89
TRIPLE EVACUATION METHOD — The triple evacuation
method should only be used when vacuum pump is capable of
pumping down to 28 in. of mercury and system does not con-
tain any liquid water. Proceed as follows:
1. Pump system down to 28 in. of mercury and allow pump
to continue operating for an additional 15 minutes.
2. Close service valves and shut off vacuum pump.
3. Connect a nitrogen cylinder and regulator to system and
open until system pressure is 2 psig.
4. Close service valve and allow system to stand for 1 hr.
During this time, dry nitrogen will be able to diffuse
throughout the system, absorbing moisture.
5. Repeat this procedure. System will then contain minimal
amounts of contaminants and water vapor.
Refrigerant Charge — Amount of refrigerant charge is
listed on unit nameplate. Refer to Carrier GTAC II; Module 5;
Charging, Recovery, Recycling, and Reclamation section for
charging methods and procedures. Unit panels must be in place
when unit is operating during charging procedure.
Puron® (R-410A) refrigerant cylinders contain a dip tube
which allows liquid refrigerant to flow from the cylinder in an
upright position. Charge units with cylinder in the upright
position and a commercial type metering device in the mani-
fold hose.
NOTE: Do not use recycled refrigerant as it may contain
contaminants.
NO CHARGE — Use standard evacuating techniques. After
evacuating system, weigh in the specified amount of refriger-
ant (refer to unit nameplate).
NOTE: System charge for units with Humidi-MiZer™ system
is greater than the system charge of the standard unit.
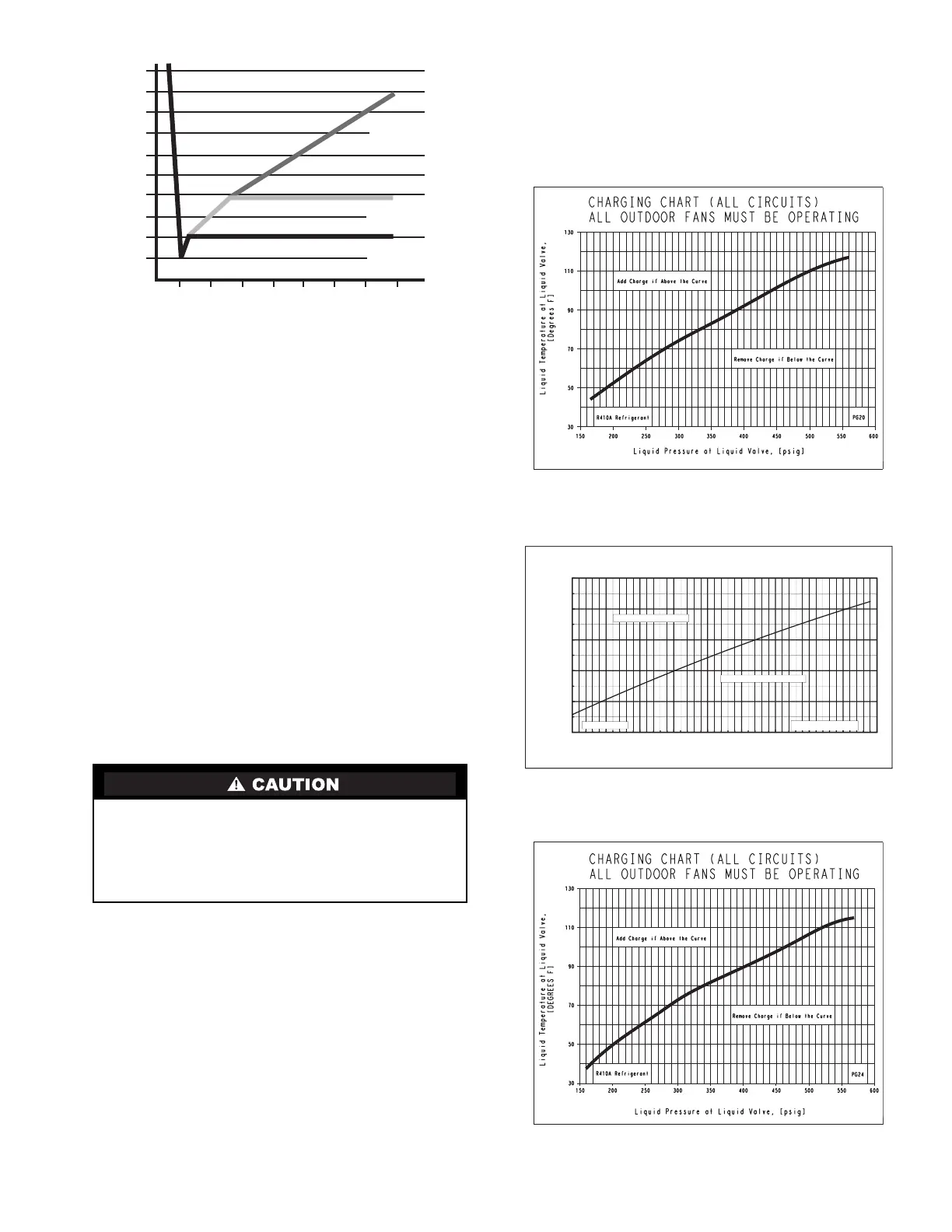
LOW CHARGE COOLING — Using cooling charging chart
(see Fig. 42-45), add or remove refrigerant until conditions of the
chart are met. An accurate pressure gage and temperature-
sensing device are required. Charging is accomplished by
ensuring the proper amount of liquid subcooling. Measure liquid
line pressure at the liquid line service valve using pressure gage.
Connect temperature sensing device to the liquid line near the
liquid line service valve and insulate it so that outdoor ambient
temperature does not affect reading.
TO USE THE COOLING CHARGING CHART, STAN-
DARD UNITS — Use the above temperature and pressure
readings, and find the intersection point on the cooling charg-
ing chart. If intersection point on chart is above line, add refrig-
erant. If intersection point on chart is below line, carefully re-
cover some of the charge. Recheck suction pressure as charge
is adjusted.
This system uses Puron refrigerant which has higher
pressures than R-22 and other refrigerants. No other refrig-
erant may be used in this system. Gage set, hoses, and
recovery system must be designed to handle Puron refrig-
erant. If unsure about equipment, consult the equipment
manufacturer.
LEAK IN
SYSTEM
VACUUM TIGHT
TOO WET
TIGHT
DRY SYSTEM
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
MINUTES
5000
4500
4000
3500
3000
2500
2000
1500
1000
500
MICRONS
Fig. 41 — Deep Vacuum Graph
a48-7167
CHARGING CHART
ALL OUTDOOR FANS MUST BE OPERATING
30
50
70
90
110
130
150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600
Liquid Pressure at Liquid Valve, [psig]
Liquid Temperature at Liquid Valve,
[Degrees F]
PG20 Humidimizer
Add Charge if Above the Curve
Remove Charge if Below the Curve
R410A Refrigerant
Fig. 42 — Charging Chart — 48/50PG20 —
Standard Unit
Fig. 44 — Charging Chart — 48/50PG24 — Standard
Unit and Unit with Humidi-MiZer™ System
Fig. 43 — Charging Chart — 48/50PG20 —
Unit with Humidi-MiZer™ System
a48-7782
a48-8231
a48-7783

 Loading...
Loading...