW3 protocol commands are
accepted – depending on the current port setting.
Pass-through mode
In pass-through mode, the given device forwards the data that is coming from one of its
ports to another same type of port. The command is not processed by the CPU. Incomming
serial data is forwarded from one port to another port inside the transmitter.
Command injection mode
In this mode, the transmitter works as an RS-232 bidirectional converter. The optical signal
is converted to RS-232 data and vice versa. Optical port numbers are dened for the serial
ports (optical and local) for this purpose. E.g. the default Command Injection port number
of the local RS-232 port is 8001. If a command is coming from the optical interface which
is address to the port no. 8001, it will be transmitted to the Tx pin of the local RS-232 port.
That works in the opposite direction of course and the method is the same on the serial
interface of the optical port. See the RS-232 settings in section 6.6.1 on page 39.
local
port
Local RS-232 / OPT converter
Device Control (Local serial)
CPU
Mode switch
Local
1
2
3
Optical
Local RS-232 / TCP converter
LAN
port
Page 24 / 106 Optical extender concept
 Loading...
Loading...











