4 - 25 4 - 25
4 SFC PROGRAM CONFIGURATION
MELSEC-Q
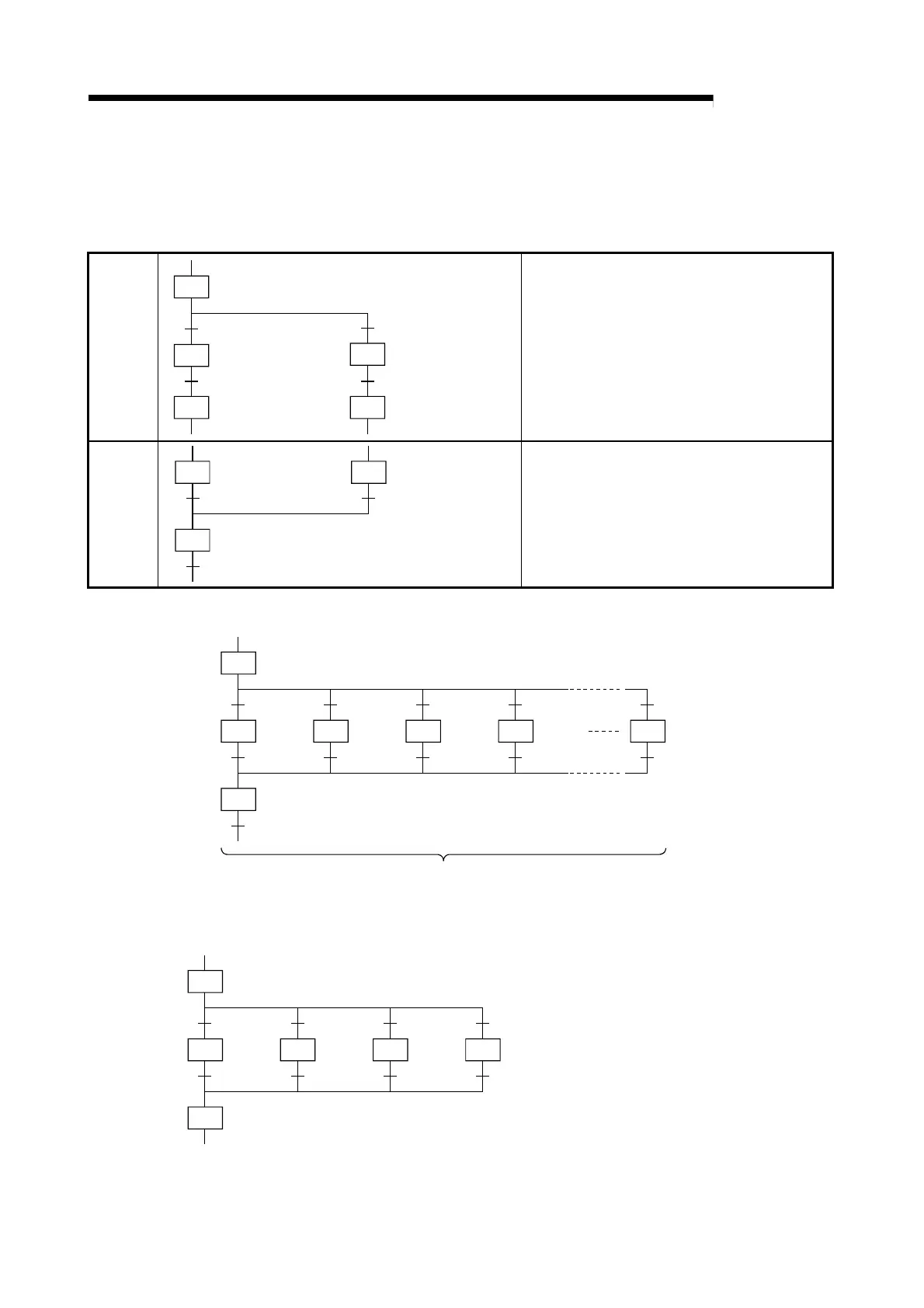
4.3.2 Selection transition
A “selection transition” is the transition format in which several steps are coupled in a parallel
manner, with processing occurring only at the step where the transition condition is satisfied first.
Branch
Step “n+1”
(operation output [B])
Step “n”
(operation output [A])
Transition condition “b”
Step “n+2”
(operation output [C])
Transition condition “c”
• From step “n”, processing will proceed to either
step “n+1” or step “n+2”, depending on which
transition condition (“b” or “c”) is satisfied first.
• If both transition conditions are satisfied
simultaneously, the condition to the left will take
precedence.
Step “n” will then be deactivated.
• Subsequent processing will proceed from step to
step in the selected column until another parallel
coupling selection occurs.
Coupling
Step “n”
(operation output [A])
Step “n+1”
(operation output [B])
Transition condition “b”
Transition condition “c”
Step “n+2”
(operation output [C])
• When the transition condition (“b” or “c”) at the
executed branch is satisfied, the executed step
([A] or [B]) will be deactivated, and processing
will proceed to step “n+2”.
(1) Up to 32 steps can be available for selection in the selection transition format.
Step
“n+1”
Step “n”
Max. of 32 steps
Step
“n+2”
Step
“n+3”
Step
“n+4”
Step
“n+32
(2) When two or more selection step transition conditions are satisfied simultaneously, the left-
most condition will take precedence.
Step
“n+1”
Step “n”
Step
“n+2”
Step
“n+3”
Step
“n+4”
Transition
condition “b”
Transition
condition “c”
Transition
condition “d”
Transition
condition “e”
Example: If transition conditions “c”
and “d” are satisfied
simultaneously, the step
“n+2” operation output will
be executed.

 Loading...
Loading...











