2-5
■ Structure and principle of AC induction motor
The AC induction motor has no brush and commutator unlike the conventional DC motor, so there is no
sliding part. It, therefore, has the following features:
1. The motor size can be reduced by dimension L for the brush and commutator if the output is the same.
2. In the size is same, the core size can be increased by dimension L for the brush and commutator,
resulting in a higher output.
3. Because of less number of parts and no sliding part, it features high reliability and efficiency. For new
models, a new AC induction motor best suitable for forklift trucks has been developed and adopted.
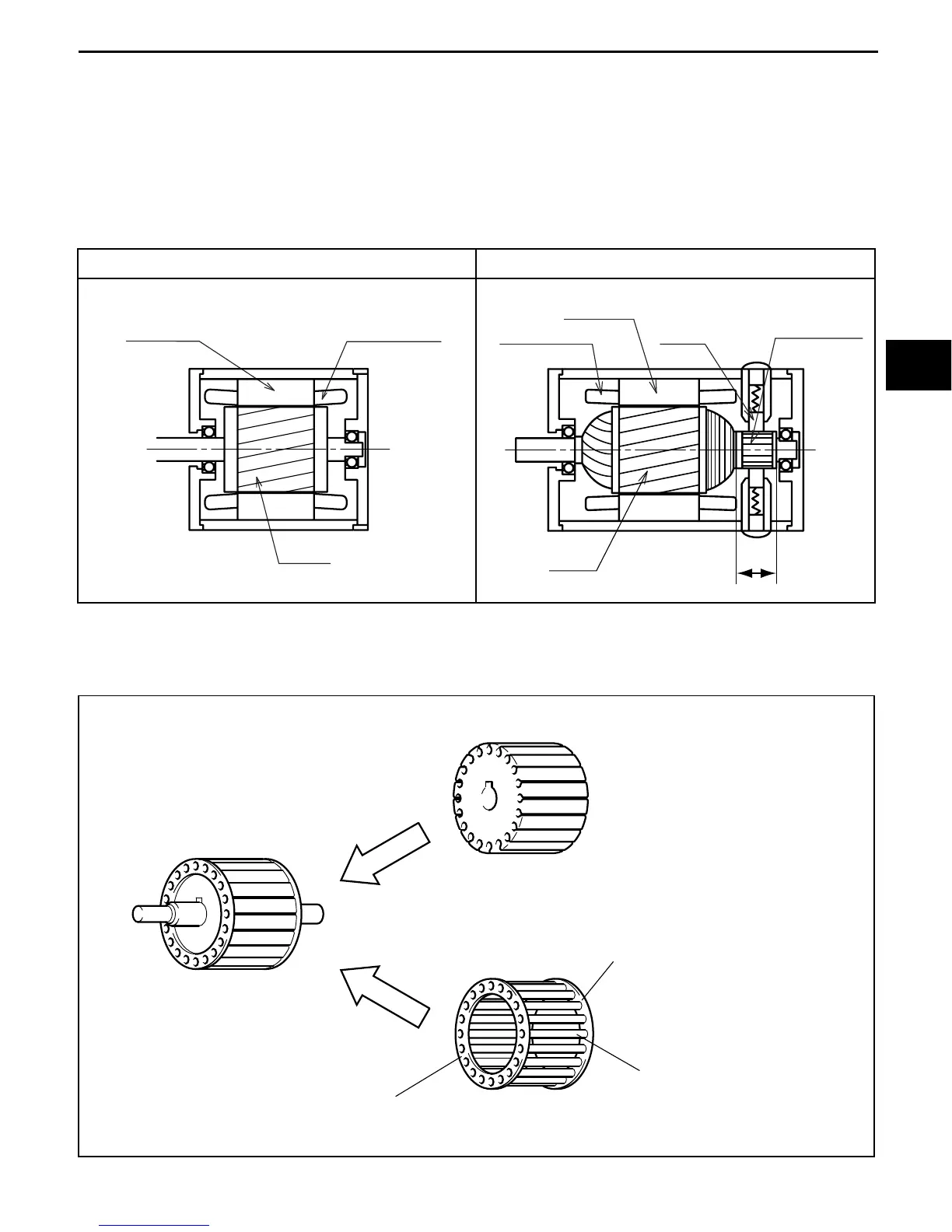
The rotor consists of the core made up of piled thin electromagnetic steel plates through the grooves in
which aluminum conductor bars pass. Both ends of conductor bars are shorted by end rings on both sides
of the core as illustrated in (b) below. When the bars and end rings are taken off, the shape is like a cage
for a squirrel or mouse as shown in (c) below. It is therefore called a cage rotor.
AC motor (for new models) DC motor (for previous models)
Field core
Field winding
Rotor
Field winding
Rotor
Field core
Brush
Commutator
L
(b) Rotor ASSY
(c) Cage rotor
(a) Core
End ring
Conductor bar
(aluminum conductor bar)
End ring
2
3
2

 Loading...
Loading...