12
Connection
6.8 Noise measures
There are two types of electrical noises: One is a noise to invade into the driver from the outside and cause the driver
malfunction, and the other is a noise to emit from the driver and cause peripheral equipments malfunction.
For the noise that is invaded from the outside, take measures to prevent the driver malfunction. It is needed to take
adequate measures because signal lines are very likely to be aected by the noise.
For the noise that is emitted from the driver, take measures to suppress it.
Measures against electrical noise
There are the following three methods mainly to take measures against the electrical noise.
z
Noise suppression
•
When relays or electromagnetic switches are used, use noise lters or CR circuits to suppress surge generated by
them.
•
Use a connection cable (sold separately) when extending the wiring distance between the motor and the driver.
This is eective in suppressing the electrical noise emitted from the motor.
•
Cover the driver by a metal plate such as aluminum. This is eective in shielding the electrical noise emitted from the
driver.
z
Prevention of noise propagation
•
Separate power lines such as motor cable and power supply cable from signal lines for a distance of 100 mm (3.94 in.)
or more, and also do not bundle them or wire them in parallel. If the power lines must cross over the signal lines, wire
them at right angles.
•
Use a cable of AWG26 (0.14 mm
2
) or thicker for the signal cable of the driver, and keep the wiring distance of 3 m (9.8ft.)
or less.
•
For more eective elimination of noise, use shielded cables for a power supply cable and I/O signal cable, or attach
ferrite cores if non-shielded cables are used.
•
Keep cables as short as possible without coiling and bundling extra lengths.
•
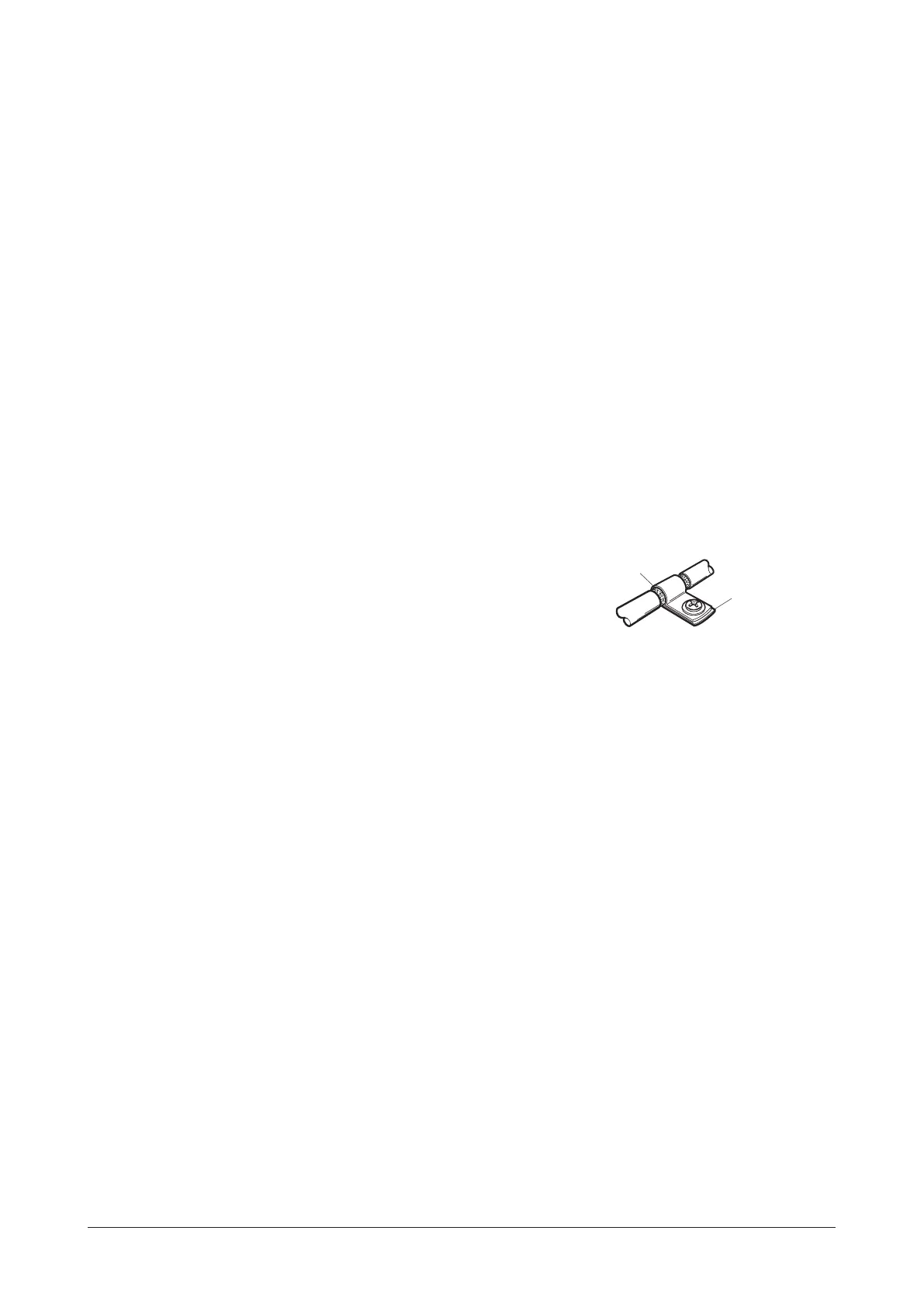
To ground a shielded cable, use a metal cable clamp that can
maintain contact with the entire circumference of the shielded
cable, and ground as near the product as possible.
Cable cramp
Shielded cable
•
Grounding multiple points will increase eect to block electrical noise because impedance on the grounding points is
decreased.
However, ground them so that a potential dierence does not occur among the grounding points.
z
Suppression of eect by noise propagation
•
Loop the noise propagated cable around a ferrite core. Doing so will prevent the propagated noise invades into the
driver or emits from the driver. The frequency band in which an eect by the ferrite core can be seen is generally
1 MHz or more. Check the frequency characteristics of the ferrite core used. When increasing the eect of noise
attenuation by the ferrite core, loop the cable a lot.
6.9 Conformity to the EMC Directive
Eective measures must be taken against the EMI that the motor and driver may give to adjacent control-system
equipment, as well as the EMS of the motor and driver itself, in order to prevent a serious functional impediment in the
machinery. The use of the following installation and wiring methods will enable the motor and driver to be compliant
with the EMC directive. Refer to p.23 for the applicable standards.
Oriental Motor conducts EMC measurements on its motors and drivers in accordance with "Example of installation and
wiring" shown on the next page.
The user is responsible for ensuring the machine’s compliance with the EMC Directive, based on the installation and
wiring explained below.
About power supply
The
BLH
Series is a product of DC power supply input. Use a DC power supply (such as a switching power supply) that
optimally conforms to the EMC Directive.
Connecting the motor cable
When extending the motor cable, use an connection cable (sold separately). The maximum extension distance including
the cable length of the motor itself should be 2 m (6.6 ft.).

 Loading...
Loading...