2205Q2JE-HO-S6-N_2020.01.
Chapter 2 Compressor Specifications and Structure
SCV-series Screw Compressor 2.4 Compressor Structure and Mechanism
2-13
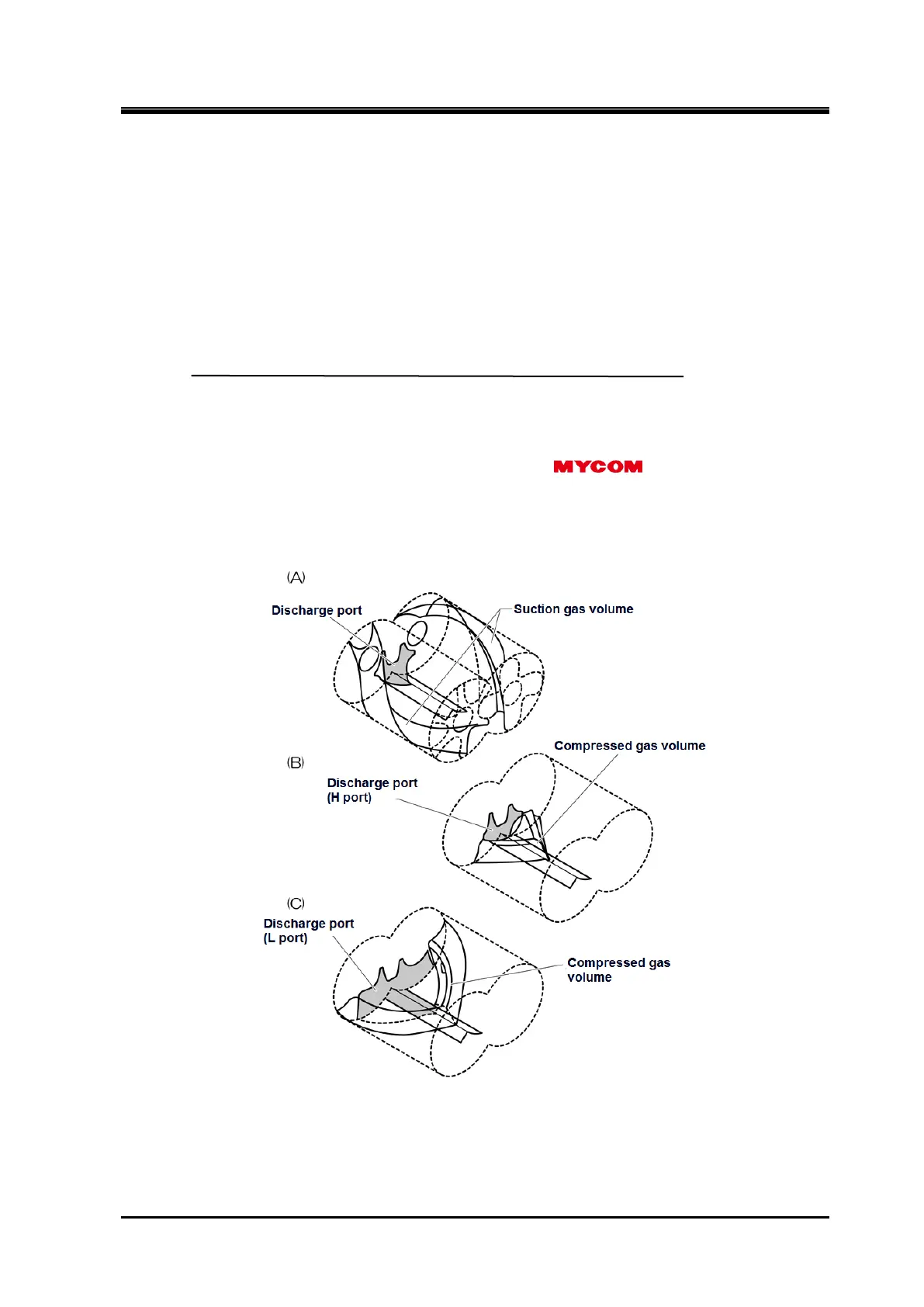
2.4.3 Internal Volume Ratio Vi
2.4.3.1 What is the Internal Volume Ratio Vi ?
In the case of reciprocating compressors, the refrigerant compression capacity is controlled by setting
the pressure attained by piston displacement to an optimum level for the intended application.
With screw compressors, on the other hand, the compression capacity is controlled by setting the
extent to which the volume of the sucked refrigerant gas is to be reduced. In other words, the
compression capacity control applied to the screw compressor is a volumetric ratio control.
This volumetric ratio is called the ‘internal volume ratio Vi’ and defined by the following formula:
Volume of suction refrigerant gas just before start of compression
Volume of refrigerant gas just before opening of discharge port
In the case of the screw compressor without the Vi variable mechanism, Vi values are fixed at a specific
value for each compressor.
For example, the Vi value is fixed at 2.63, 3.65, or 5.80 for
UD/G-series compressor;
compressors with Vi at 2.63 are called the L-port compressors, those with Vi at 3.65 are called the
M-port compressors, and those with Vi at 5.80 are called the H-port compressors.
Also, the Vi of SCV-series compressors with variable Vi mechanism are these three types i.e. L port, M
port, H port.
Figure 2-9 Internal Volume Ratio Vi
 Loading...
Loading...