E1/E20/E2/E2 Lite Additional Document 3. Notes on Usage
R20UT2937EJ0301 Rev.3.01 Page 38 of 45
Jul 1, 2020
3.3.4 Setting a Security ID
This setting is required to prevent the memory from being read by an unauthorized person. Embed a
security ID at addresses 0xC4 to 0xCD in the internal flash memory. The debugger starts only when the
security ID that is set during debugger startup and the security ID set at addresses 0xC4 to 0xCD match.
If the ID codes do not match, the debugger manipulates the target device in accordance with the value
set to the on-chip debug option byte area (refer to the hardware manual for each MCU).
If the user has forgotten the security ID to enable debugging, erase the flash memory and set the
security ID again.
Set the security ID in either of the following ways. When both methods (a) and (b) are carried out at the
same time, method (b) has priority.
(a) Embed the security ID at addresses 0xC4 to 0xCD in the user program.
For example if the security ID is embedded as follows, the security ID set by the debugger
is ″0123456789ABCDEF1234″ (not case-sensitive).*
1,
*
2
(b) Set the security ID by common options of the build tool.
For details on the setting method, refer to the user's manual for the build tool.
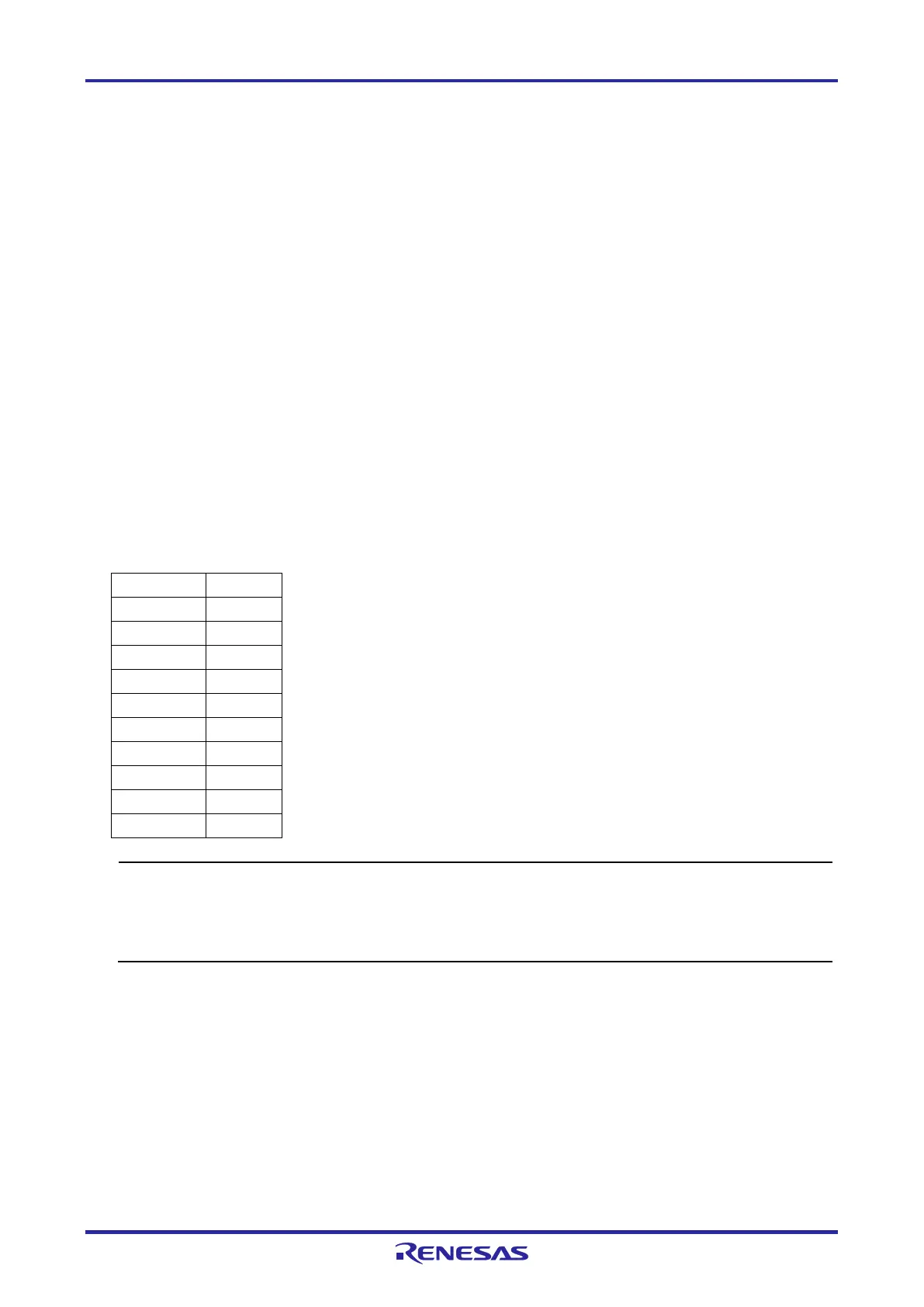
Table 3-1 Example of Security ID Setting
0x000C5 0x23
0x000C7 0x67
0x000C9 0xAB
0x000CB 0xEF
0x000CD 0x34
When connecting a debugger to a device for which the security ID has been set, the security ID
needs to be entered in the debugger. For details on the authentication method, refer to the
user's manual for the debugger in use.
The setting "0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF", in which the value at all addresses is "0xFF", is
prohibited.
3.3.5 Area for Pseudo-RRM/Pseudo-DMM
To use the pseudo-RRM/pseudo-DMM function in the RL78-S1 core device, a part (4 bytes) of the RAM
area is used for the pseudo-RRM/pseudo-DMM function. Information, such as whether this area can be
allocated by the build tool, can be confirmed in the user's manual for the build tool.

 Loading...
Loading...











