5 Configuration D-Link Web Smart Switch User Manual
Figure 54 – Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN > Asymmetric VLAN – Create VLANs
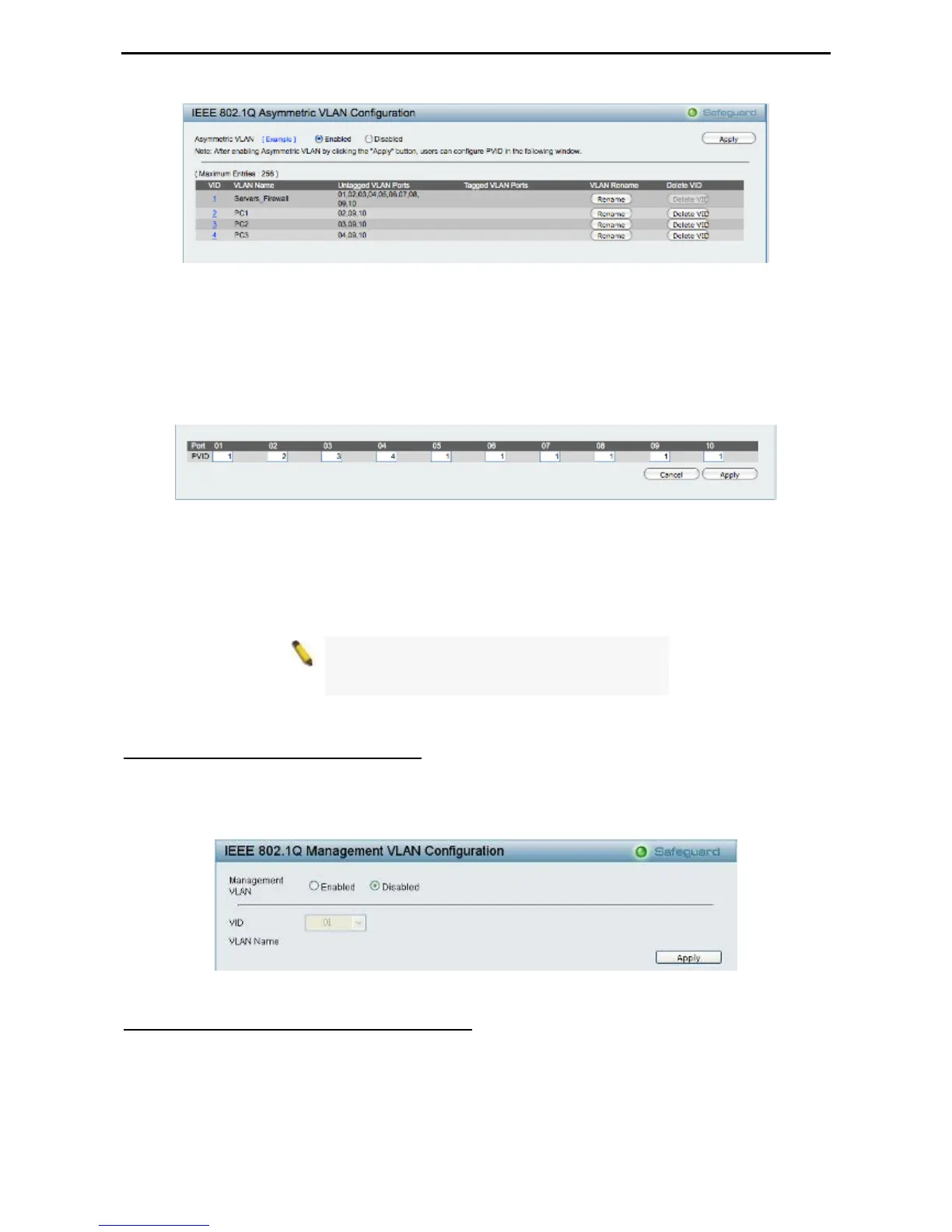
3. Configuring the PVID of access VLAN
Configure the PVID setting located at the bottom of the VLAN configuration page. The user needs to
set the shared set of ports as PVID 1, and the other separated groups of ports (for example, port 2, 3,
and 4) as PVID 2, 3 and 4 respectively.
The purpose of assigning PVID is to make sure the untagged packets will be transmitted correctly.
Figure 55 – Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN > Asymmetric VLAN – Assign PVID
After configuration, the user will be able to share the network resources set on the shared group of ports
(nominated as PVID 1), with both smaller subsets of VLANs (nominated PVID 2, 3 and 4). However, VLAN 2,
3 and 4 groups are incapable of sharing information with each other directly. Click Example to see the
example to configure asymmetric VLAN in larger networks.
Note: When Asymmetric VLAN is enabled, IGMP
Snooping, Management VLAN, and MAC address
table will be reset to default.
Configuration > 802.1Q Management VLAN
The 802.1Q Management VLAN setting allows you to transfer the authority of the switch from the default
VLAN to others created by users. This allows managing the whole network more flexible.
By default, the Management VLAN is disabled. You can select any existing VLAN as the management VLAN
when this function is enabled. There can only be one management VLAN at a time.
Figure 56 – Configuration > 802.1Q Management VLAN
Configuration > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Setting
Voice VLAN is a feature that allows you to automatically place the voice traffic from IP phone to an assigned
VLAN to enhance the VoIP service. With a higher priority and individual VLAN, the quality and the security of
VoIP traffic are guaranteed. The Voice VLAN function will only insert the Voice VLAN tag to untagged
packets under corresponding ports. If a VoIP packet comes with a VLAN tag, the Voice VLAN function won’t
replace the original VLAN tag.
3
3
3
3
 Loading...
Loading...











