Control Specification SiBE121021_C
126 Function and Control
4.13 Malfunctions
4.13.1 Sensor Malfunction Detection
Sensor malfunction may occur either in the thermistor or current transformer (CT) system.
Relating to Thermistor Malfunction
1. Outdoor heat exchanger thermistor
2. Discharge pipe thermistor
3. Radiation fin thermistor
4. Gas pipe thermistor
5. Outdoor temperature thermistor
6. Liquid pipe thermistor
Relating to CT Malfunction
When the output frequency is more than 55 Hz (50/52/58/68/75 class) or 32 Hz (80/90 class),
and the input current is less than 0.5 A, adjustment is carried out.
4.13.2 Detection of Overcurrent and Overload
Outline In order to protect the inverter, an excessive output current is detected, the OL temperature is
observed to protect the compressor.
Detail
If the inverter current exceeds 16.5 ~ 20.0 A (depending on the model), the system shuts
down the compressor.
If the OL (compressor head) temperature exceeds 120 ~ 130°C, the compressor stops.
4.13.3 Refrigerant Shortage Control
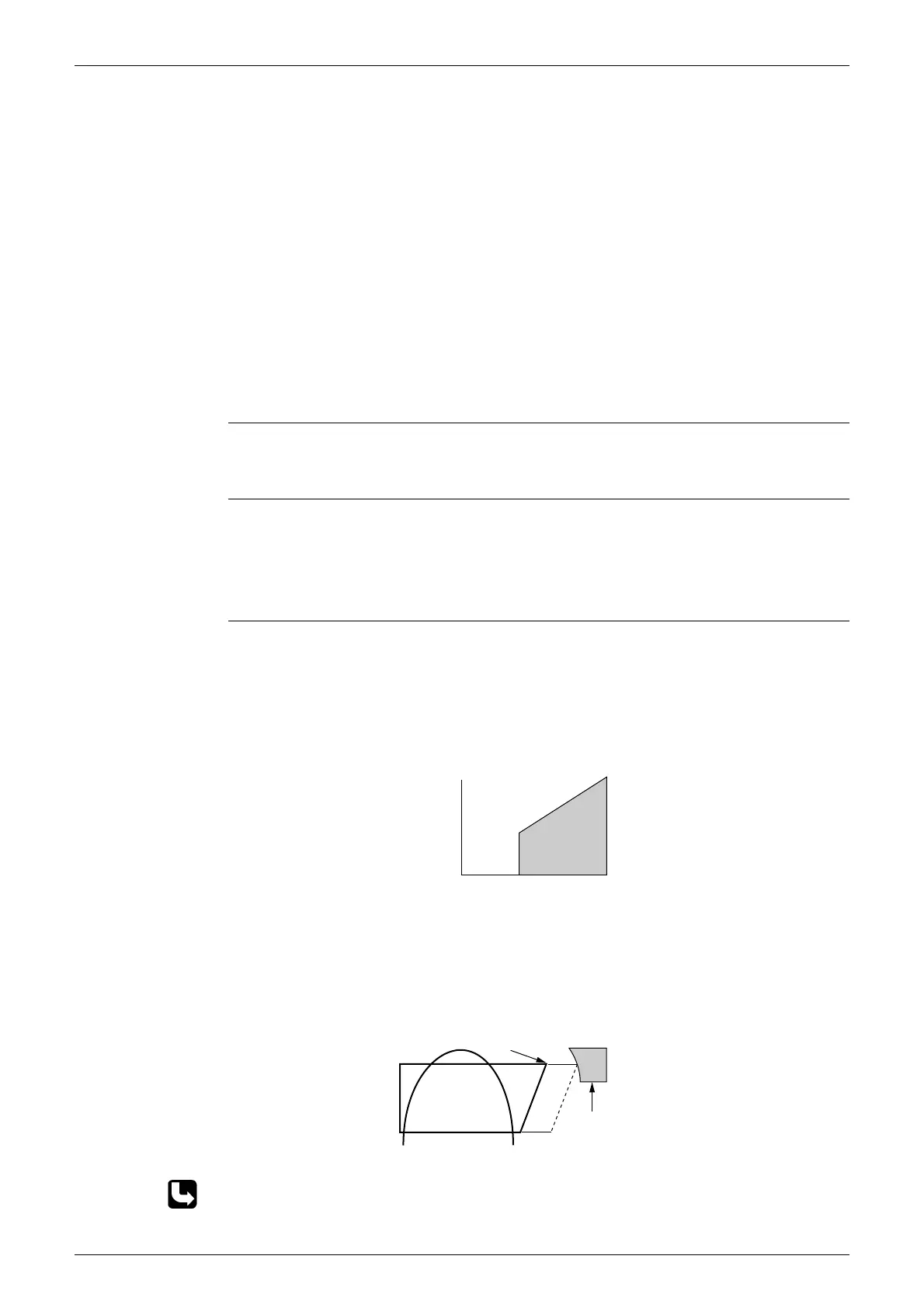
Outline I Detecting by power consumption
If the power consumption is below the specified value and the frequency is higher than the
specified frequency, it is regarded as refrigerant shortage.
The power consumption is small comparing with that in the normal operation when refrigerant is
insufficient, and refrigerant shortage is detected by checking a power consumption.
II Detecting by discharge pipe temperature
If the discharge pipe temperature is higher than the target discharge pipe temperature, and the
electronic expansion valve is fully open for more than the specified time, it is regarded as
refrigerant shortage.
Refer to “Refrigerant shortage” on page 357 for detail.
Frequency
Power consumption
Refrigerant shortage zone
(R11685)
40 ~ 55 Hz
(depending on
the model)
(R1391)
Refrigerant shortage
zone
Target discharge
pipe temperature

 Loading...
Loading...











