Appendix D: N-Command Failover Configuration
encrypts its database, and then the slave transfers, decrypts, and imports it in to itself. The transferred
database contains essentially all static settings (scripts, tasks, units, users, panels, system settings, etc.).
NOTE: The LocalPlay audio/image library is not part of the transferred database.
Failover Scenarios
The following scenarios constitute a failover, causing the slave to take control.
Loss of communication with the master for a period of three minutes (on both network cards).
Every minute, the slave queries the master. If it gets no response three times in a row, the slave assumes
the master is offline.
Both network cards need to be down for communication to be lost. If eth1 is down and eth0 is working,
the status is considered good.
Database errors for a period of three minutes.
Every minute, the slave asks the master the status of its database. If the master reports a database
problem three times in a row, the slave takes over.
System services down for a period of three minutes.
Every minute, the slave asks the master the status of its system services. If the master reports services are
down three times in a row, the slave takes over and the master shuts itself down. The master determines
the state of system services by monitoring a list of running processes.
Any combination of the above has occurred for a period of three minutes.
For example, if the master is reported offline, followed by a report of services down, followed by database
errors, then the slave will take over (due to too many errors in a row). The error count restarts only if the
master reports a full level of health.
Override Mechanisms
To override a unit, one unit (usually the master) sends the other unit a command to shut down. This causes the
receiving unit to turn off SVSI system services, release its old IP addresses, and then begin monitoring.
Overriding mechanisms include the following:
Slave overriding master. Slave only overrides master during the failover scenarios.
Master overriding slave. If at any time the master detects the slave has taken control, and the master has
determined its own health is good, it will send the override command.
User overriding. During initial setup, when an administrator is determining the master and slave, the master
N-Command will send an override command to the slave N-Command.
Setup
1. Decide which unit will be the master and which unit will be the slave. Units are shipped from the factory with this
setting unassigned.
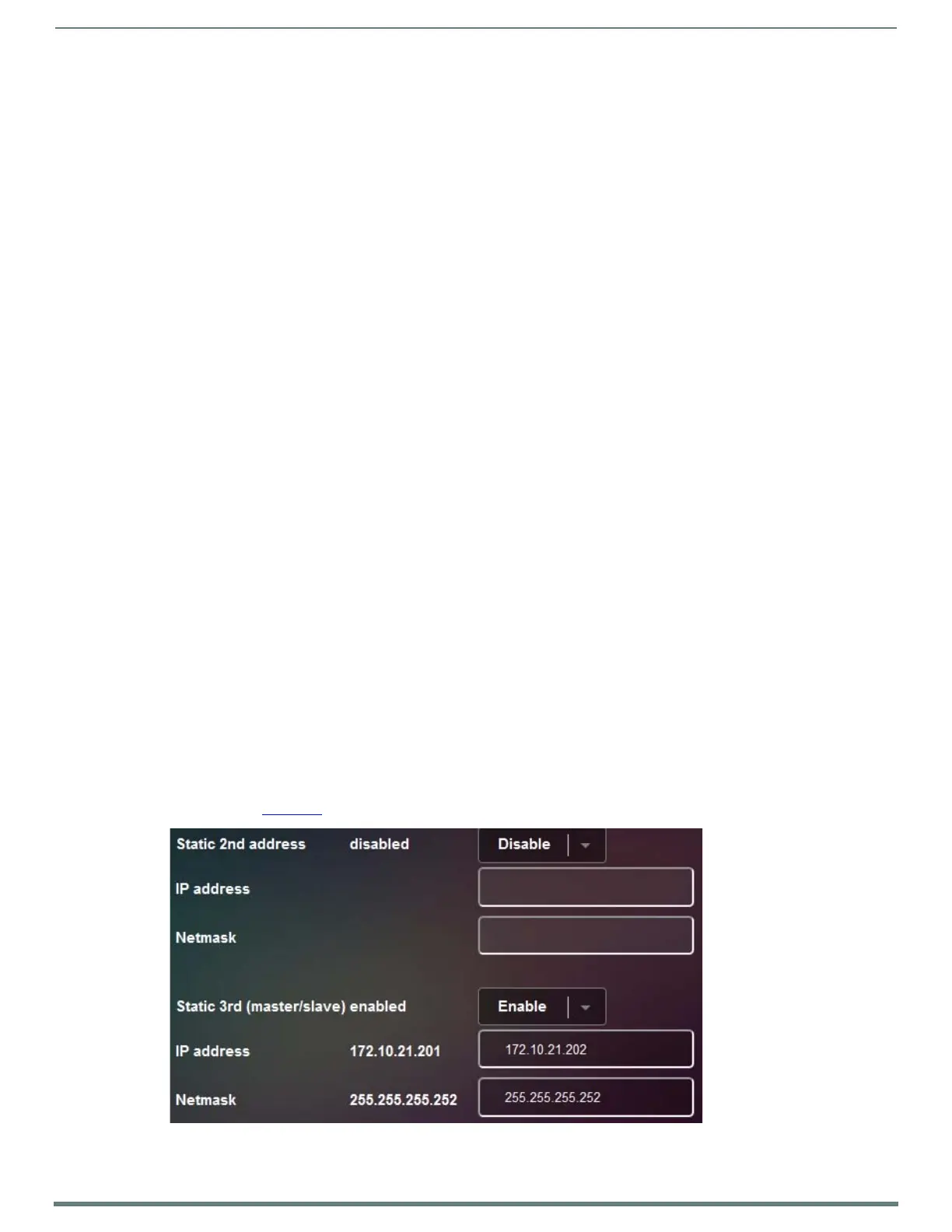
2. Configure the Static 3rd IP addresses for each unit and eth card. It is highly recommended that the master and
slave 3rd IPs are in their own subnet. They will not need to communicate with any other device except each
other. See Figure 55
.
FIG. 55 Configure IP Addresses

 Loading...
Loading...











