1.1
1.1.
1FPD-2010
1 Outline
1.1
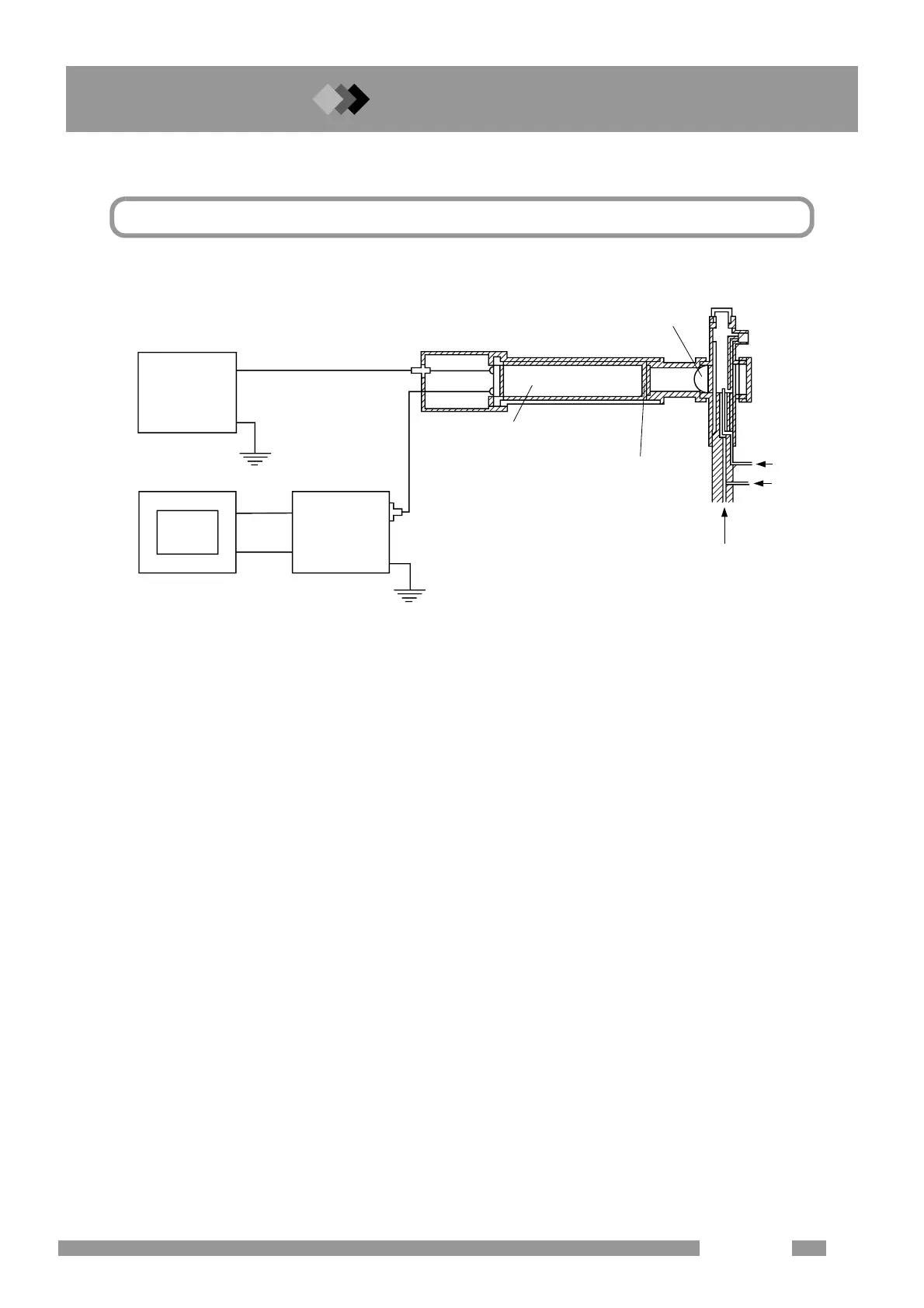
Principle of the FPD (Flame Photometric Detector)
This detector is a hydrogen flame photometric detector.
Carrier gas
Ai
H2
Flat convex lens
Optical filter
Photomultiplier
Data processing unit
Electrometer
High voltage
supply
Fig. 1.1.1 Block Diagram
Air is mixed with the hydrogen/carrier gas mixture at the nozzle producing a hydrogen flame. The sample
gas, carried by the carrier gas, is burnt by the hydrogen flame at the nozzle, emitting light of a certain wave
-
length. The light emitted by the hydrogen flame at the nozzle is converted into a parallel light through the flat
convex lens and reaches to the interference filter. The interference filter passes only light of a specific wave
-
length. A 394nm S-type filter is used for detecting sulfur components, a 526nm P-type is used for phospho-
rus components and a 610nm Sn-type filter is used for detecting tin components.
If sulfur, phosphorus or tin components are included in the sample gas, they are burnt at the nozzle, emitting
light of wavelengths 394nm, 526nm or 610nm respectively.
Light having only these wavelengths passes through the respective filters and reaches the photomultiplier.
The light intensity is converted into electrical signals by the photomultiplier, the signals are amplified in the
electrometer, and then output to the data processor.
Approximately -700V is applied to the cathode of the photsomultiplier.

 Loading...
Loading...











