Application Notes
HOLD Function
The input value and alarms are frozen while the logic input is closed.
With logic input closed, a reset turns OFF both the relay outputs and the alarms latch.
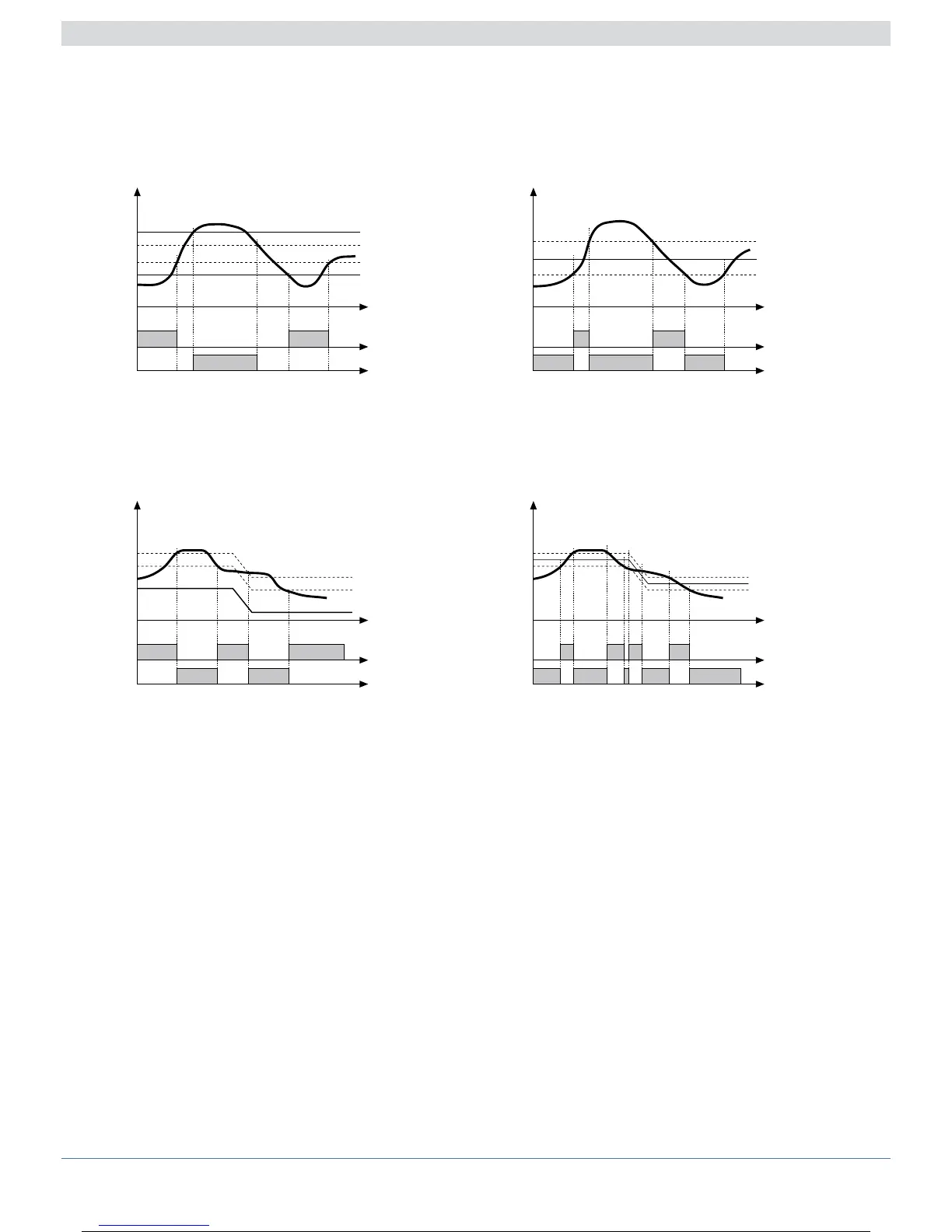
Alarms
time
AL1 + Hy1
AL2 + Hy2
AL2
AL1
alarm 1
alarm 2
(*)
For AL1 = reverse absolute alarm (low) with positive Hyst1, AL1 t = 1
(*) = OFF if disabled on power-up
For AL2 = direct absolute alarm (high) with negative Hyst2, AL2 t = 0
For AL1 = symmetrical Lo absolute alarm with Hyst1, AL1 t = 5
For AL1 = symmetrical Hi absolute alarm with Hyst1, AL1 t = 4
* Minimum hysteresis = 2 scale points
Normal absolute alarm Symmetrical absolute alarm
reverse
direct
AL1
AL1 + [ Hy1* ]
AL1 - [ Hy1* ]
time
For AL1 = Lo deviation alarm with negative Hyst 1, AL1 t = 3
For AL1 = Hi deviation alarm with negative Hyst 1, AL1 t = 2
For AL1 = Symmetrical Lo deviation alarm with Hyst 1, AL1 t = 7
For AL1 = Symmetrical Hi deviation alarm with Hyst 1, AL1 t = 6
time
SP+AL1
SP
reverse
direct
SP+AL1
SP
inverso
direct
time
Hy1
Deviation alarm Symmetrical deviation Alarm
SP-AL1
N.B.: For deviation alarms (At.n = deviation) with different reference quantities (Ar.n), which are set with different decimal points, the switch setpoint always refers
to scale points without considering decimal point.
ex.: if Ar.n = 0 (referred to IN1) and At.n = 6 (deviation referred to IN3) and IN1 with dP = 1, IN3 with dP = 2 AL1 = 200.0 IN3 = 10.00 dS.SP = 1, the alarm
setpoint is 300.0
Control actions
Proportional Action:
action in which contribution to output is proportional to deviation at input (deviation = difference between controlled
variable and setpoint).
Derivative Action:
action in which contribution to output is proportional to rate of variation input deviation.
Integral Action:
action in which contribution to output is proportional to integral of time of input deviation.
48 80291G_MHW_2500_08-2010_ENG
48 / 77
 Loading...
Loading...











