DigitAx User Guide
Issue code: dgxu4
4-7
Insert the following values:
P = 827W (from Losses and Efficiency
table)
T
i
= 50°C (122°F)
T
amb
= 25°C (77°F)
k = 5.5 (typical value for painted 2mm
(
1
/
16
inch) sheet steel)
The minimum required heat conducting area is then:
(())
Am
e
==
−−
==
827
5 5 50 25
60
2
.
.
The unobstructed heat-conducting area of the
enclosure is:
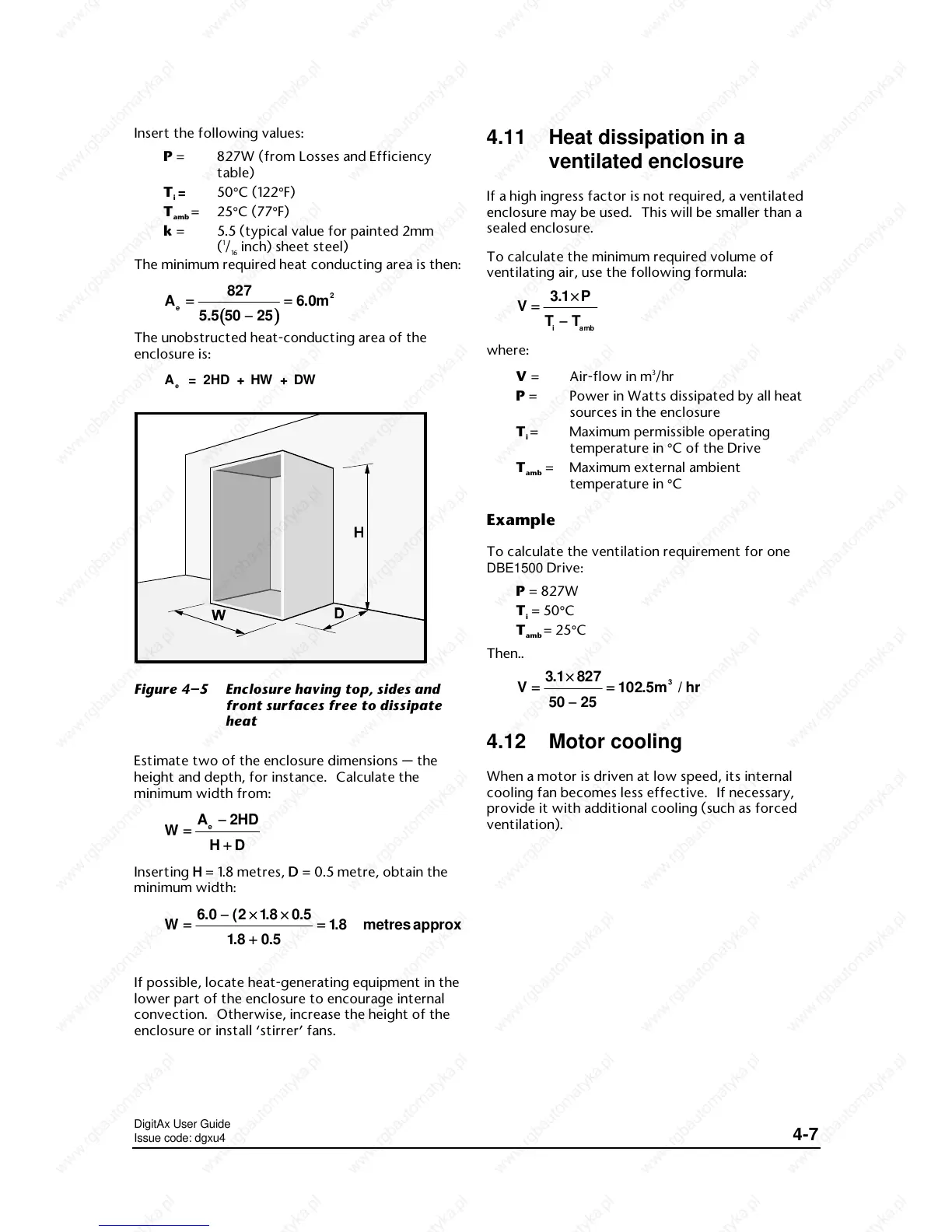
A = 2HD + HW + DW
e
Figure 4–5 Enclosure having top, sides and
front surfaces free to dissipate
heat
Estimate two of the enclosure dimensions — the
height and depth, for instance. Calculate the
minimum width from:
W
AHD
HD
e
==
−−
++
2
Inserting HH = 1.8 metres, D D = 0.5 metre, obtain the
minimum width:
W metresapprox==
−−××××
++
==
60 2 18 05
18 05
18
.( . .
..
.
If possible, locate heat-generating equipment in the
lower part of the enclosure to encourage internal
convection. Otherwise, increase the height of the
enclosure or install ‘stirrer’ fans.
4.11 Heat dissipation in a
ventilated enclosure
If a high ingress factor is not required, a ventilated
enclosure may be used. This will be smaller than a
sealed enclosure.
To calculate the minimum required volume of
ventilating air, use the following formula:
V
P
TT
iamb
==
××
−−
31.
where:
V = Air-flow in m
3
/hr
P = Power in Watts dissipated by all heat
sources in the enclosure
T
i
= Maximum permissible operating
temperature in °C of the Drive
T
amb
= Maximum external ambient
temperature in °C
Example
To calculate the ventilation requirement for one
DBE1500 Drive:
P = 827W
T
i
= 50°C
T
amb
= 25°C
Then..
4.12 Motor cooling
When a motor is driven at low speed, its internal
cooling fan becomes less effective. If necessary,
provide it with additional cooling (such as forced
ventilation).

 Loading...
Loading...