All snooping statistics are generated on the stack master. If a new stack master is elected, the statistics counters
reset.
When a stack merge occurs, all DHCP snooping bindings in the stack master are lost if it is no longer the
stack master. With a stack partition, the existing stack master is unchanged, and the bindings belonging to the
partitioned switches age out. The new master of the partitioned stack begins processing the new incoming
DHCP packets.
How to Configure DHCP Features
Default DHCP Snooping Configuration
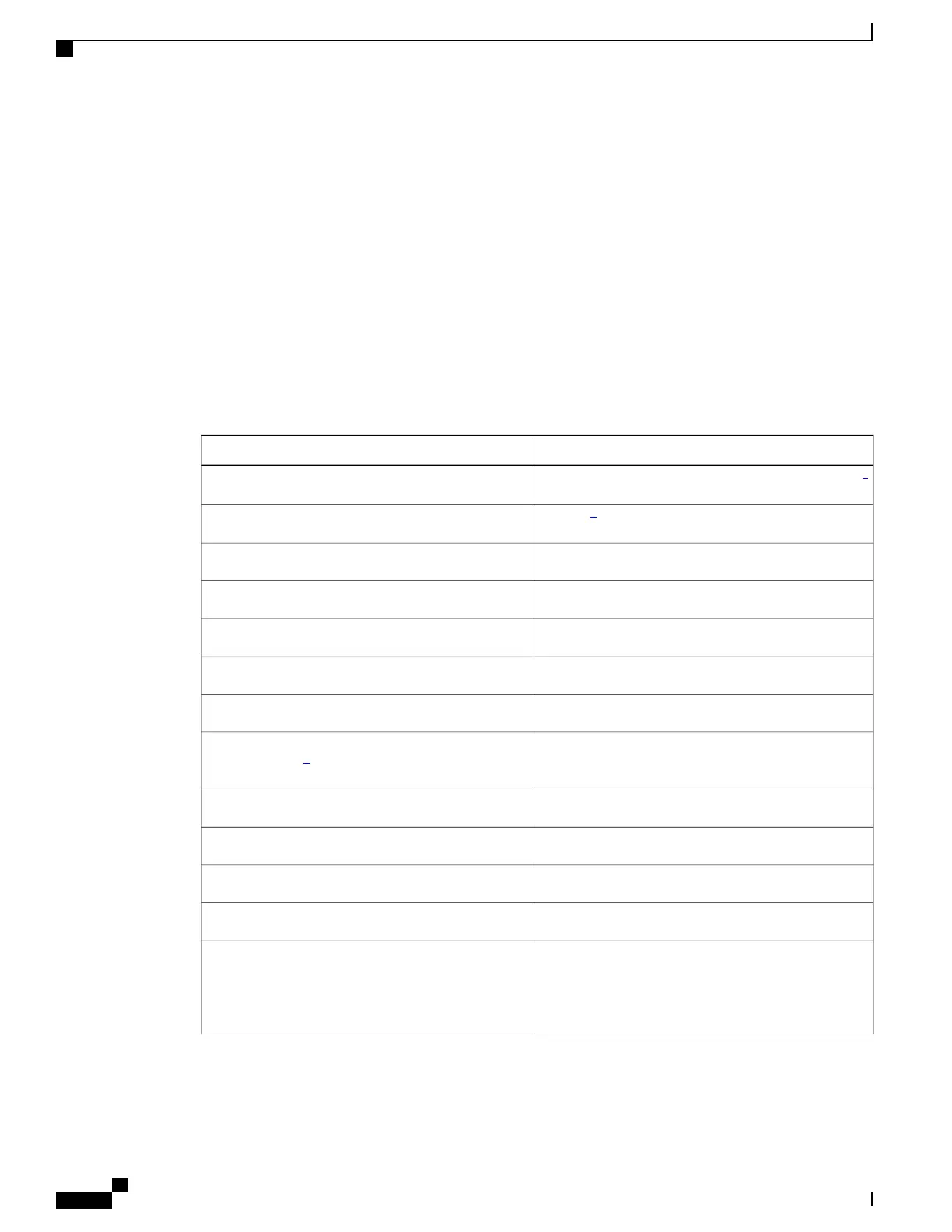
Table 17: Default DHCP Configuration
Default SettingFeature
Enabled in Cisco IOS software, requires configuration
2
DHCP server
Enabled
3
DHCP relay agent
None configuredDHCP packet forwarding address
Enabled (invalid messages are dropped)Checking the relay agent information
Replace the existing relay agent informationDHCP relay agent forwarding policy
DisabledDHCP snooping enabled globally
EnabledDHCP snooping information option
DisabledDHCP snooping option to accept packets on untrusted
input interfaces
4
None configuredDHCP snooping limit rate
UntrustedDHCP snooping trust
DisabledDHCP snooping VLAN
EnabledDHCP snooping MAC address verification
Enabled in Cisco IOS software, requires configuration.
The switch gets network addresses and
configuration parameters only from a device
configured as a DHCP server.
Note
Cisco IOS DHCP server binding database
Catalyst 2960-XR Switch Security Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2)EX1
172 OL-29434-01
Configuring DHCP
How to Configure DHCP Features
 Loading...
Loading...











