Rockwell Automation Publication 520-UM001I-EN-E - July 2016 227
Appendix F
PID Set Up
PID Loop
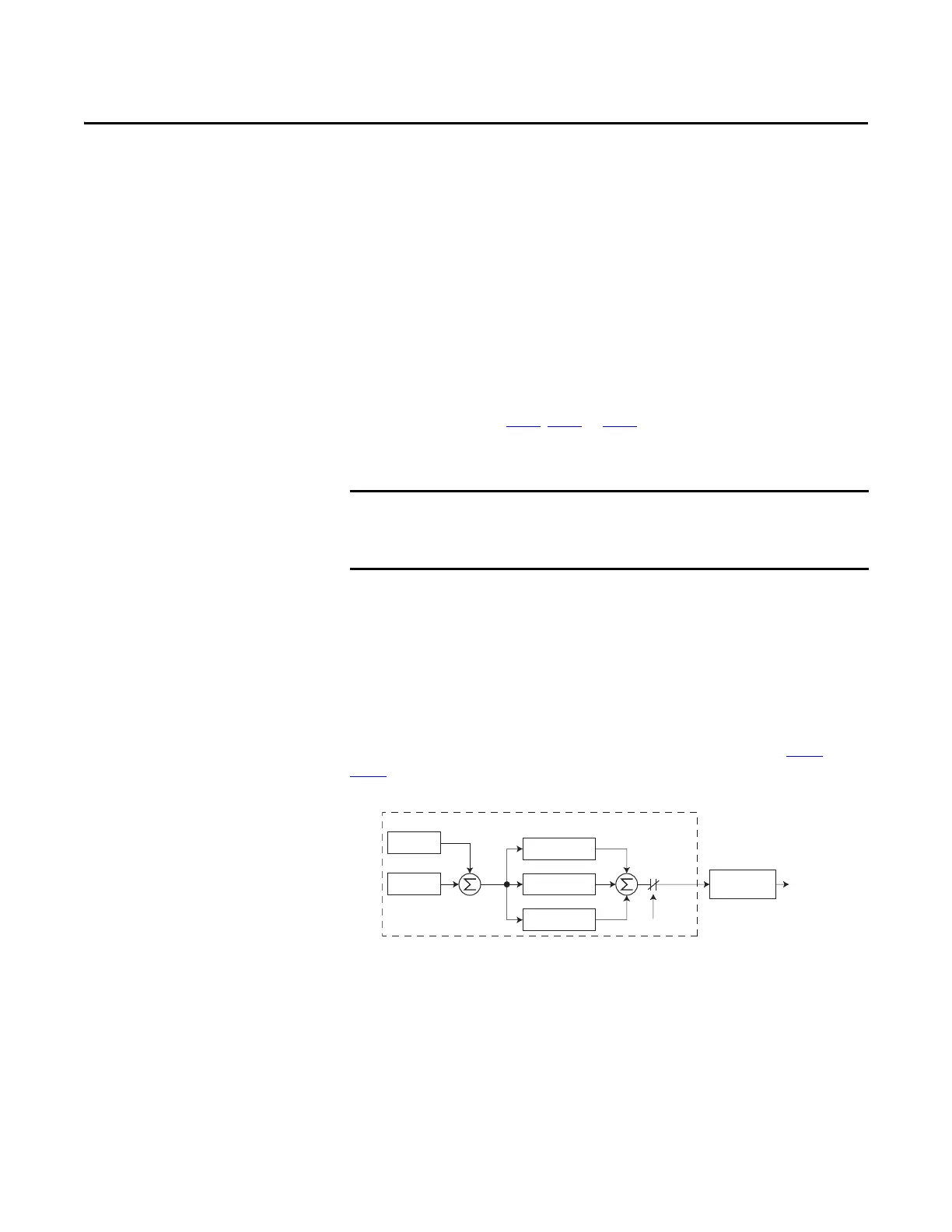
The PowerFlex 520-series drive features built-in PID (proportional, integral,
derivative) control loops. The PID loop is used to maintain a process feedback
(such as pressure, flow or tension) at a desired set point. The PID loop works by
subtracting the PID feedback from a reference and generating an error value. The
PID loop reacts to the error, based on the PID Gains, and outputs a frequency to
try to reduce the error value to 0.
To enable the PID loop, P047
, P049 or P051 [Speed Referencex] must be set to
11 “PID1 Output” or 12 “PID2 Output”, and the corresponding speed reference
activated.
Exclusive Control and Trim Control are two basic configurations where the PID
loop may be used.
Exclusive Control
In Exclusive Control, the Speed Reference becomes 0, and the PID Output
becomes the entire Freq Command. Exclusive Control is used when A458
or
A470
[PID x Trim Sel] is set to option 0. This configuration does not require a
master reference, only a desired set point, such as a flow rate for a pump.
Example
• In a pumping application, the PID Reference equals the Desired System
Pressure set point.
• The Pressure Transducer signal provides PID Feedback to the drive.
Fluctuations in actual system pressure, due to changes in flow, result in a
PID Error value.
• The drive output frequency increases or decreases to vary motor shaft
speed to correct for the PID Error value.
PowerFlex 523 has one PID control loop.
PowerFlex 525 has two PID control loops, of which only one can be in use at any
time.
–
+
PID Prop Gain
PID Loop
PID Integ Time
PID Di Rate
PID Selected
PID Fdbk
PID Ref
PID
Error
+
+
+
PID
Output
Accel/Decel
Ramp
Freq
Command

 Loading...
Loading...