batched. Therefore, when the master sends out a read/
write request, it must wait for the response before it sends
a new request. The request or response data value is
limited to maximum 4 bytes (see RC characteristics in
Table 5.14), which implies that text strings are not
transferable. For further information, see
chapter 7 Application Examples.
5.3.2 PCA - Parameter Characteristics
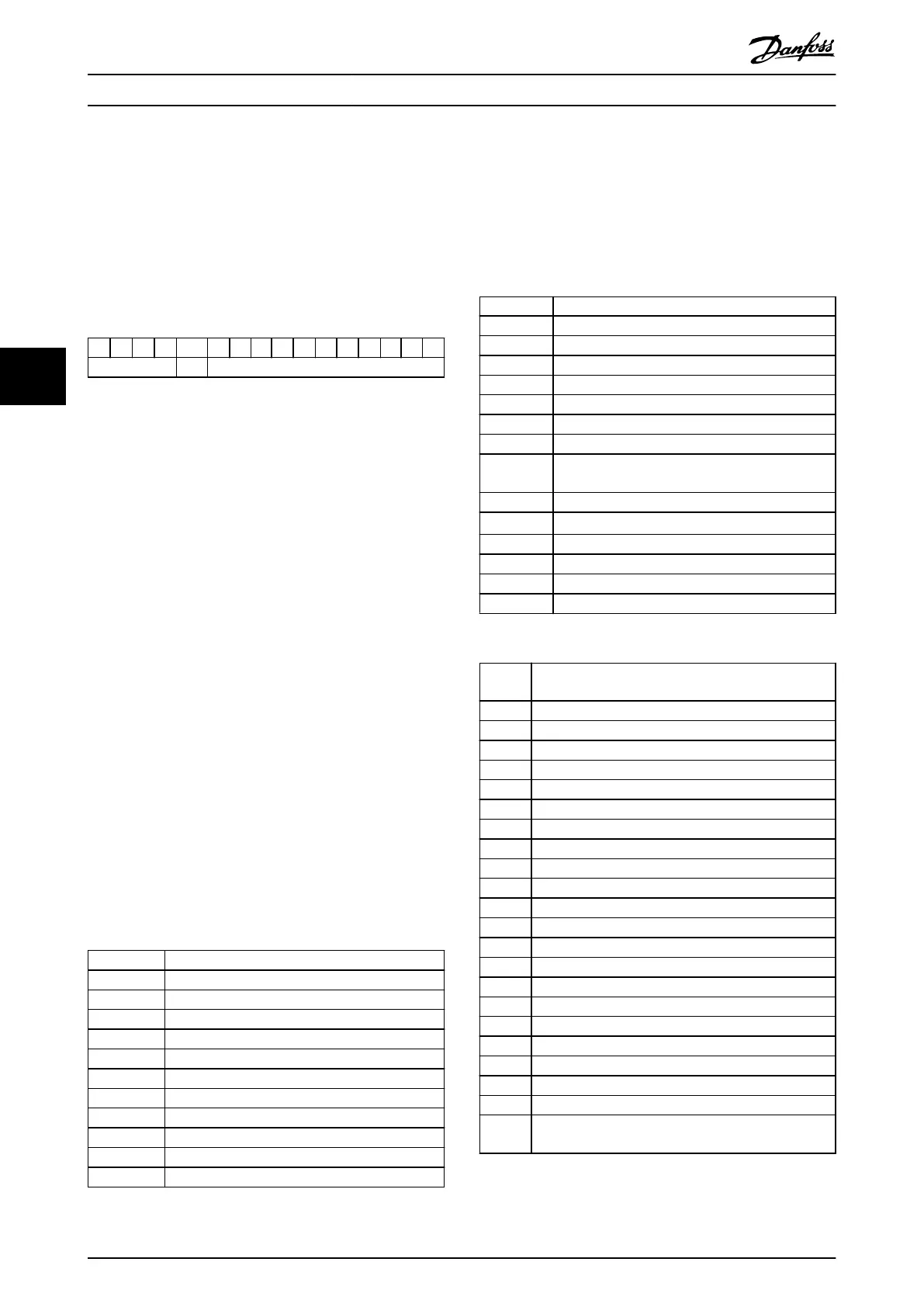
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RC SMP PNU
Table 5.14 PCA - Parameter Characteristics
•
RC: Request/response characteristics (range 0–15).
•
SMP: Spontaneous message (not supported).
•
PNU: Parameter no. (range 1–1999).
5.3.3 Request/Response Handling
The RC portion of the PCA word denes:
•
The requests issued from the master to the slave.
•
Other portions of the PCV involved:
- PVA: The PVA portion transmits word-
size parameter values in bytes 7 and 8,
while long word size values require
bytes 5–8 (32 bits).
- IND: When the response/request
contains array elements, the IND carries
the array subindex. When parameter
descriptions are involved, the IND holds
the record subindex of the parameter
description.
5.3.4 RC Content
Request
The content of the RC portion of the PCA word for a
request is listed in Table 5.15.
Request Function
0 No request.
1 Request parameter value.
2 Change parameter value (word).
3 Change parameter value (long word).
4 Request description element.
5 Change description element.
6 Request parameter value (array).
7 Change parameter value (array word).
8 Change parameter value (array long word).
9 Request number of array elements.
10–15 Not used.
Table 5.15 Request
Response
When the slave rejects a request from the master, the RC
word in the PPO-read indicates the rejection by assuming
the value 7. Bytes 7 and 8 in the PVA element carry the
fault number.
The content of the RC portion of the PCA word for a
response is listed in Table 5.16.
Response Function
0 No response.
1 Transfer parameter value (word).
2 Transfer parameter value (long word).
3 Transfer description element.
4 Transfer parameter value (array word).
5 Transfer parameter value (array long word).
6 Transfer number of array elements.
7 Request rejected (including fault number, see
Table 5.17).
8 Not serviceable by PCV interface.
9 Not used.
10 Not used.
11 Not used.
12 Not used.
13–15 Not used.
Table 5.16 Response
Fault
number
Interpretation
0 Illegal PNU.
1 Parameter value cannot be changed.
2 Upper or lower limit exceeded.
3 Subindex corrupted.
4 No array.
5 Data type false.
6 Cannot be set by user (reset only).
7 Description element cannot be changed.
8 IR required PPO-write not available.
9 Description data not available.
10 Access group.
11 No parameter write access.
12 Key word missing.
13 Text in cyclic transmission not readable.
14 Name in cyclic transmission not readable.
15 Text array not available.
16 PPO-write missing.
17 Request temporarily rejected.
18 Other fault.
19 Data in cyclic transmission not readable.
130 There is no bus access to the parameter called.
131 Data change is not possible because factory set-up is
selected.
Table 5.17 Fault Numbers
Parameter Access
VLT
®
PROFIBUS DP MCA 101
32 Danfoss A/S © 01/2016 All rights reserved. MG37G202
55
 Loading...
Loading...











